Abstract
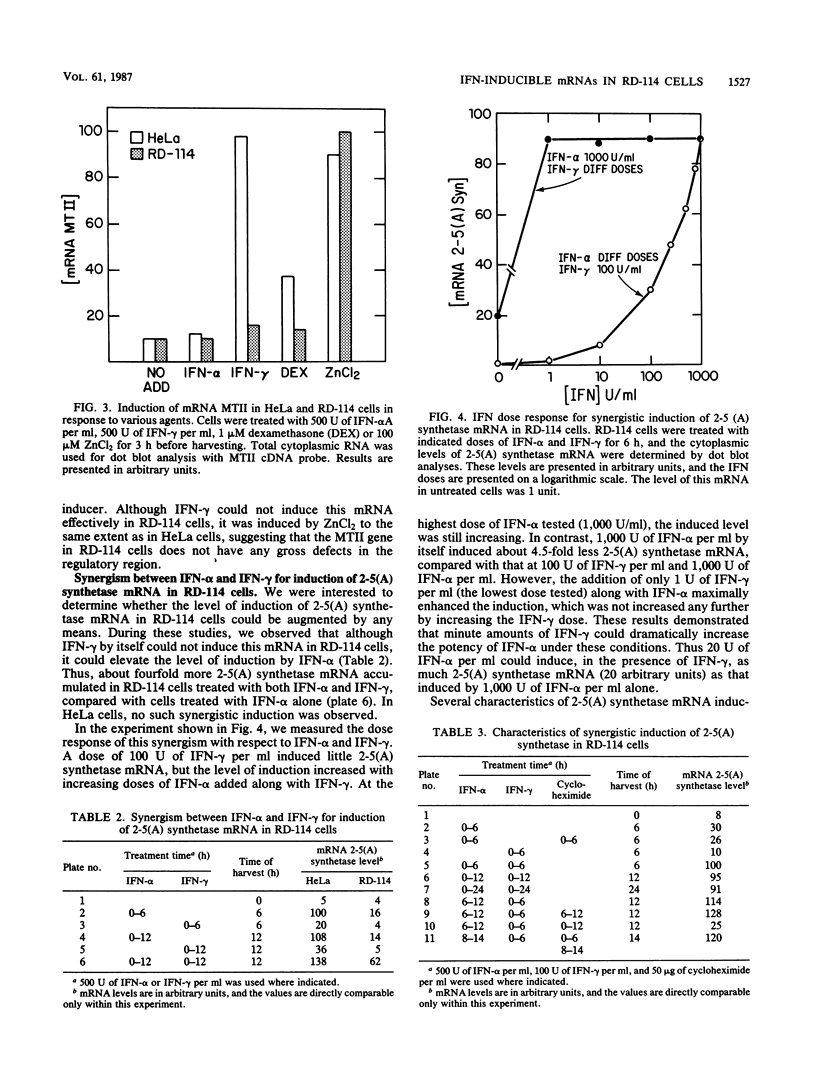
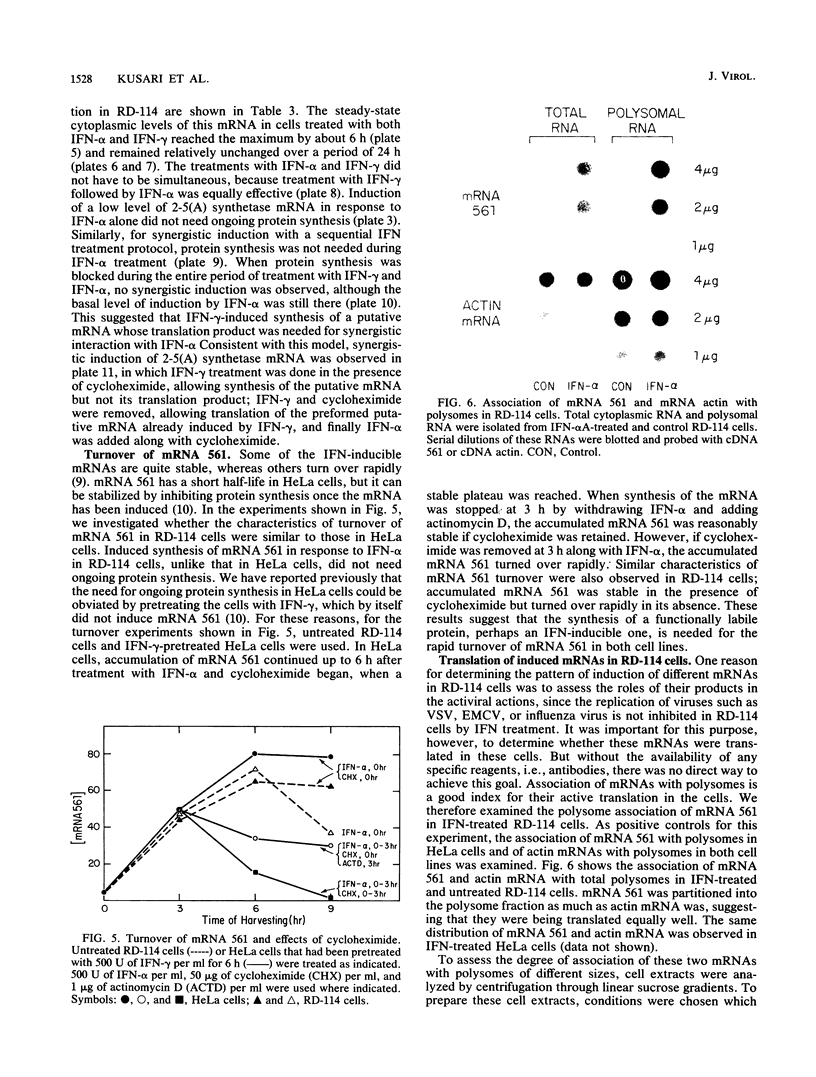
RD-114 is a cell line which is partially responsive to interferon (IFN). Although both IFN-alpha and IFN gamma inhibit production of the resident retrovirus, they do not inhibit replication of other viruses, such as vesicular stomatitis virus and encephalomyocarditis virus, in these cells. In the studies reported here, we studied the characteristics of induction of seven IFN-inducible mRNAs in RD-114 cells. We observed that mRNAs 561, 6-16, 1-8, 2A, and 6-26 have similar induction characteristics in RD-114 cells and in HeLa cells, a fully responsive line. mRNA 2'-5'-oligo-adenylate synthetase (2-5(A) synthetase), however, was induced more efficiently by IFN-alpha in HeLa cells than in RD-114 cells. The same was true for the induction of metallothionein II mRNA by IFN-gamma. However, the latter mRNA was induced equally strongly in both lines when ZnCl2 was used as the inducer, suggesting that the gene is not defective in RD-114 cells. Although IFN-alpha induced 2-5(A) synthetase mRNA poorly and IFN-gamma did not induce it at all in these cells, a mixture of IFN-alpha and IFN-gamma induced this mRNA quite effectively, to a level of induction comparable to that in HeLa cells. Only 1 U of IFN-gamma per ml was sufficient to elicit this synergism, and the data suggested that an IFN-gamma-inducible protein was needed for this process. Induction of mRNA 561 by IFN-alpha in RD-114 cells, unlike that in HeLa cells, did not need ongoing protein synthesis. Once induced, this mRNA turned over rapidly in both cell lines, and this turnover could be slowed down by inhibiting protein synthesis in either cell line. IFN-induced mRNAs, such as 561 and 1-8, were polysome associated in IFN-treated RD-114 cells, suggesting that they were actively translated. Therefore, it is unlikely that the products of these IFN-inducible genes, by themselves, mediate the inhibition of replication of those viruses which are insensitive to IFN action in RD-114 cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belkowski L. S., Sen G. C. Inhibition of vesicular stomatitis viral mRNA synthesis by interferons. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):653–660. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.653-660.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourrie B. J., Casellas P., Blythman H. E., Jansen F. K. Study of the plasma clearance of antibody--ricin-A-chain immunotoxins. Evidence for specific recognition sites on the A chain that mediate rapid clearance of the immunotoxin. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Feb 17;155(1):1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09451.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chebath J., Merlin G., Metz R., Benech P., Revel M. Interferon-induced 56,000 Mr protein and its mRNA in human cells: molecular cloning and partial sequence of the cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1213–1226. