Abstract
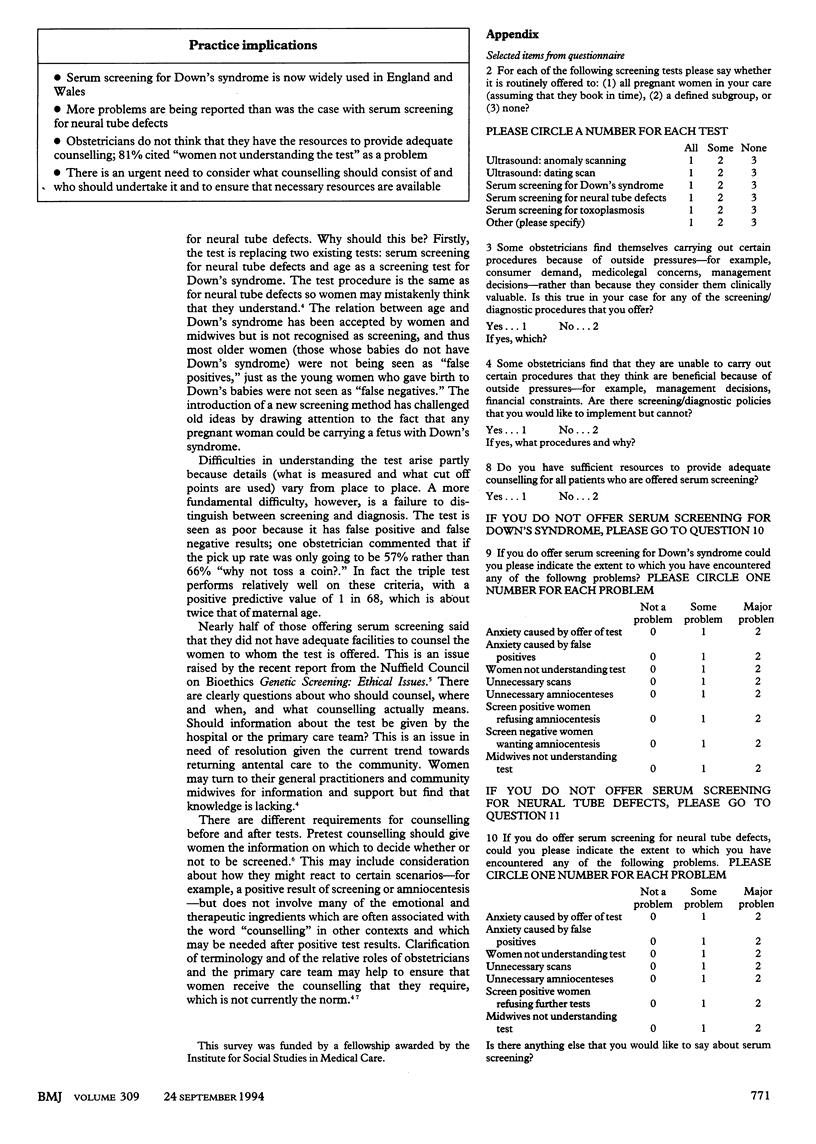
OBJECTIVES--To assess the experiences of obstetricians in England and Wales of serum screening for Down's syndrome. DESIGN--Postal questionnaire survey. SUBJECTS--Questionnaires were sent to all practising obstetricians in England and Wales with nonacademic appointments who had not participated in an earlier (randomly sampled) survey of obstetricians' attitudes (n = 555). Responses were received from 393 (71%), of which 351 were analysed. The data represent about one third of obstetric consultants in England and Wales. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES--The extent of use of serum screening for Down's syndrome, and the problems encountered. RESULTS--Serum screening for Down's syndrome was being offered on some basis by virtually all obstetricians in the survey. Nearly half the sample said that they did not have adequate resources for counselling all the women to whom screening was offered. Many problems were reported, which in all cases were more common than equivalent problems encountered with serum screening for neural tube defects. Over 80% (289) said that women not understanding the test was a problem. CONCLUSIONS--There is considerable confusion associated with serum screening for Down's syndrome. The precedent of serum screening for neural tube defects does not seem to have lessened the problems experienced, rather the contrary. Many obstetricians report inadequate resources for counselling, which is consistent with the high prevalence of problems associated with women not understanding the test. There is an urgent need to consider what counselling should consist of and who should undertake it and to ensure that necessary resources are available.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Do doctors short-change old people? Lancet. 1993 Jul 3;342(8862):1–2. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marteau T. M., Slack J., Kidd J., Shaw R. W. Presenting a routine screening test in antenatal care: practice observed. Public Health. 1992 Mar;106(2):131–141. doi: 10.1016/s0033-3506(05)80390-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Statham H., Green J. Serum screening for Down's syndrome: some women's experiences. BMJ. 1993 Jul 17;307(6897):174–176. doi: 10.1136/bmj.307.6897.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald N., Wald K., Smith D. The extent of Down's syndrome screening in Britain in 1991. Lancet. 1992 Aug 22;340(8817):494–494. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91822-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


