Abstract
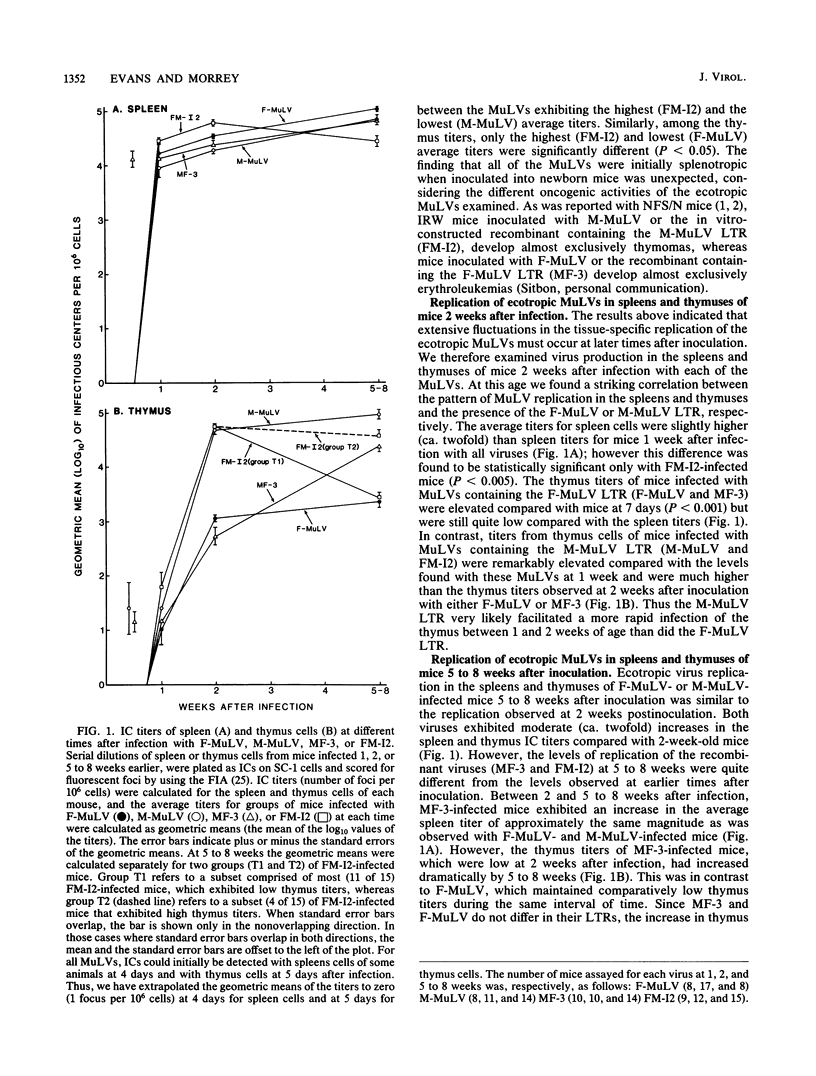
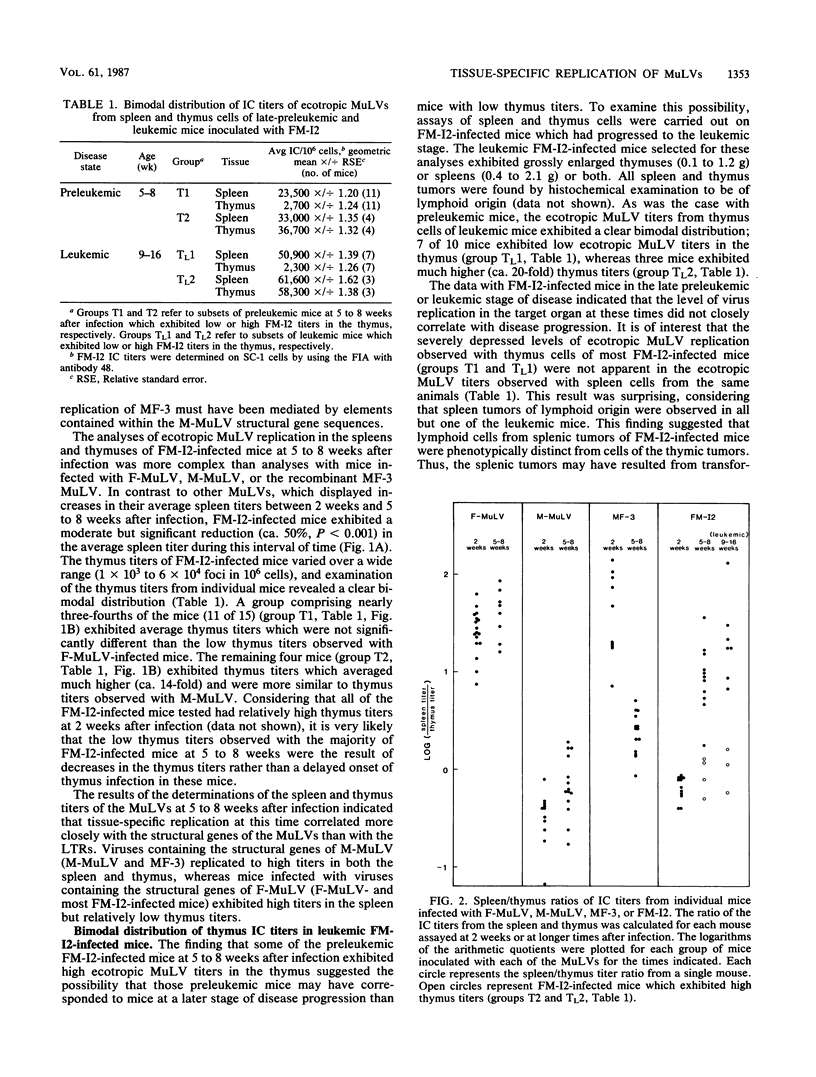
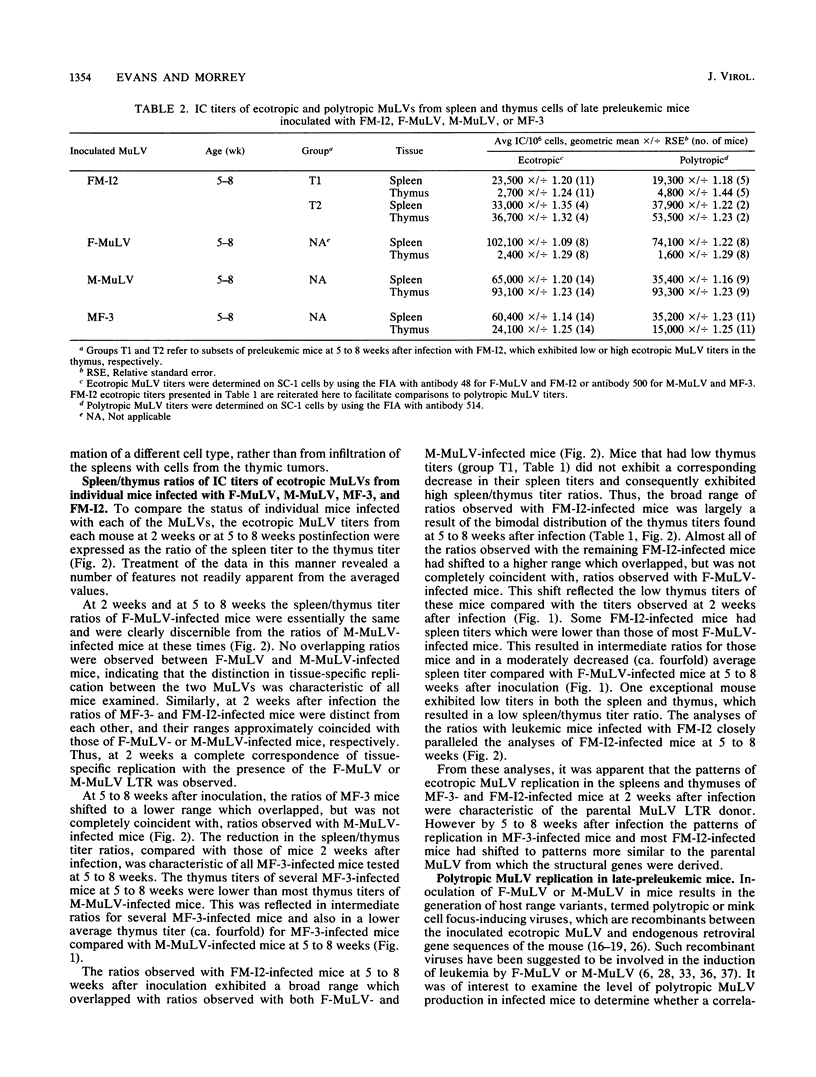
We have studied the replication of ecotropic murine leukemia viruses (MuLV) in the spleens and thymuses of mice infected with the lymphocytic leukemia-inducing virus Moloney MuLV (M-MuLV), with the erythroleukemia-inducing virus Friend MuLV (F-MuLV), or with in vitro-constructed recombinants between these viruses in which the long terminal repeat (LTR) sequences have been exchanged. At 1 week after infection both the parents and the LTR recombinants replicated predominantly in the spleens with only low levels of replication in the thymus. At 2 weeks after infection, the patterns of replication in the spleens and thymuses were strongly influenced by the type of LTR. Viruses containing the M-MuLV LTR exhibited a remarkable elevation in thymus titers which frequently exceeded the spleen titers, whereas viruses containing the F-MuLV LTR replicated predominantly in the spleen. In older preleukemic mice (5 to 8 weeks of age) the structural genes of M-MuLV or F-MuLV predominantly influenced the patterns of replication. Viruses containing the structural genes of M-MuLV replicated efficiently in both the spleen and thymus, whereas viruses containing the structural genes of F-MuLV replicated predominantly in the spleen. In leukemic mice infected with the recombinant containing F-MuLV structural genes and the M-MuLV LTR, high levels of virus replication were observed in splenic tumors but not in thymic tumors. This phenotypic difference suggested that tumors of the spleen and thymus may have originated by the independent transformation of different cell types. Quantification of polytropic MulVs in late-preleukemic mice infected with each of the ecotropic MuLVs indicated that the level of polytropic MuLV replication closely paralleled the level of replication of the ecotropic MuLVs in all instances. These studies indicated that determinants of tissue tropism are contained in both the LTR and structural gene sequences of F-MuLV and M-MuLV and that high levels of ecotropic or polytropic MuLV replication, per se, are not sufficient for leukemia induction. Our results further suggested that leukemia induction requires a high level of virus replication in the target organ only transiently during an early preleukemic stage of disease.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chatis P. A., Holland C. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. Role for the 3' end of the genome in determining disease specificity of Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4408–4411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Holland C. A., Silver J. E., Frederickson T. N., Hopkins N., Hartley J. W. A 3' end fragment encompassing the transcriptional enhancers of nondefective Friend virus confers erythroleukemogenicity on Moloney leukemia virus. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):248–254. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.248-254.