Abstract
Rotaviruses are the major pathogens that cause life-threatening diarrhea in young children and animals. We inserted a simian rotavirus SA11 gene 6 cDNA into the genome of the baculovirus Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus adjacent to the strong polyhedrin promoter. The major capsid antigen (VP6) was expressed in high yields (20 to 150 micrograms/10(6) cells) when Spodoptera frugiperda cells were infected with baculovirus recombinants containing SA11 gene 6 inserts. Reactivity with monospecific polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies suggested that VP6, expressed intracellularly or found in the media, maintained native antigenic determinants. VP6 purified from the media from infected cells also possessed a native oligomeric structure, was immunogenic in guinea pigs, and was able to spontaneously assemble into morphologic subunits. Antisera from immunized guinea pigs failed to neutralize virus in plaque reduction assays, but detected homologous and heterologous rotavirus strains when tested by immunofluorescence, immunoprecipitation, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays.
Full text
PDF
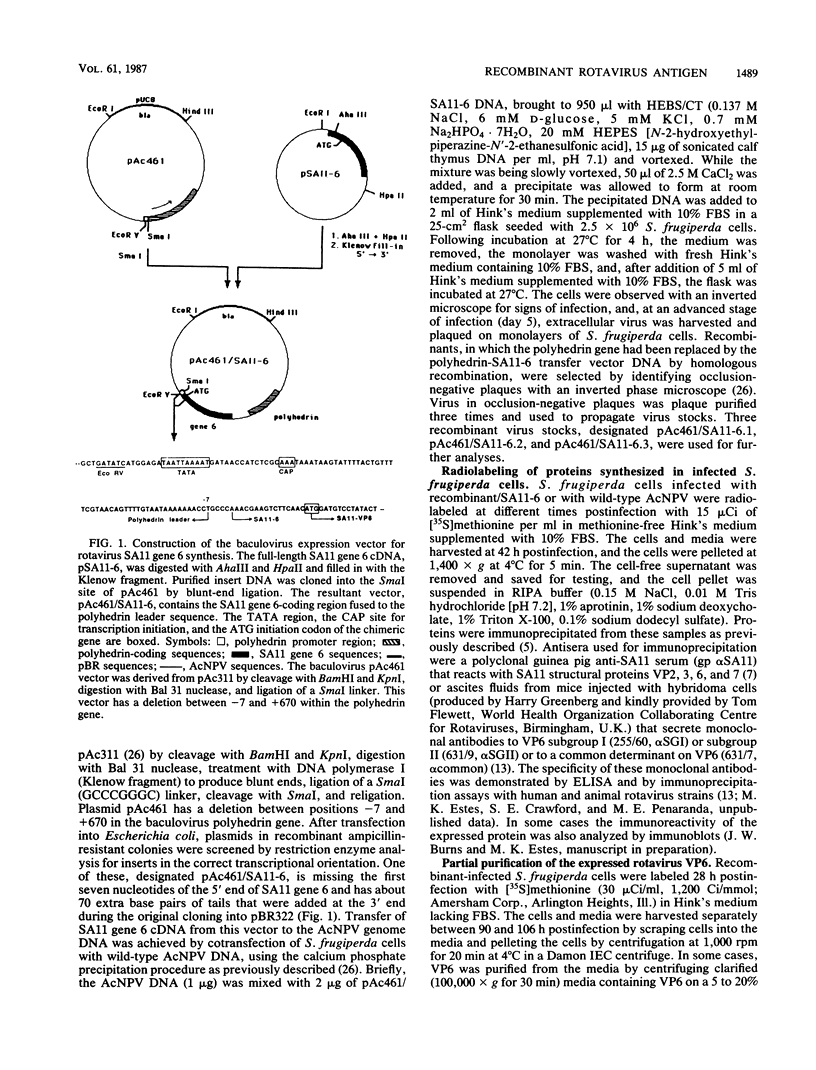


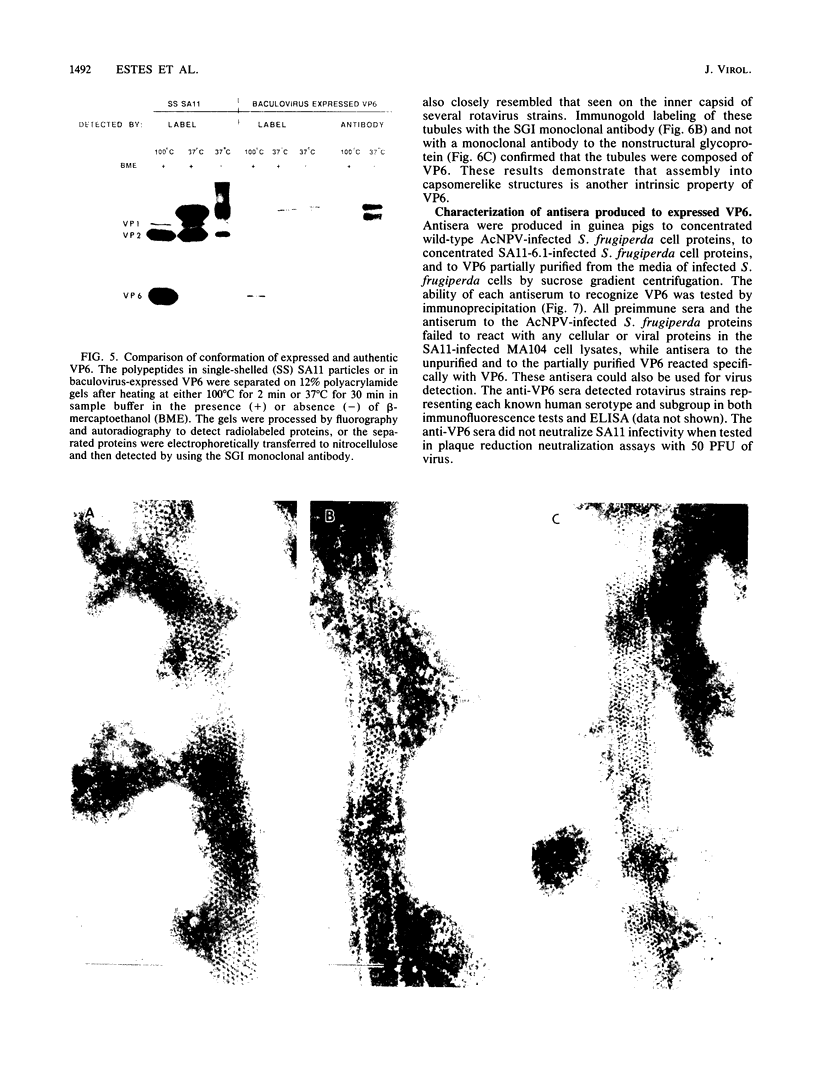


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bastardo J. W., McKimm-Breschkin J. L., Sonza S., Mercer L. D., Holmes I. H. Preparation and characterization of antisera to electrophoretically purified SA11 virus polypeptides. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):641–647. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.641-647.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beards G. M., Campbell A. D., Cottrell N. R., Peiris J. S., Rees N., Sanders R. C., Shirley J. A., Wood H. C., Flewett T. H. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays based on polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies for rotavirus detection. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):248–254. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.248-254.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bican P., Cohen J., Charpilienne A., Scherrer R. Purification and characterization of bovine rotavirus cores. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1113–1117. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1113-1117.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. K., Penaranda M. E., Crawford S. E., Estes M. K. Two glycoproteins are produced from the rotavirus neutralization gene. Virology. 1986 Jun;151(2):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson B. L., Graham D. Y., Mason B. B., Estes M. K. Identification, synthesis, and modifications of simian rotavirus SA11 polypeptides in infected cells. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):825–839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.825-839.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Gerba C. P., Smith E. M. Simian rotavirus SA11 replication in cell cultures. J Virol. 1979 Sep;31(3):810–815. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.3.810-815.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Graham D. Y. Rotavirus antigens. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1985;185:201–214. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-7974-4_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Mason B. B., Crawford S., Cohen J. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the simian rotavirus gene 6 that codes for the major inner capsid protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 24;12(4):1875–1887. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.4.1875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorziglia M., Larrea C., Liprandi F., Esparza J. Biochemical evidence for the oligomeric (possibly trimeric) structure of the major inner capsid polypeptide (45K) of rotaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1985 Sep;66(Pt 9):1889–1900. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-9-1889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H., McAuliffe V., Valdesuso J., Wyatt R., Flores J., Kalica A., Hoshino Y., Singh N. Serological analysis of the subgroup protein of rotavirus, using monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):91–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.91-99.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killen H. M., Dimmock N. J. Identification of a neutralization-specific antigen of a calf rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1982 Oct;62(Pt 2):297–311. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-62-2-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda S., Kawai T., Obinata M., Fujiwara H., Horiuchi T., Saeki Y., Sato Y., Furusawa M. Production of human alpha-interferon in silkworm using a baculovirus vector. Nature. 1985 Jun 13;315(6020):592–594. doi: 10.1038/315592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason B. B., Graham D. Y., Estes M. K. Biochemical mapping of the simian rotavirus SA11 genome. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):413–423. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.413-423.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto C., Smith G. E., Farrell-Towt J., Chizzonite R., Summers M. D., Ju G. Production of human c-myc protein in insect cells infected with a baculovirus expression vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2860–2865. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata S., Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Loosle R., Tao H., Wang S. H., Saif L. J., Melnick J. L. Antigenic characterization and ELISA detection of adult diarrhea rotaviruses. J Infect Dis. 1986 Sep;154(3):448–455. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.3.448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Clark H. F., Blavat G., Greenberg H. B. Reassortant rotaviruses containing structural proteins vp3 and vp7 from different parents induce antibodies protective against each parental serotype. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):491–496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.491-496.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roseto A., Scherrer R., Cohen J., Guillemin M. C., Charpilienne A., Feynerol C., Peries J. Isolation and characterization of anti-rotavirus immunoglobulins secreted by cloned hybridoma cell lines. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jan;64(Pt 1):237–240. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-1-237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabara M., Gilchrist J. E., Hudson G. R., Babiuk L. A. Preliminary characterization of an epitope involved in neutralization and cell attachment that is located on the major bovine rotavirus glycoprotein. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):58–66. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.58-66.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salunke D. M., Caspar D. L., Garcea R. L. Self-assembly of purified polyomavirus capsid protein VP1. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):895–904. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90071-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider C., Newman R. A., Sutherland D. R., Asser U., Greaves M. F. A one-step purification of membrane proteins using a high efficiency immunomatrix. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10766–10769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Fraser M. J., Summers M. D. Molecular Engineering of the Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus Genome: Deletion Mutations Within the Polyhedrin Gene. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):584–593. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.584-593.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Ju G., Ericson B. L., Moschera J., Lahm H. W., Chizzonite R., Summers M. D. Modification and secretion of human interleukin 2 produced in insect cells by a baculovirus expression vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8404–8408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D., Fraser M. J. Production of human beta interferon in insect cells infected with a baculovirus expression vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2156–2165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Urasawa T., Urasawa S., Yasuhara T. Production of subgroup-specific monoclonal antibodies against human rotaviruses and their application to an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for subgroup determination. J Med Virol. 1984;14(2):115–125. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890140205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. M., Askonas B. A. Influenza nucleoprotein-specific cytotoxic T-cell clones are protective in vivo. Immunology. 1986 Jul;58(3):417–420. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A. R., McMichael A. J., Carter N. P., Huddleston J. A., Brownlee G. G. Cytotoxic T cell recognition of the influenza nucleoprotein and hemagglutinin expressed in transfected mouse L cells. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90187-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wraith D. C., Askonas B. A. Induction of influenza A virus cross-reactive cytotoxic T cells by a nucleoprotein/haemagglutinin preparation. J Gen Virol. 1985 Jun;66(Pt 6):1327–1331. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-6-1327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]