Abstract
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) isolates show sequence divergence in the BamHI YH region of the genome which encodes the nuclear antigen EBNA 2, a protein thought to be involved in the initiation of virus-induced B-cell transformation; type A isolates (such as B95-8 EBV) encode a 82- to 87-kilodalton EBNA 2A protein, whereas type B isolates (such as AG876 EBV) encode an antigenically distinct 75-kilodalton EBNA 2B protein. In the present work 12 type A isolates and 8 type B isolates have been compared for their ability to transform resting human B cells in vitro into permanent lymphoblastoid cell lines. Although the kinetics of initial focus formation was not markedly dependent upon the EBNA 2 type of the transforming virus, on subsequent passage type A virus-transformed cells (type A transformants) yielded cell lines much more readily than did type B transformants. Direct comparison between the two types of transformant revealed clear differences in several aspects of growth phenotype. Compared with type A transformants, cell lines established with type B virus isolates consistently displayed an unusual growth pattern with poor survival of individual cells shed from lymphoblastoid clumps, a lower growth rate and a greater sensitivity to seeding at limiting dilutions, and a significantly lower saturation density that could not be corrected by supplementation of the medium with culture supernatant containing B-cell growth factors. This is the first direct evidence that, in EBV-transformed B-cell lines, the EBNA 2 protein plays a continuing role in determining the cellular growth phenotype.
Full text
PDF

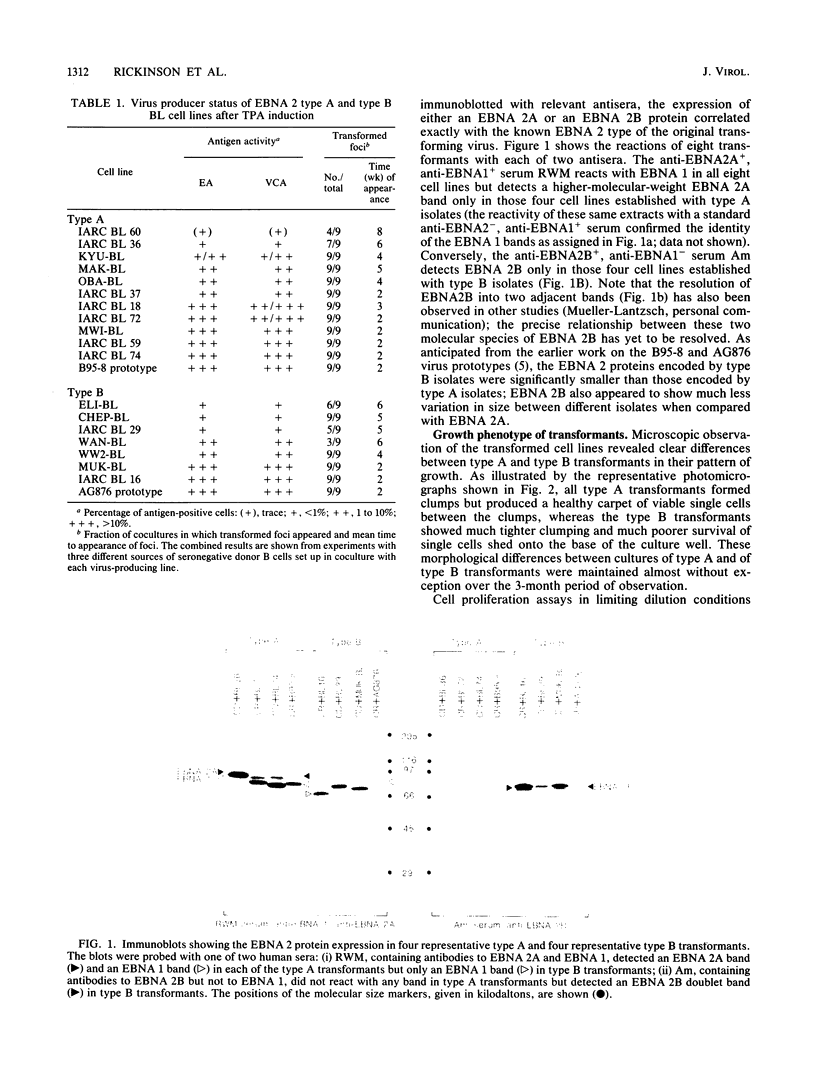
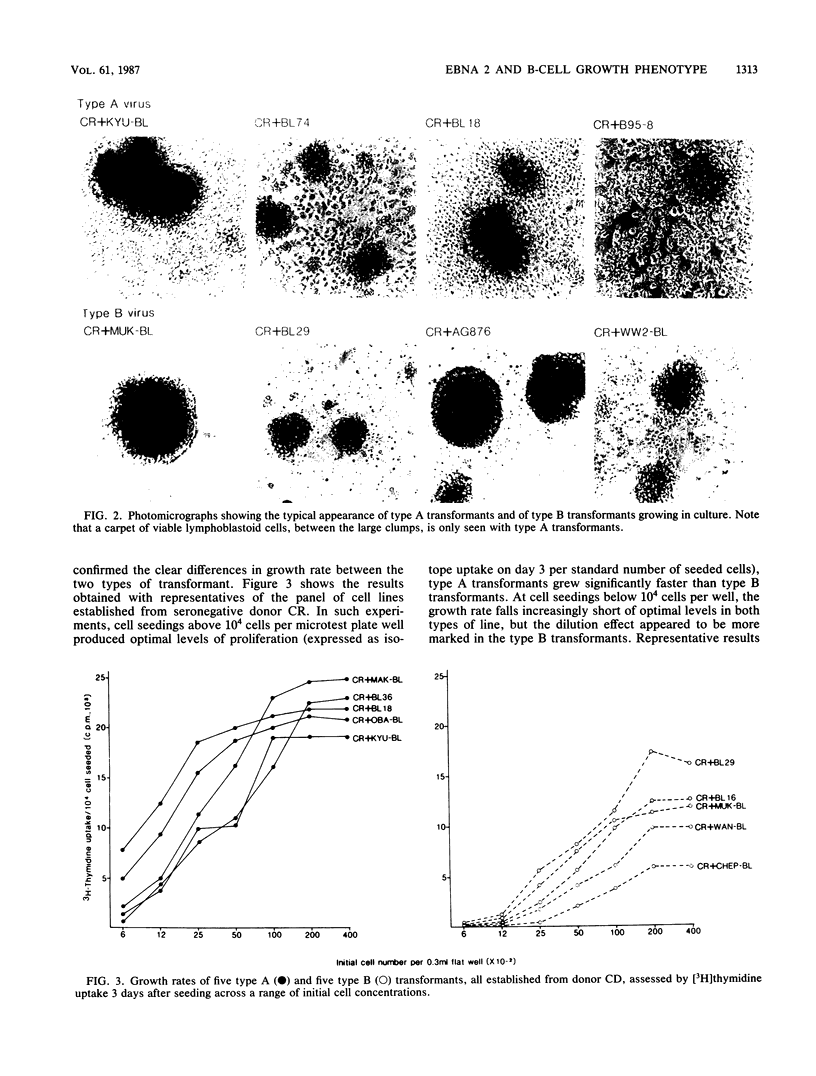
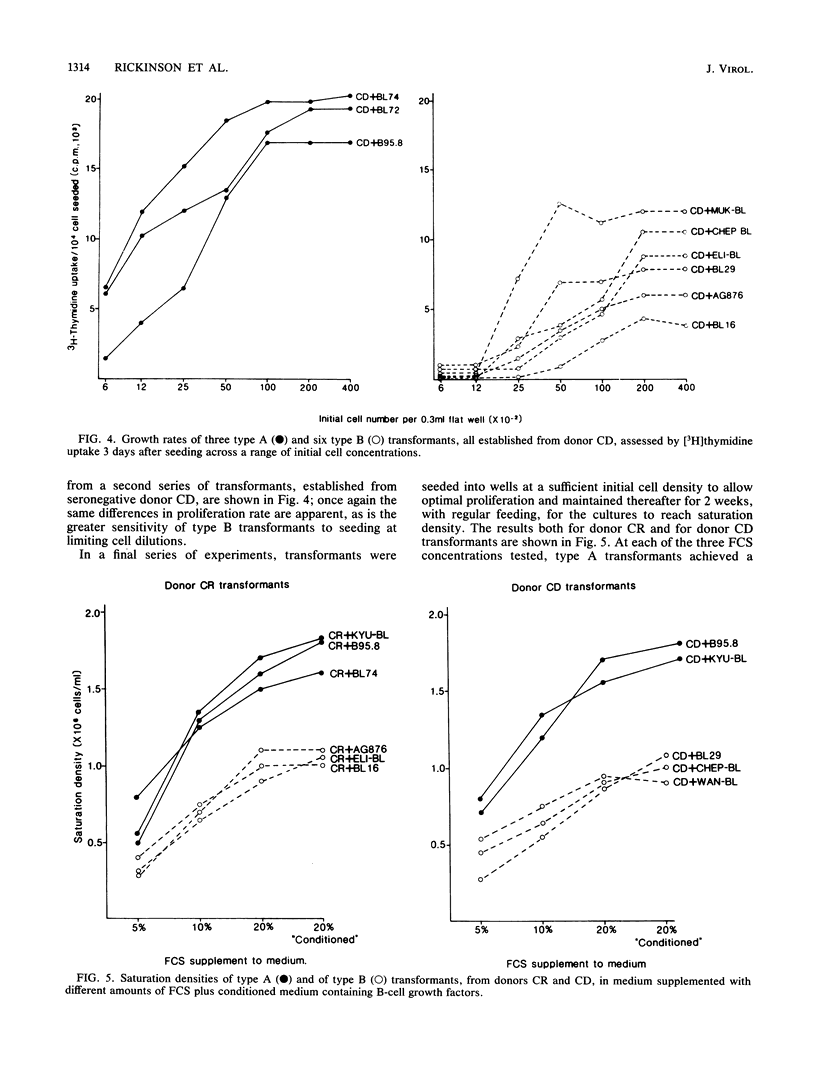



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adldinger H. K., Delius H., Freese U. K., Clarke J., Bornkamm G. W. A putative transforming gene of Jijoye virus differs from that of Epstein-Barr virus prototypes. Virology. 1985 Mar;141(2):221–234. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90253-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornkamm G. W., Hudewentz J., Freese U. K., Zimber U. Deletion of the nontransforming Epstein-Barr virus strain P3HR-1 causes fusion of the large internal repeat to the DSL region. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):952–968. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.952-968.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambaugh T., Hennessy K., Chamnankit L., Kieff E. U2 region of Epstein-Barr virus DNA may encode Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7632–7636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambaugh T., Wang F., Hennessy K., Woodland E., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Expression of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 in rodent cells. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):453–462. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.453-462.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Kallin B., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Timar L., Klein G. Characterization of a second Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen associated with the BamHI WYH region of EBV DNA. Int J Cancer. 1985 Mar 15;35(3):359–366. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910350312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Ley S. C., Melamed M. D., Aman P., Hughes-Jones N. C. Soluble factor requirements for the autostimulatory growth of B lymphoblasts immortalized by Epstein-Barr virus. J Exp Med. 1984 May 1;159(5):1554–1559. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.5.1554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Ley S. C., Melamed M. D., English L. S., Hughes-Jones N. C. Immortalized B lymphocytes produce B-cell growth factor. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):145–147. doi: 10.1038/310145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Walker L., Guy G., Brown G., Rowe M., Rickinson A. Control of human B-lymphocyte replication. II. Transforming Epstein-Barr virus exploits three distinct viral signals to undermine three separate control points in B-cell growth. Immunology. 1986 Aug;58(4):591–595. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith I. P. Immediate visualization of proteins in dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels by prestaining with Remazol dyes. Anal Biochem. 1972 Apr;46(2):402–412. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90313-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W. Immunofluorescence in cells derived from Burkitt's lymphoma. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1248–1256. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1248-1256.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Diehl V., Kohn G., Zur Hausen H., Henle G. Herpes-type virus and chromosome marker in normal leukocytes after growth with irradiated Burkitt cells. Science. 1967 Sep 1;157(3792):1064–1065. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3792.1064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G., Zajac B. A., Pearson G., Waubke R., Scriba M. Differential reactivity of human serums with early antigens induced by Epstein-Barr virus. Science. 1970 Jul 10;169(3941):188–190. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3941.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Fennewald S., Hummel M., Cole T., Kieff E. A membrane protein encoded by Epstein-Barr virus in latent growth-transforming infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7207–7211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Kieff E. A second nuclear protein is encoded by Epstein-Barr virus in latent infection. Science. 1985 Mar 8;227(4691):1238–1240. doi: 10.1126/science.2983420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Wang F., Bushman E. W., Kieff E. Definitive identification of a member of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 3 family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5693–5697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallin B., Dillner J., Ernberg I., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Rosén A., Henle W., Henle G., Klein G. Four virally determined nuclear antigens are expressed in Epstein-Barr virus-transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1499–1503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King W., Dambaugh T., Heller M., Dowling J., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus DNA XII. A variable region of the Epstein-Barr virus genome is included in the P3HR-1 deletion. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):979–986. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.979-986.