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Britt W., Evans L., Wehrly K., Nishio J., Cloyd M. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies reactive with murine leukemia viruses: use in analysis of strains of friend MCF and Friend ecotropic murine leukemia virus. Virology. 1983 May;127(1):134–148. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90378-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Portis J. L., Wehrly K., Nishio J. Effect of murine host genotype on MCF virus expression, latency, and leukemia cell type of leukemias induced by Friend murine leukemia helper virus. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):221–233. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90332-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Wehrly K., Cloyd M., Britt W., Portis J., Collins J., Nishio J. Characterization of mouse monoclonal antibodies specific for Friend murine leukemia virus-induced erythroleukemia cells: friend-specific and FMR-specific antigens. Virology. 1981 Jul 15;112(1):131–144. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90619-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Wehrly K., Nishio J., Evans L. Leukemia induction by a new strain of Friend mink cell focus-inducing virus: synergistic effect of Friend ecotropic murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):63–70. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.63-70.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W. Characterization of target cells for MCF viruses in AKR mice. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90512-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Lymphomagenicity of recombinant mink cell focus-inducing murine leukemia viruses. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):542–552. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. R., Chandy K. G., Brightman B. K., Gupta S., Fan H. Effects of nonleukemogenic and wild-type Moloney murine leukemia virus on lymphoid cells in vivo: identification of a preleukemic shift in thymocyte subpopulations. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):423–430. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.423-430.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B., Linney E., Fan H. Suppression of leukaemia virus pathogenicity by polyoma virus enhancers. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):550–553. doi: 10.1038/314550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Jolicoeur P. Mapping the viral sequences conferring leukemogenicity and disease specificity in Moloney and amphotropic murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):448–456. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.448-456.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Jolicoeur P. The tandem direct repeats within the long terminal repeat of murine leukemia viruses are the primary determinant of their leukemogenic potential. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):945–952. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.945-952.