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarniecki C. W., Fennie C. W., Powers D. B., Estell D. A. Synergistic antiviral and antiproliferative activities of Escherichia coli-derived human alpha, beta, and gamma interferons. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):490–496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.490-496.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faltynek C. R., McCandless S., Chebath J., Baglioni C. Different mechanisms for activation of gene transcription by interferons alpha and gamma. Virology. 1985 Jul 15;144(1):173–180. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90315-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmann W. R., Jr, Georgiades J. A., Osborne L. C., Johnson H. M. Potentiation of interferon activity by mixed preparations of fibroblast and immune interferon. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):248–253. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.248-253.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Manly S. P., McMahon M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of interferon-induced gene expression in human cells. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):745–755. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90270-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Stark G. R. alpha-Interferon-induced transcription of HLA and metallothionein genes containing homologous upstream sequences. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):637–639. doi: 10.1038/314637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz R. E., Rubin B. Y., Sen G. C. Human interferon-alpha-and-gamma-mediated inhibition of retrovirus production in the absence of an inhibitory effect on vesicular stomatitis virus and encephalomyocarditis virus replication in RD-114 cells. Virology. 1983 Feb;125(1):246–250. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. M., Gilbert C. S., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Differential regulation of interferon-induced mRNAs and c-myc mRNA by alpha- and gamma-interferons. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Dec 2;153(2):367–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusari J., Sen G. C. Regulation of synthesis and turnover of an interferon-inducible mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2062–2067. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner A. C., Jonak G., Cheng Y. S., Korant B., Knight E., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional induction of two genes in human cells by beta interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6733–6737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel P. Biochemistry of interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:251–282. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luster A. D., Unkeless J. C., Ravetch J. V. Gamma-interferon transcriptionally regulates an early-response gene containing homology to platelet proteins. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):672–676. doi: 10.1038/315672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon M., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Interferon-induced gene expression in wild-type and interferon-resistant human lymphoblastoid (Daudi) cells. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):362–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.362-366.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlin G., Chebath J., Benech P., Metz R., Revel M. Molecular cloning and sequence of partial cDNA for interferon-induced (2'-5')oligo(A) synthetase mRNA from human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4904–4908. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders M. E., Gewert D. R., Tugwell M. E., McMahon M., Williams B. R. Human 2-5A synthetase: characterization of a novel cDNA and corresponding gene structure. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1761–1768. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03848.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C. Biochemical pathways in interferon-action. Pharmacol Ther. 1984;24(2):235–257. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(84)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Herz R. E. Differential antiviral effects of interferon in three murine cell lines. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1017–1027. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1017-1027.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Herz R. E., Rubin B. Y. Antiviral, anticellular and enzyme-inducing activities of interferons in RD-114 cells. J Gen Virol. 1983 Oct;64(Pt 10):2213–2220. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-10-2213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Herz R., Davatelis V., Pestka S. Antiviral and protein-inducing activities of recombinant human leukocyte interferons and their hybrids. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):445–450. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.445-450.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Racevskis J., Sarkar N. H. Synthesis of murine mammary tumor viral proteins in vitro. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):963–975. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.963-975.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G., Belkowski L., Kusari J. Analysis of interferon actions using partially resistant cell variants. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1985;202:175–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






