Abstract
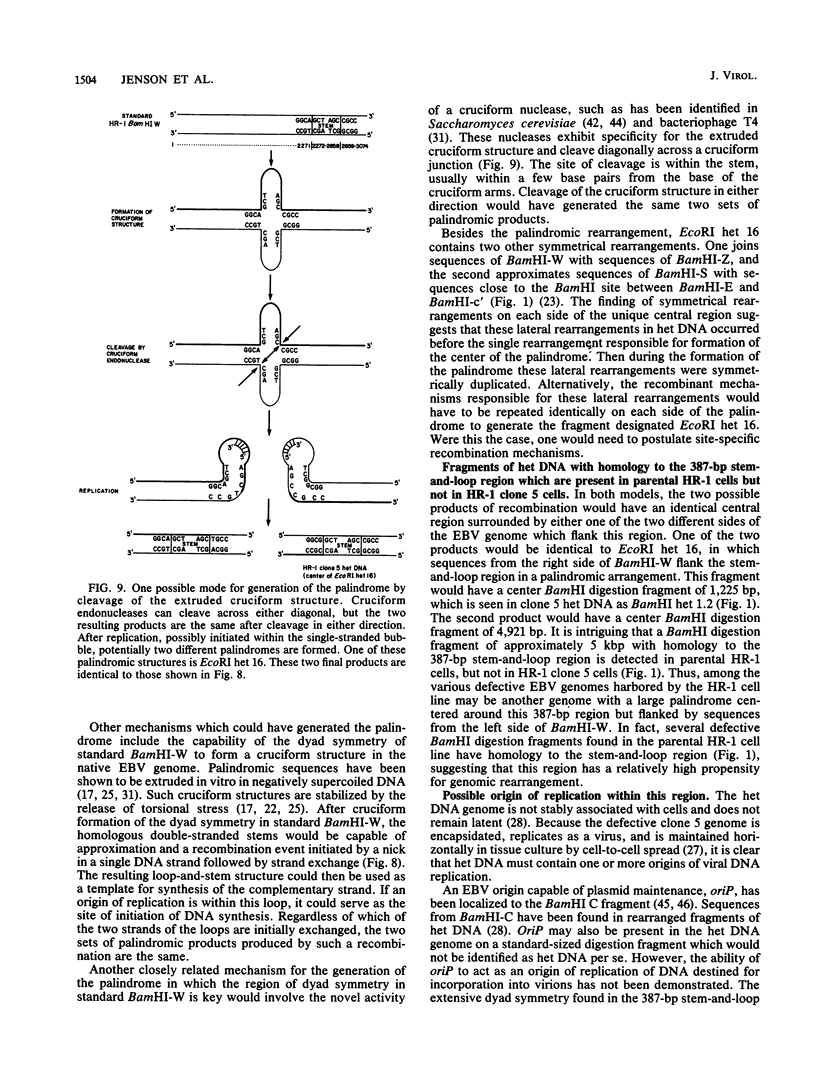
We have previously characterized several genomic rearrangements of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA contained in one of the defective EBV genomes harbored by the P3HR-1 (HR-1) line (H. B. Jenson, M. S. Rabson, and G. Miller, J. Virol. 58:475-486, 1986). One recombinant clone of heterogeneous DNA (het DNA) from this defective genome is an EcoRI fragment of 16 kilobase pairs (kbp) which is a palindrome. DNA digestion fragments specific for the center of this palindrome were present in cells which contained het DNA but not in cells which lacked het DNA. Thus, the palindrome was not an artifact of DNA cloning. The organization of the center of this palindrome was studied by DNA sequencing. The comparable region of the parental HR-1 genome was also studied by DNA sequencing. The central 3,495 base pairs (bp) of the palindrome were composed of sequences derived exclusively from internal repeat 1 of EBV, represented by BamHI W fragment. At each end of the central 3,495 hp was a symmetrical recombination with sequences of BamHI-Z, located more than 50 kbp away on the standard EBV genome. The central 3,495 bp were composed of an unduplicated 341 bp flanked by two perfect palindromic repeats of 1,577 bp. The 341-bp unique region was a portion of a 387-bp region of standard HR-1 BamHI-W which was identical to the central 387 bp of the palindrome. This central 387-bp region contained numerous stretches of dyad symmetry capable of forming a large stem-and-loop structure. The palindromic rearrangement had created two novel open reading frames in het DNA derived from standard HR-1 BamHI-W sequences. These two het DNA open reading frames had different amino termini but identical carboxy termini derived from the large open reading frame in standard HR-1 BamHI-W (HR-1 BWRF1). The BamHI-W sequences found in het DNA did not include either the TATA box of standard HR-1 BamHI-W or the exons which are present in the potentially polycistronic latent mRNAs encoding EBV nuclear antigens. These marked alterations in genomic structure may relate to the unique biologic properties of virus stocks containing het DNA by creation of new polypeptides or by formation or deletion of regulatory or functional signals.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M., Farrell P. J., Barrell B. G. Transcription and DNA sequence of the BamHI L fragment of B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1083–1090. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01933.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Brison O., Perricaudet M. An Epstein-Barr virus transcription unit is at least 84 kilobases long. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2611–2620. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Chambraud B., Farrell P., Perricaudet M. Spliced RNA from the IR1-U2 region of Epstein-Barr virus: presence of an open reading frame for a repetitive polypeptide. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1913–1917. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02067.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornkamm G. W., Hudewentz J., Freese U. K., Zimber U. Deletion of the nontransforming Epstein-Barr virus strain P3HR-1 causes fusion of the large internal repeat to the DSL region. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):952–968. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.952-968.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A., Kieff E. Long internal direct repeat in Epstein-Barr virus DNA. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):286–294. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.286-294.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho M. S., Bornkamm G. W., zur Hausen H. Structure of defective DNA molecules in Epstein-Barr virus preparations from P3HR-1 cells. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):199–207. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.199-207.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Countryman J., Miller G. Activation of expression of latent Epstein-Barr herpesvirus after gene transfer with a small cloned subfragment of heterogeneous viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4085–4089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis D. B., Kingsbury D. T. Quantitation of the viral DNA present in cells transformed by UV-irradiated herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):788–793. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.788-793.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L. Random subcloning of sonicated DNA: application to shotgun DNA sequence analysis. Anal Biochem. 1983 Feb 15;129(1):216–223. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Kallin B., Alexander H., Ernberg I., Uno M., Ono Y., Klein G., Lerner R. A. An Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-determined nuclear antigen (EBNA5) partly encoded by the transformation-associated Bam WYH region of EBV DNA: preferential expression in lymphoblastoid cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6641–6645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fresen K. O., Cho M. S., zur Hausen H. Heterogeneity of Epstein-Barr virus. IV. Induction of a specific antigen by EBV from two transformed marmoset cell lines in Ramos cells. Int J Cancer. 1978 Aug 15;22(2):160–165. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910220209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fresen K. O., Merkt B., Bornkamm G. W., Hausen H. Heterogeneity of Epstein-Barr virus originating from P3HR-1 cells. I. Studies on EBNA induction. Int J Cancer. 1977 Mar 15;19(3):317–323. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Ohmori H., Tomizawa J. DNA gyrase and DNA supercoiling. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):35–40. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G., Zajac B. A., Pearson G., Waubke R., Scriba M. Differential reactivity of human serums with early antigens induced by Epstein-Barr virus. Science. 1970 Jul 10;169(3941):188–190. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3941.