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Rassart E., Jolicoeur P. Thymotropism of murine leukemia virus is conferred by its long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4203–4207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. H. Characterization of polytropic MuLVs from three-week-old AKR/J mice. Virology. 1986 Aug;153(1):122–136. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. H., Cloyd M. W. Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses specifically recombine with different endogenous retroviral sequences to generate mink cell focus-forming viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):459–463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. H., Cloyd M. W. Generation of mink cell focus-forming viruses by Friend murine leukemia virus: recombination with specific endogenous proviral sequences. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):772–781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.772-781.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischinger P. J., Nomura S., Bolognesi D. P. A novel murine oncornavirus with dual eco- and xenotropic properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5150–5155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Wolford N. K., Old L. J., Rowe W. P. A new class of murine leukemia virus associated with development of spontaneous lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):789–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemay G., Jolicoeur P. Rearrangement of a DNA sequence homologous to a cell-virus junction fragment in several Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced rat thymomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):38–42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Holland C. A., Hartley J. W., Hopkins N. Viral integration near c-myc in 10-20% of mcf 247-induced AKR lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6808–6811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell P. V., Fleissner E., Lonial H., Koehne C. F., Reicin A. Early clonality and high-frequency proviral integration into the c-myc locus in AKR leukemias. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):500–503. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.500-503.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell P. V., Stockert E., Obata Y., DeLeo A. B., Old L. J. Murine-leukemia-virus-related cell-surface antigens as serological markers of AKR ecotropic, xenotropic, and dualtropic viruses. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):1255–1264. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein A. Interference grouping of murine leukemia viruses: a distinct receptor for the MCF-recombinant viruses in mouse cells. Virology. 1982 Jul 15;120(1):251–257. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommelaere J., Faller D. V., Hopkins N. Characterization and mapping of RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides derived from the genomes of Akv and MCF murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):495–499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Haseltine W. A., Lenz J., Ruprecht R., Cloyd M. W. Tissue selectivity of murine leukemia virus infection is determined by long terminal repeat sequences. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):862–866. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.862-866.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti S., Davis L., Feild J., Oliff A. Friend murine leukemia virus-induced leukemia is associated with the formation of mink cell focus-inducing viruses and is blocked in mice expressing endogenous mink cell focus-inducing xenotropic viral envelope genes. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):907–920. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selten G., Cuypers H. T., Zijlstra M., Melief C., Berns A. Involvement of c-myc in MuLV-induced T cell lymphomas in mice: frequency and mechanisms of activation. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3215–3222. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02281.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon M., Nishio J., Wehrly K., Chesebro B. Pseudotyping of dual-tropic recombinant viruses generated by infection of mice with different ecotropic murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1985 Jan 15;140(1):144–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90453-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon M., Nishio J., Wehrly K., Lodmell D., Chesebro B. Use of a focal immunofluorescence assay on live cells for quantitation of retroviruses: distinction of host range classes in virus mixtures and biological cloning of dual-tropic murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1985 Feb;141(1):110–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90187-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen D. Proviruses are adjacent to c-myc in some murine leukemia virus-induced lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2097–2101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troxler D. H., Scolnick E. M. Rapid leukemia induced by cloned friend strain of replicating murine type-C virus. Association with induction of xenotropic-related RNA sequences contained in spleen focus-forming virus. Virology. 1978 Mar;85(1):17–27. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90408-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Strauss P. G., Hu L. F. A common region for proviral DNA integration in MoMuLV-induced rat thymic lymphomas. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):445–449. doi: 10.1038/302445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt M. Properties of "mink cell focus-inducing" (MCF) virus isolated from spontaneous lymphoma lines of BALB/c mice carrying Moloney leukemia virus as an endogenous virus. Virology. 1979 Feb;93(1):226–236. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90290-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Putten H., Quint W., van Raaij J., Maandag E. R., Verma I. M., Berns A. M-MuLV-induced leukemogenesis: integration and structure of recombinant proviruses in tumors. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



