Abstract
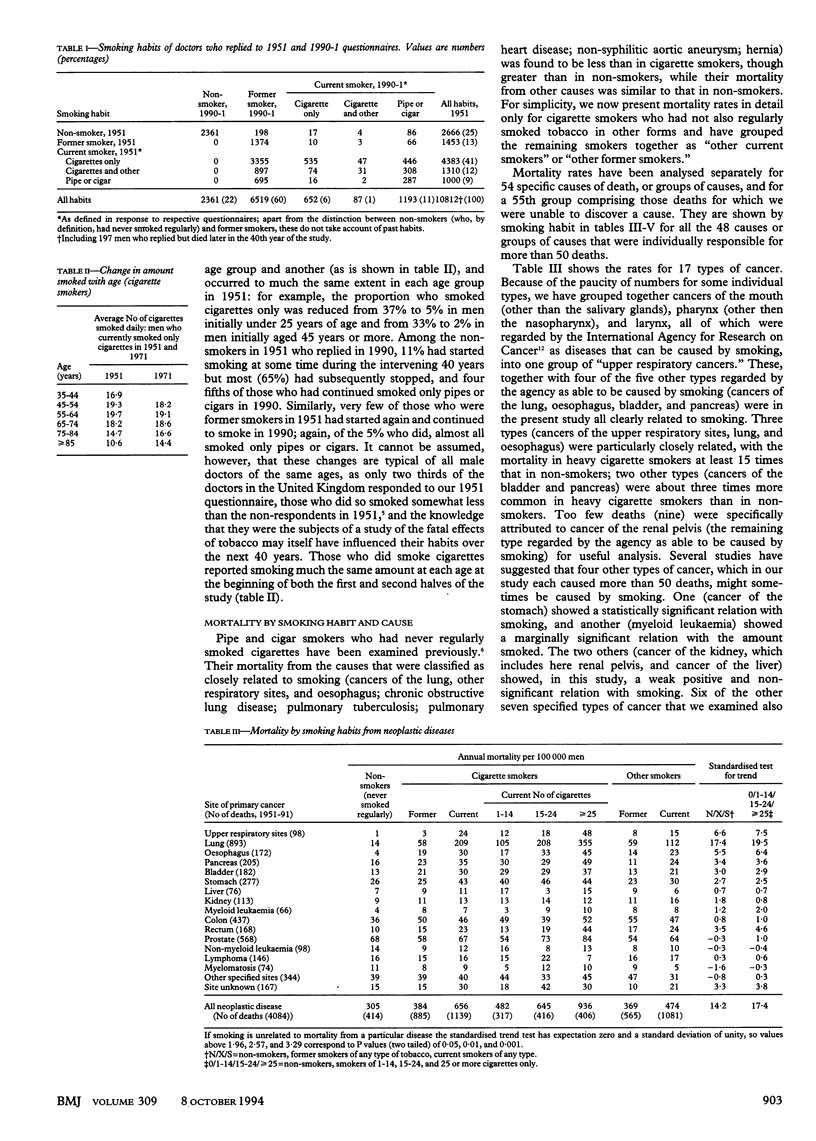
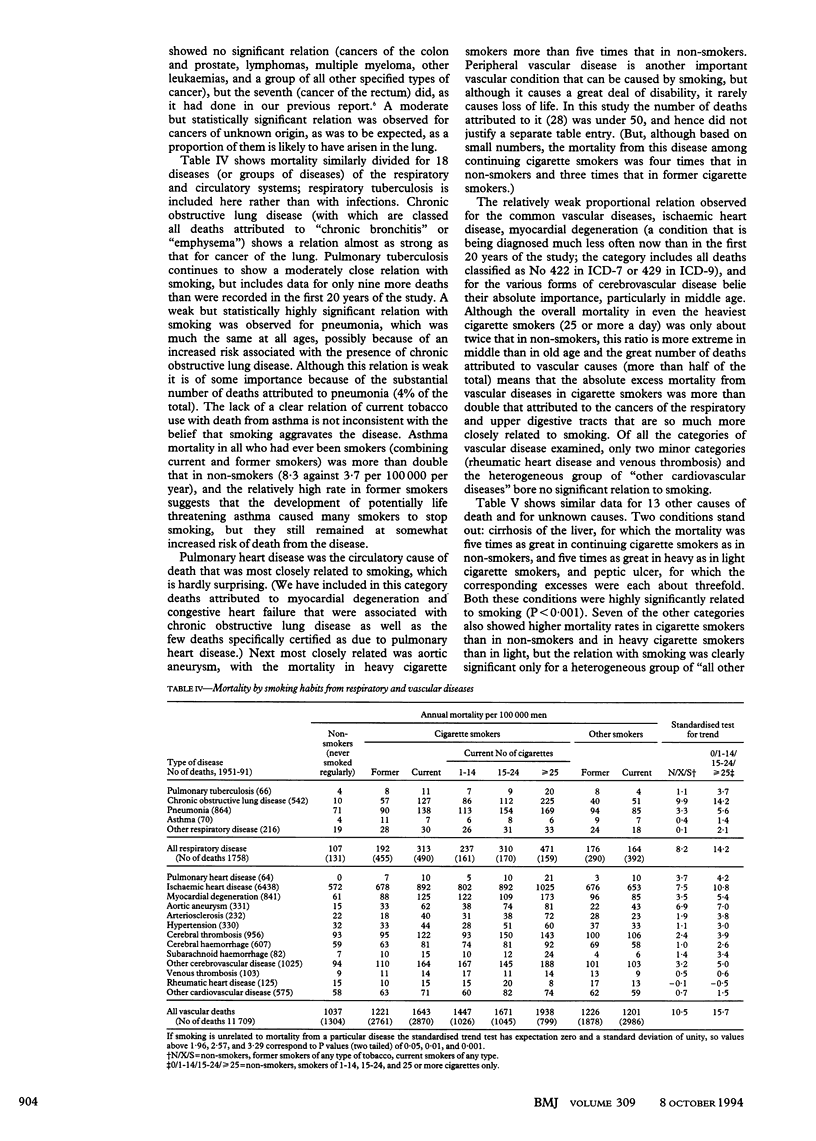
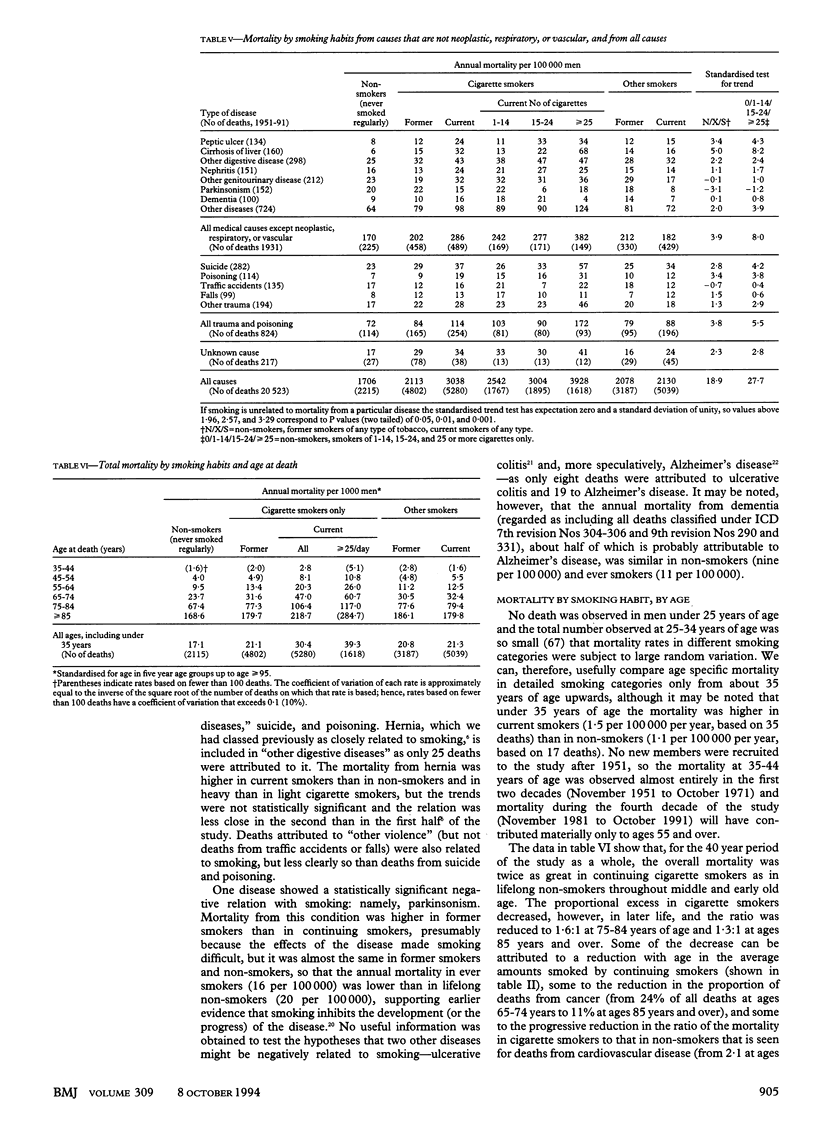
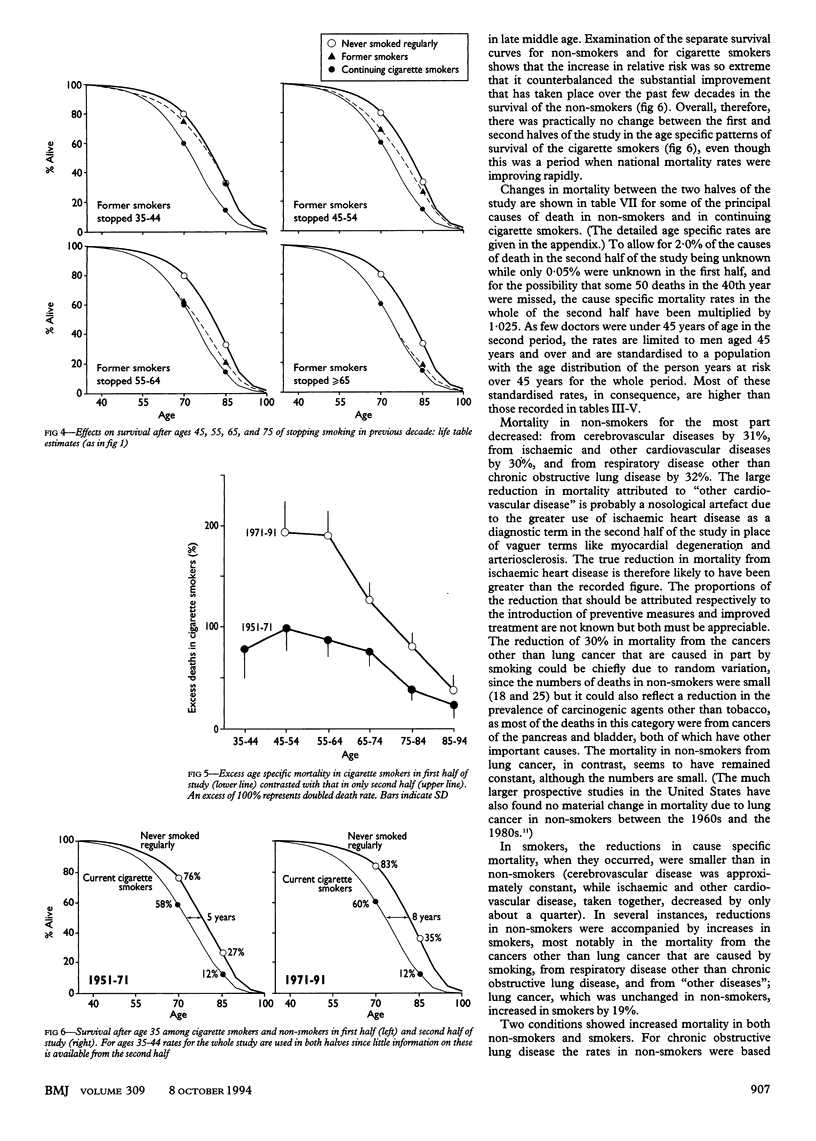
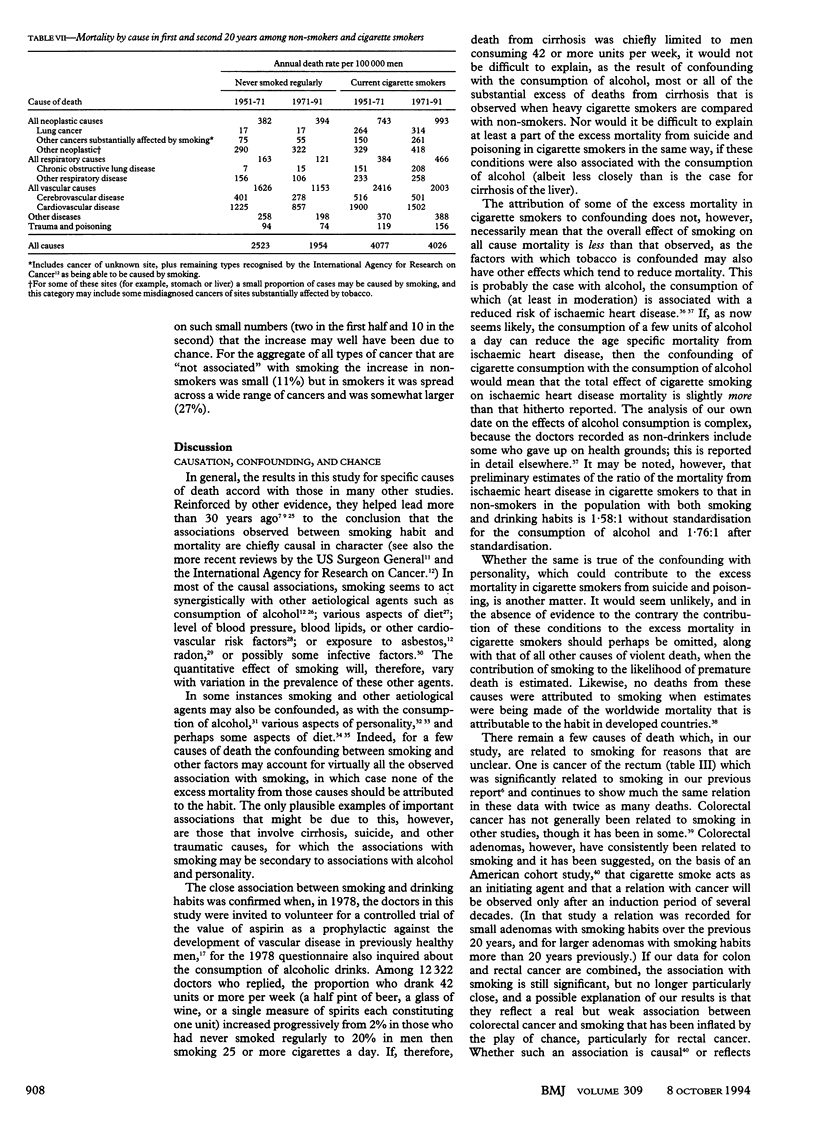
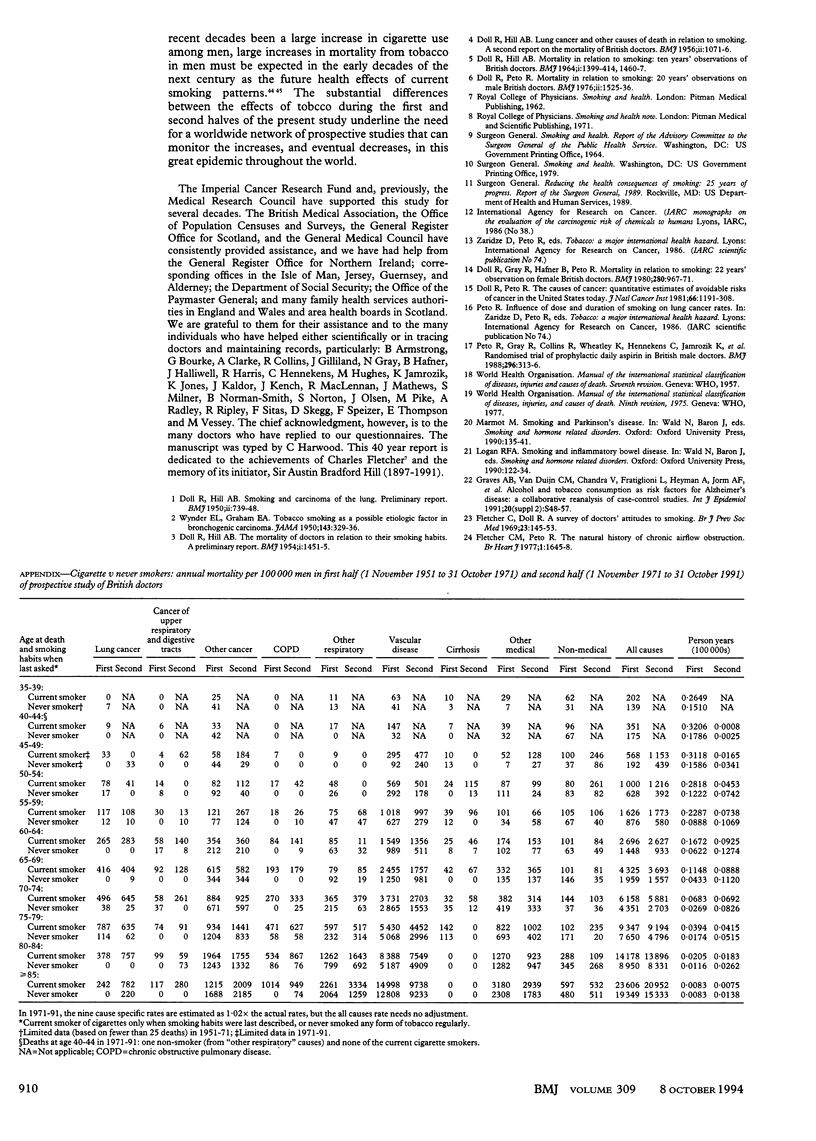
OBJECTIVE--To assess the hazards associated with long term use of tobacco. DESIGN--Prospective study of mortality in relation to smoking habits assessed in 1951 and again from time to time thereafter, with causes sought of deaths over 40 years (to 1991). Continuation of a study that was last reported after 20 years' follow up (1951-71). SUBJECTS--34,439 British male doctors who replied to a postal questionnaire in 1951, of whom 10,000 had died during the first 20 years and another 10,000 have died during the second 20 years. RESULTS--Excess mortality associated with smoking was about twice as extreme during the second half of the study as it had been during the first half. The death rate ratios during 1971-91 (comparing continuing cigarette smokers with life-long non-smokers) were approximately threefold at ages 45-64 and twofold at ages 65-84. The excess mortality was chiefly from diseases that can be caused by smoking. Positive associations