Abstract
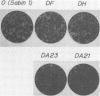
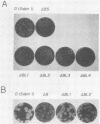
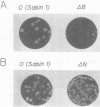
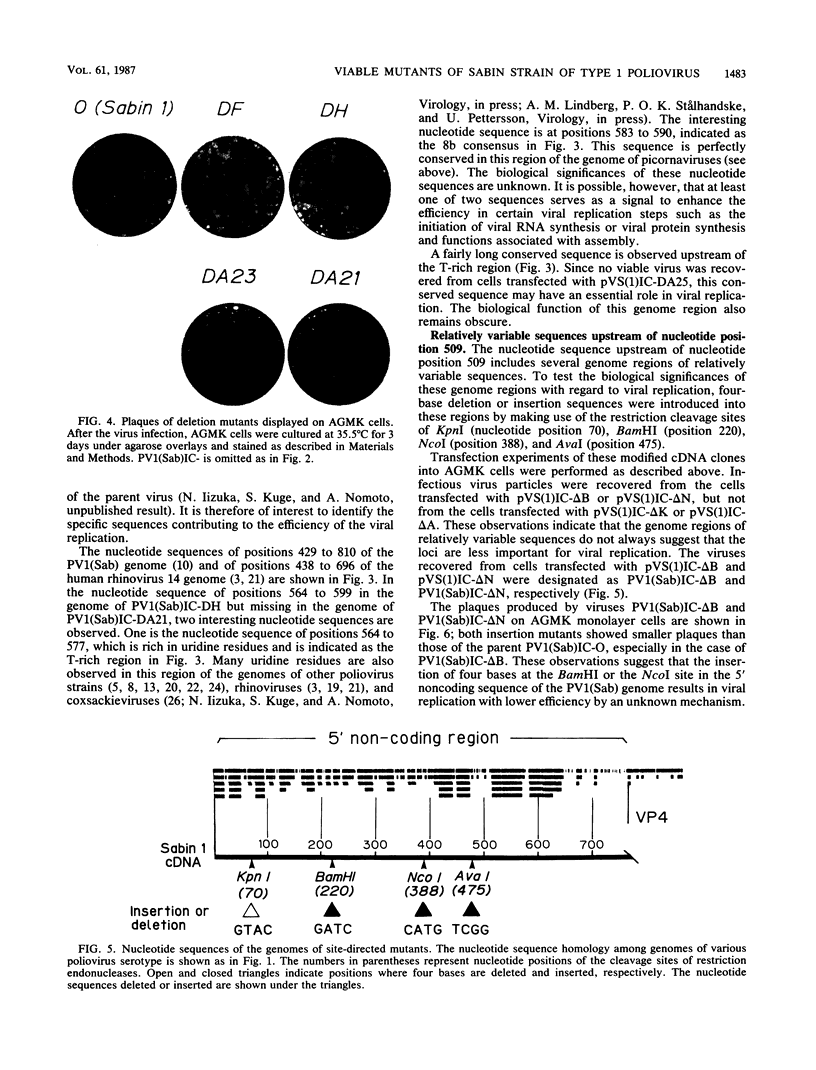
A number of deletion and insertion sequences were introduced into the 5' noncoding sequence (742 nucleotides long) of the genome of the Sabin strain of type 1 poliovirus by using an infectious cDNA clone of the virus strain. The genomes of all three poliovirus serotypes contained highly homologous sequences (nucleotide positions 509 to 639) as well as highly variable sequences (positions 640 to 742) in the 5' noncoding region. The viability of mutant viruses was tested by transfecting mutant cDNA clones into African green monkey kidney cells and then estimating the plaque sizes displayed on the cells. The results suggested that the highly variable sequence next to the VP4 coding region did not play an important role, at least in the in vitro culture system used, that the loci of highly conserved nucleotide sequences were not always expected to be the genome regions essential for viral replication, that the sequence between positions 564 and 599 carried genetic information to maintain the efficiency of certain steps in viral replication, and that the sequence between positions 551 to 563 might play an essential role in viral replication. Four-base deletion or insertion mutations were introduced into relatively variable sequences in the genome region upstream of position 509. The results suggest that variable sequences do not always indicate that the corresponding genome regions are less important. Apparent revertants (large-plaque variants) were easily generated from one of the viable mutants with the small-plaque phenotype. The determination of nucleotide sequences of the revertant genomes revealed the second mutation site. The results suggested that the different loci at around positions 200 and 500 might specifically interact with each other. This interaction may result in the formation of a functional structure that influences the efficiency of certain steps in the viral replication.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J., Lee F., Harrison T., Williams J., Sharp P. A. Pre-early adenovirus 5 gene product regulates synthesis of early viral messenger RNAs. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):935–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Sonenberg N., Baltimore D. Poliovirus mutant that does not selectively inhibit host cell protein synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2913–2923. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan P. L., Mizutani S., Colonno R. J. Molecular cloning and complete sequence determination of RNA genome of human rhinovirus type 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):732–736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanecak R., Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Proteolytic processing of poliovirus polypeptides: antibodies to polypeptide P3-7c inhibit cleavage at glutamine-glycine pairs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3973–3977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Semler B. L., Rothberg P. G., Larsen G. R., Adler C. J., Dorner A. J., Emini E. A., Hanecak R., Lee J. J., van der Werf S. Primary structure, gene organization and polypeptide expression of poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):547–553. doi: 10.1038/291547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara M., Abe S., Kuge S., Semler B. L., Komatsu T., Arita M., Itoh H., Nomoto A. An infectious cDNA clone of the poliovirus Sabin strain could be used as a stable repository and inoculum for the oral polio live vaccine. Virology. 1986 May;151(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90100-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara M., Omata T., Kameda A., Semler B. L., Itoh H., Wimmer E., Nomoto A. In vitro phenotypic markers of a poliovirus recombinant constructed from infectious cDNA clones of the neurovirulent Mahoney strain and the attenuated Sabin 1 strain. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):786–792. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.786-792.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Monica N., Meriam C., Racaniello V. R. Mapping of sequences required for mouse neurovirulence of poliovirus type 2 Lansing. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):515–525. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.515-525.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Kitamura N., Golini F., Wimmer E. The 5'-terminal structures of poliovirion RNA and poliovirus mRNA differ only in the genome-linked protein VPg. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5345–5349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Omata T., Toyoda H., Kuge S., Horie H., Kataoka Y., Genba Y., Nakano Y., Imura N. Complete nucleotide sequence of the attenuated poliovirus Sabin 1 strain genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5793–5797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omata T., Kohara M., Kuge S., Komatsu T., Abe S., Semler B. L., Kameda A., Itoh H., Arita M., Wimmer E. Genetic analysis of the attenuation phenotype of poliovirus type 1. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):348–358. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.348-358.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omata T., Kohara M., Sakai Y., Kameda A., Imura N., Nomoto A. Cloned infectious complementary DNA of the poliovirus Sabin 1 genome: biochemical and biological properties of the recovered virus. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(1-2):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Cloned poliovirus complementary DNA is infectious in mammalian cells. Science. 1981 Nov 20;214(4523):916–919. doi: 10.1126/science.6272391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Molecular cloning of poliovirus cDNA and determination of the complete nucleotide sequence of the viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4887–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P., Bernstein H. D., Baltimore D. A poliovirus temperature-sensitive RNA synthesis mutant located in a noncoding region of the genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):571–575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Dorner A. J., Wimmer E. Production of infectious poliovirus from cloned cDNA is dramatically increased by SV40 transcription and replication signals. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 25;12(12):5123–5141. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.12.5123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Johnson V. H., Tracy S. A chimeric plasmid from cDNA clones of poliovirus and coxsackievirus produces a recombinant virus that is temperature-sensitive. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1777–1781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skern T., Sommergruber W., Blaas D., Gruendler P., Fraundorfer F., Pieler C., Fogy I., Kuechler E. Human rhinovirus 2: complete nucleotide sequence and proteolytic processing signals in the capsid protein region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):2111–2126. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.2111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanway G., Cann A. J., Hauptmann R., Hughes P., Clarke L. D., Mountford R. C., Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Almond J. W. The nucleotide sequence of poliovirus type 3 leon 12 a1b: comparison with poliovirus type 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5629–5643. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanway G., Hughes P. J., Mountford R. C., Minor P. D., Almond J. W. The complete nucleotide sequence of a common cold virus: human rhinovirus 14. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7859–7875. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanway G., Hughes P. J., Mountford R. C., Reeve P., Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Almond J. W. Comparison of the complete nucleotide sequences of the genomes of the neurovirulent poliovirus P3/Leon/37 and its attenuated Sabin vaccine derivative P3/Leon 12a1b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1539–1543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanway G., Hughes P. J., Westrop G. D., Evans D. M., Dunn G., Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Almond J. W. Construction of poliovirus intertypic recombinants by use of cDNA. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1187–1190. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1187-1190.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Kohara M., Kataoka Y., Suganuma T., Omata T., Imura N., Nomoto A. Complete nucleotide sequences of all three poliovirus serotype genomes. Implication for genetic relationship, gene function and antigenic determinants. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 25;174(4):561–585. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90084-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Nicklin M. J., Murray M. G., Anderson C. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W., Wimmer E. A second virus-encoded proteinase involved in proteolytic processing of poliovirus polyprotein. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):761–770. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90790-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy S., Liu H. L., Chapman N. M. Coxsackievirus B3: primary structure of the 5' non-coding and capsid protein-coding regions of the genome. Virus Res. 1985 Oct;3(3):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimmer E. Genome-linked proteins of viruses. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):199–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90335-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Polyadenylic acid at the 3'-terminus of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1877–1882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]