Abstract
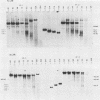
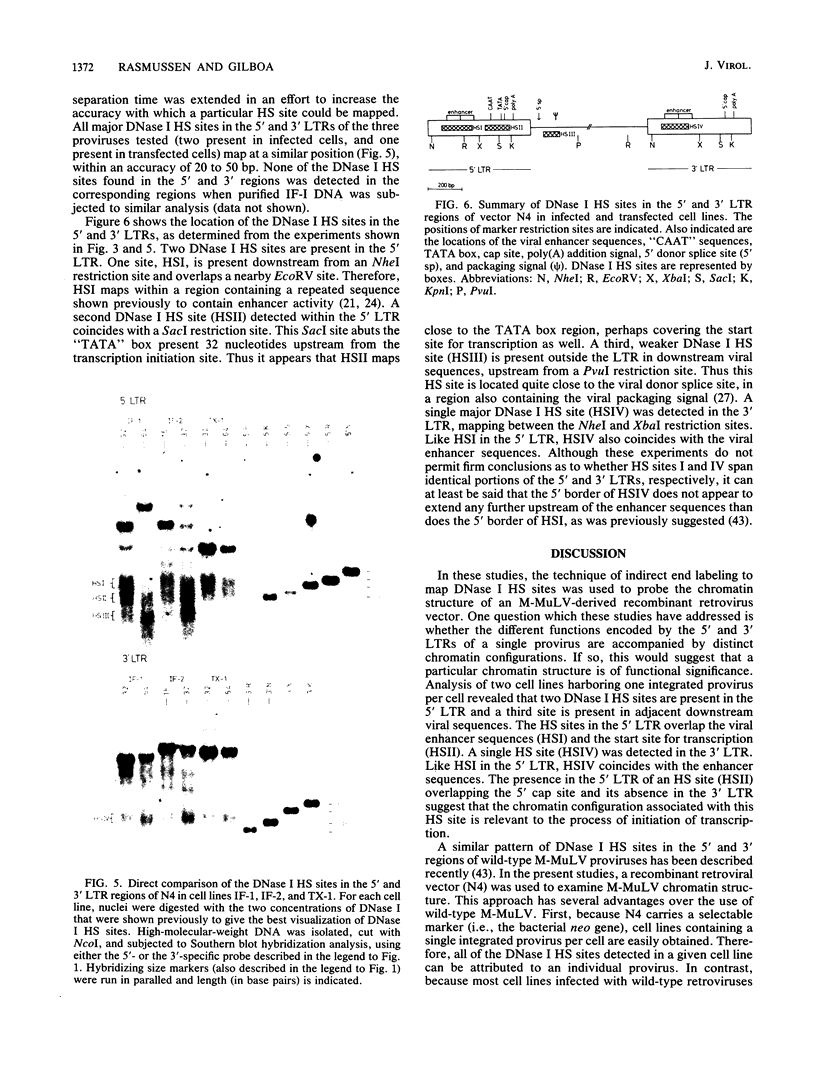
A Moloney murine leukemia virus-derived retroviral vector (N4) carrying the bacterial neomycin resistance gene (neo) was used to study the chromatin configuration of integrated proviral DNA in NIH 3T3-derived cell lines containing one copy of the vector DNA per cell. Three independently obtained cell lines were examined. In two of these cell lines, the vector was introduced by viral infection, while in the third the construct was introduced by DNA transfection. Such transfected cell lines (including the one examined) usually express 10- to 50-fold less virus-specific RNA than do cell lines obtained by viral infection. All three cell lines exhibited similar patterns of DNase I-hypersensitive (HS) sites. Two strong DNase I HS sites were detected in the 5' long terminal repeat, which contains signals required for proper and efficient initiation of viral transcription. One of these sites was found to overlap the viral enhancer sequences, while the other site mapped very close to the start site for viral transcription. A third HS site was detected in nearby internal viral sequences. Only one HS site was found in the 3' long terminal repeat, which contains the signal(s) required for proper addition of a poly(A) tail to viral transcripts. This HS site was located in the region of the viral enhancer. Several weak DNase I HS sites were also found in the cellular sequences adjacent to the integration sites, at different locations in each cell line analyzed. No common pattern of cellular DNase I HS sites was found. These observations suggest that the 5' and 3' long terminal repeats of integrated retroviral proviruses exhibit different chromatin conformations, possibly reflecting the different functions encoded by the otherwise identical sequences, and the DNase I HS sites detected in these studies reflect only a potential for transcription and are not a reflection of the high transcriptional activity characteristic of retroviruses.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacheler L. T., Fan H. Multiple integration sites for Moloney murine leukemia virus in productively infected mouse fibroblasts. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):657–667. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.657-667.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay P. K., Temin H. M. Expression of complete chicken thymidine kinase gene inserted in a retrovirus vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):749–754. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bier E., Hashimoto Y., Greene M. I., Maxam A. M. Active T-cell receptor genes have intron deoxyribonuclease hypersensitive sites. Science. 1985 Aug 9;229(4713):528–534. doi: 10.1126/science.3927483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch J. B., Weintraub H. Temporal order of chromatin structural changes associated with activation of the major chicken vitellogenin gene. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright I. L., Elgin S. C. Nucleosomal instability and induction of new upstream protein-DNA associations accompany activation of four small heat shock protein genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):779–791. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiswell D. J., Gillespie D. A., Wyke J. A. The changes in proviral chromatin that accompany morphological variation in avian sarcoma virus-infected rat cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 10;10(13):3967–3980. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.13.3967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conklin K. F., Coffin J. M., Robinson H. L., Groudine M., Eisenman R. Role of methylation in the induced and spontaneous expression of the avian endogenous virus ev-1: DNA structure and gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;2(6):638–652. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.6.638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. Chromatin structure, DNA structure. Nature. 1982 Dec 2;300(5891):402–403. doi: 10.1038/300402a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. DNAase I-hypersensitive sites of chromatin. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):413–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90381-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein S. C., Ross S. R., Yamamoto K. R. Chromosomal position effects determine transcriptional potential of integrated mammary tumor virus DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 15;156(3):549–565. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90266-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garel A., Axel R. Selective digestion of transcriptionally active ovalbumin genes from oviduct nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3966–3970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garel A., Zolan M., Axel R. Genes transcribed at diverse rates have a similar conformation in chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4867–4871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Eisenman R., Weintraub H. Chromatin structure of endogenous retroviral genes and activation by an inhibitor of DNA methylation. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):311–317. doi: 10.1038/292311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Weintraub H. Propagation of globin DNAase I-hypersensitive sites in absence of factors required for induction: a possible mechanism for determination. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Shank P. R., Spector D. H., Kung H. J., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E., Vogt P. K., Breitman M. L. Proviruses of avian sarcoma virus are terminally redundant, co-extensive with unintegrated linear DNA and integrated at many sites. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1397–1410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang L. H., Gilboa E. Expression of genes introduced into cells by retroviral infection is more efficient than that of genes introduced into cells by DNA transfection. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):417–424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.417-424.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch R., Jähner D., Nobis P., Simon I., Löhler J., Harbers K., Grotkopp D. Chromosomal position and activation of retroviral genomes inserted into the germ line of mice. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):519–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90343-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolly D. J., Esty A. C., Subramani S., Friedmann T., Verma I. M. Elements in the long terminal repeat of murine retroviruses enhance stable transformation by thymidine kinase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1855–1872. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen R. A., Rothstein S. J., Reznikoff W. S. A restriction enzyme cleavage map of Tn5 and location of a region encoding neomycin resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1979;177(1):65–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00267254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene M. A., Corces V., Lowenhaupt K., Elgin S. C. DNase I hypersensitive sites in Drosophila chromatin occur at the 5' ends of regions of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):143–146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Khoury G., Gorman C., Howard B., Gruss P. Host-specific activation of transcription by tandem repeats from simian virus 40 and Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6453–6457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A., Weintraub H. An altered DNA conformation detected by S1 nuclease occurs at specific regions in active chick globin chromatin. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):609–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D., Oudet P., Chambon P. Structure of transcribing chromatin. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1980;24:1–55. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60670-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Wood W. I., Dolan M., Engel J. D., Felsenfeld G. A 200 base pair region at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene is accessible to nuclease digestion. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):45–55. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90359-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Jolly D. J., Friedmann T., Verma I. M. A transmissible retrovirus expressing human hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT): gene transfer into cells obtained from humans deficient in HPRT. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4709–4713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Law M. F., Verma I. M. Generation of helper-free amphotropic retroviruses that transduce a dominant-acting, methotrexate-resistant dihydrofolate reductase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):431–437. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills F. C., Fisher L. M., Kuroda R., Ford A. M., Gould H. J. DNase I hypersensitive sites in the chromatin of human mu immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):809–812. doi: 10.1038/306809a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon P. E., Montandon F., Fan H. Methylation state and DNase I sensitivity of chromatin containing Moloney murine leukemia virus DNA in exogenously infected mouse cells. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):475–486. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.475-486.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shermoen A. W., Beckendorf S. K. A complex of interacting DNAase I-hypersensitive sites near the Drosophila glue protein gene, Sgs4. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):601–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotohno K., Temin H. M. No apparent nucleotide sequence specificity in cellular DNA juxtaposed to retrovirus proviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7357–7361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorge J., Cutting A. E., Erdman V. D., Gautsch J. W. Integration-specific retrovirus expression in embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6627–6631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalder J., Groudine M., Dodgson J. B., Engel J. D., Weintraub H. Hb switching in chickens. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):973–980. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90088-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalder J., Larsen A., Engel J. D., Dolan M., Groudine M., Weintraub H. Tissue-specific DNA cleavages in the globin chromatin domain introduced by DNAase I. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90631-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet R. W., Chao M. V., Axel R. The structure of the thymidine kinase gene promoter: nuclease hypersensitivity correlates with expression. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):347–353. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90128-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson T., Fan H. Mapping of DNase I-hypersensitive sites in the 5' and 3' long terminal repeats of integrated moloney murine leukemia virus proviral DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):601–609. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Groudine M. Chromosomal subunits in active genes have an altered conformation. Science. 1976 Sep 3;193(4256):848–856. doi: 10.1126/science.948749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Larsen A., Groudine M. Alpha-Globin-gene switching during the development of chicken embryos: expression and chromosome structure. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):333–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90323-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrod S. Active chromatin. Nature. 1982 May 27;297(5864):289–295. doi: 10.1038/297289a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Bingham P. M., Livak K. J., Holmgren R., Elgin S. C. The chromatin structure of specific genes: I. Evidence for higher order domains of defined DNA sequence. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Gilbert W. Tissue-specific exposure of chromatin structure at the 5' terminus of the rat preproinsulin II gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1577–1580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Yamamoto K. R. Reversible and persistent changes in chromatin structure accompany activation of a glucocorticoid-dependent enhancer element. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90523-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Putten H., Quint W., Verma I. M., Berns A. Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced tumors: recombinant proviruses in active chromatin regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):577–592. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]