with smoking were confirmed for death from cancers of the mouth, oesophagus, pharynx, larynx, lung, pancreas, and bladder; from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and other respiratory diseases; from vascular diseases; from peptic ulcer; and (perhaps because of confounding by personality and alcohol use) from cirrhosis, suicide, and poisoning. A negative association was confirmed with death from Parkinson's disease. Those who stopped smoking before middle age subsequently avoided almost all of the excess risk that they would otherwise have suffered, but even those who stopped smoking in middle age were subsequently at substantially less risk than those who continued to smoke. CONCLUSION--Results from the first 20 years of this study, and of other studies at that time, substantially underestimated the hazards of long term use of tobacco. It now seems that about half of all regular cigarette smokers will eventually be killed by their habit.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bosch F. X., Muñoz N., de Sanjosé S., Izarzugaza I., Gili M., Viladiu P., Tormo M. J., Moreo P., Ascunce N., Gonzalez L. C. Risk factors for cervical cancer in Colombia and Spain. Int J Cancer. 1992 Nov 11;52(5):750–758. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910520514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLL R., HILL A. B. Lung cancer and other causes of death in relation to smoking; a second report on the mortality of British doctors. Br Med J. 1956 Nov 10;2(5001):1071–1081. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5001.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLL R., HILL A. B. MORTALITY IN RELATION TO SMOKING: TEN YEARS' OBSERVATIONS OF BRITISH DOCTORS. Br Med J. 1964 May 30;1(5395):1399–1410. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5395.1399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLL R., HILL A. B. Smoking and carcinoma of the lung; preliminary report. Br Med J. 1950 Sep 30;2(4682):739–748. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4682.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLL R., HILL A. B. The mortality of doctors in relation to their smoking habits; a preliminary report. Br Med J. 1954 Jun 26;1(4877):1451–1455. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4877.