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenoir G. M., Vuillaume M., Bonnardel C. The use of lymphomatous and lymphoblastoid cell lines in the study of Burkitt's lymphoma. IARC Sci Publ. 1985;(60):309–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Lipman M. Release of infectious Epstein-Barr virus by transformed marmoset leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):190–194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Robinson J., Heston L., Lipman M. Differences between laboratory strains of Epstein-Barr virus based on immortalization, abortive infection, and interference. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4006–4010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss D. J., Rickinson A. B., Pope J. H. Long-term T-cell-mediated immunity to Epstein-Barr virus in man. I. Complete regression of virus-induced transformation in cultures of seropositive donor leukocytes. Int J Cancer. 1978 Dec;22(6):662–668. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910220604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss D. J., Sculley T. B., Pope J. H. Induction of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigens. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):988–990. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.988-990.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller-Lantzsch N., Lenoir G. M., Sauter M., Takaki K., Béchet J. M., Kuklik-Roos C., Wunderlich D., Bornkamm G. W. Identification of the coding region for a second Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (EBNA 2) by transfection of cloned DNA fragments. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1805–1811. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzo P. A., Magrath I. T., Chattopadhyay S. K., Biggar R. J., Gerber P. A new tumour-derived transforming strain of Epstein-Barr virus. Nature. 1978 Apr 13;272(5654):629–631. doi: 10.1038/272629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope J. H., Horne M. K., Scott W. Transformation of foetal human keukocytes in vitro by filtrates of a human leukaemic cell line containing herpes-like virus. Int J Cancer. 1968 Nov 15;3(6):857–866. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910030619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabson M., Gradoville L., Heston L., Miller G. Non-immortalizing P3J-HR-1 Epstein-Barr virus: a deletion mutant of its transforming parent, Jijoye. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):834–844. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.834-844.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlins D. R., Milman G., Hayward S. D., Hayward G. S. Sequence-specific DNA binding of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (EBNA-1) to clustered sites in the plasmid maintenance region. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):859–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman D., Yates J., Sugden B. A putative origin of replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus is composed of two cis-acting components. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1822–1832. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickinson A. B., Rowe M., Hart I. J., Yao Q. Y., Henderson L. E., Rabin H., Epstein M. A. T-cell-mediated regression of "spontaneous" and of Epstein-Barr virus-induced B-cell transformation in vitro: studies with cyclosporin A. Cell Immunol. 1984 Sep;87(2):646–658. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90032-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickinson A. B., Yao Q. Y., Wallace L. E. The Epstein-Barr virus as a model of virus-host interactions. Br Med Bull. 1985 Jan;41(1):75–79. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney C. M., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Finerty S., Edwards C., Rupani H., Rickinson A. B. Endemic Burkitt's lymphoma: phenotypic analysis of tumor biopsy cells and of derived tumor cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Sep;77(3):681–687. doi: 10.1093/jnci/77.3.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney C. M., Rickinson A. B., Moss D. J., Lenoir G. M., Epstein M. A. Paired Epstein-Barr virus-carrying lymphoma and lymphoblastoid cell lines from Burkitt's lymphoma patients: comparative sensitivity to non-specific and to allo-specific cytotoxic responses in vitro. Int J Cancer. 1984 Sep 15;34(3):339–348. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910340310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. T., Rowe M., Evan G. I., Wallace L. E., Farrell P. J., Rickinson A. B. Restricted expression of EBV latent genes and T-lymphocyte-detected membrane antigen in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2599–2607. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04540.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D., Heston L., Metlay J., Miller G. Identification and expression of a nuclear antigen from the genomic region of the Jijoye strain of Epstein-Barr virus that is missing in its nonimmortalizing deletion mutant, P3HR-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7429–7433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rymo L., Klein G., Ricksten A. Expression of a second Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen in mouse cells after gene transfer with a cloned fragment of the viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3435–3439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Hummel M., Braun D., Birkenbach M., Kieff E. Nucleotide sequences of mRNAs encoding Epstein-Barr virus nuclear proteins: a probable transcriptional initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5096–5100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skare J., Farley J., Strominger J. L., Fresen K. O., Cho M. S., zur Hausen H. Transformation by Epstein-Barr virus requires DNA sequences in the region of BamHI fragments Y and H. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):286–297. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.286-297.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strnad B. C., Schuster T. C., Hopkins R. F., 3rd, Neubauer R. H., Rabin H. Identification of an Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen by fluoroimmunoelectrophoresis and radioimmunoelectrophoresis. J Virol. 1981 Jun;38(3):996–1004. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.3.996-1004.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. P., Grogan E. A., Shedd D., Robert M., Liu C. R., Miller G. Stable expression in mouse cells of nuclear neoantigen after transfer of a 3.4-megadalton cloned fragment of Epstein-Barr virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5688–5692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Warren N., Sugden B. Stable replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus in various mammalian cells. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):812–815. doi: 10.1038/313812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimber U., Adldinger H. K., Lenoir G. M., Vuillaume M., Knebel-Doeberitz M. V., Laux G., Desgranges C., Wittmann P., Freese U. K., Schneider U. Geographical prevalence of two types of Epstein-Barr virus. Virology. 1986 Oct 15;154(1):56–66. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90429-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]