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heston L., Rabson M., Brown N., Miller G. New Epstein-Barr virus variants from cellular subclones of P3J-HR-1 Burkitt lymphoma. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):160–163. doi: 10.1038/295160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinuma Y., Konn M., Yamaguchi J., Wudarski D. J., Blakeslee J. R., Jr, Grace J. T., Jr Immunofluorescence and herpes-type virus particles in the P3HR-1 Burkitt lymphoma cell line. J Virol. 1967 Oct;1(5):1045–1051. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.5.1045-1051.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh T. S., Wang J. C. Thermodynamic properties of superhelical DNAs. Biochemistry. 1975 Feb 11;14(3):527–535. doi: 10.1021/bi00674a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenson H. B., Rabson M. S., Miller G. Palindromic structure and polypeptide expression of 36 kilobase pairs of heterogeneous Epstein-Barr virus (P3HR-1) DNA. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):475–486. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.475-486.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. D., Griffin B. E. Clustered repeat sequences in the genome of Epstein Barr virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):3919–3937. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.3919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M., Gough G. W., Hallam L. R., Sullivan K. M. The physical chemistry of cruciform structures in supercoiled DNA molecules. Biochimie. 1985 Jul-Aug;67(7-8):697–706. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(85)80157-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Heston L., Countryman J. P3HR-1 Epstein-Barr virus with heterogeneous DNA is an independent replicon maintained by cell-to-cell spread. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):45–52. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.45-52.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Rabson M., Heston L. Epstein-Barr virus with heterogeneous DNA disrupts latency. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):174–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.174-182.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Robinson J., Heston L., Lipman M. Differences between laboratory strains of Epstein-Barr virus based on immortalization, abortive infection, and interference. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4006–4010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. R., Kramer F. R. Structure-independent nucleotide sequence analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2232–2235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Kemper B., Hays J., Weisberg R. A. T4 endonuclease VII cleaves holliday structures. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabson M., Gradoville L., Heston L., Miller G. Non-immortalizing P3J-HR-1 Epstein-Barr virus: a deletion mutant of its transforming parent, Jijoye. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):834–844. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.834-844.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabson M., Heston L., Miller G. Identification of a rare Epstein-Barr virus variant that enhances early antigen expression in Raji cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2762–2766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. T., Farrell P. J., Miller G. Novel nuclear antigens recognized by human sera in lymphocytes latently infected by Epstein-Barr virus. Virology. 1987 Jan;156(1):153–162. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90446-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Hummel M., Braun D., Birkenbach M., Kieff E. Nucleotide sequences of mRNAs encoding Epstein-Barr virus nuclear proteins: a probable transcriptional initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5096–5100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt J. J., Cohen B. N. Quantitative isolation of DNA restriction fragments from low-melting agarose by Elutip-d affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1983 Sep;133(2):462–464. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck S. H., Strominger J. L. Analysis of the transcript encoding the latent Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen I: a potentially polycistronic message generated by long-range splicing of several exons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8305–8309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Automation of the computer handling of gel reading data produced by the shotgun method of DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4731–4751. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. The current status and portability of our sequence handling software. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):217–231. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symington L. S., Kolodner R. Partial purification of an enzyme from Saccharomyces cerevisiae that cleaves Holliday junctions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7247–7251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. C., Körner A. Cleavage of cruciform DNA structures by an activity from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6445–6449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Warren N., Sugden B. Stable replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus in various mammalian cells. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):812–815. doi: 10.1038/313812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J., Warren N., Reisman D., Sugden B. A cis-acting element from the Epstein-Barr viral genome that permits stable replication of recombinant plasmids in latently infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3806–3810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Santen V., Cheung A., Hummel M., Kieff E. RNA encoded by the IR1-U2 region of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in latently infected, growth-transformed cells. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):424–433. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.424-433.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