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doll R., Gray R., Hafner B., Peto R. Mortality in relation to smoking: 22 years' observations on female British doctors. Br Med J. 1980 Apr 5;280(6219):967–971. doi: 10.1136/bmj.280.6219.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doll R., Peto R. Mortality in relation to smoking: 20 years' observations on male British doctors. Br Med J. 1976 Dec 25;2(6051):1525–1536. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6051.1525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher C., Doll R. A survey of doctors' attitudes to smoking. Br J Prev Soc Med. 1969 Aug;23(3):145–153. doi: 10.1136/jech.23.3.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher C., Peto R. The natural history of chronic airflow obstruction. Br Med J. 1977 Jun 25;1(6077):1645–1648. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6077.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannucci E., Rimm E. B., Stampfer M. J., Colditz G. A., Ascherio A., Kearney J., Willett W. C. A prospective study of cigarette smoking and risk of colorectal adenoma and colorectal cancer in U.S. men. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994 Feb 2;86(3):183–191. doi: 10.1093/jnci/86.3.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves A. B., van Duijn C. M., Chandra V., Fratiglioni L., Heyman A., Jorm A. F., Kokmen E., Kondo K., Mortimer J. A., Rocca W. A. Alcohol and tobacco consumption as risk factors for Alzheimer's disease: a collaborative re-analysis of case-control studies. EURODEM Risk Factors Research Group. Int J Epidemiol. 1991;20 (Suppl 2):S48–S57. doi: 10.1093/ije/20.supplement_2.s48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker M. P., Orza M. J., Adams M. E., Vioque J., Chalmers T. C. A meta-analysis of alcoholic beverage consumption in relation to risk of colorectal cancer. Cancer Causes Control. 1990 Jul;1(1):59–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00053184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margetts B. M., Jackson A. A. Interactions between people's diet and their smoking habits: the dietary and nutritional survey of British adults. BMJ. 1993 Nov 27;307(6916):1381–1384. doi: 10.1136/bmj.307.6916.1381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmot M., Brunner E. Alcohol and cardiovascular disease: the status of the U shaped curve. BMJ. 1991 Sep 7;303(6802):565–568. doi: 10.1136/bmj.303.6802.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peto R., Gray R., Collins R., Wheatley K., Hennekens C., Jamrozik K., Warlow C., Hafner B., Thompson E., Norton S. Randomised trial of prophylactic daily aspirin in British male doctors. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1988 Jan 30;296(6618):313–316. doi: 10.1136/bmj.296.6618.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peto R., Lopez A. D., Boreham J., Thun M., Heath C., Jr Mortality from tobacco in developed countries: indirect estimation from national vital statistics. Lancet. 1992 May 23;339(8804):1268–1278. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91600-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamler J., Vaccaro O., Neaton J. D., Wentworth D. Diabetes, other risk factors, and 12-yr cardiovascular mortality for men screened in the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial. Diabetes Care. 1993 Feb;16(2):434–444. doi: 10.2337/diacare.16.2.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYNDER E. L., GRAHAM E. A. Tobacco smoking as a possible etiologic factor in bronchiogenic carcinoma; a study of 684 proved cases. J Am Med Assoc. 1950 May 27;143(4):329–336. doi: 10.1001/jama.1950.02910390001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


