Abstract
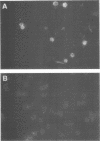
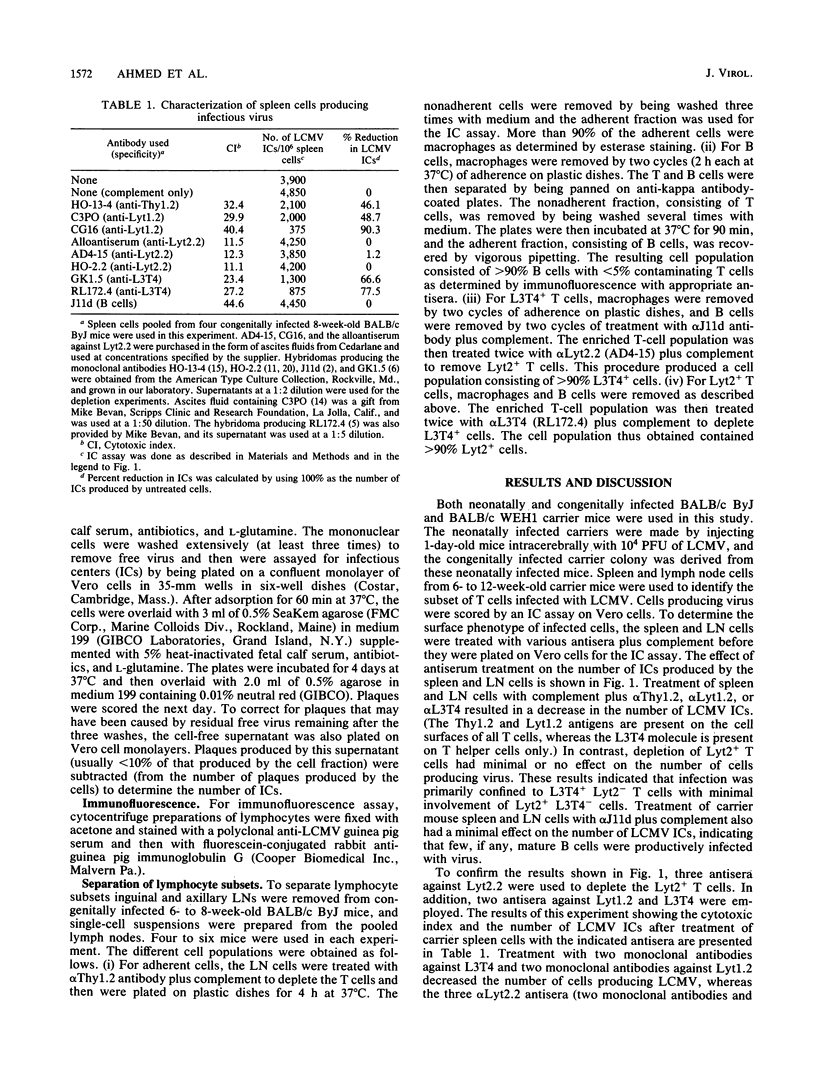
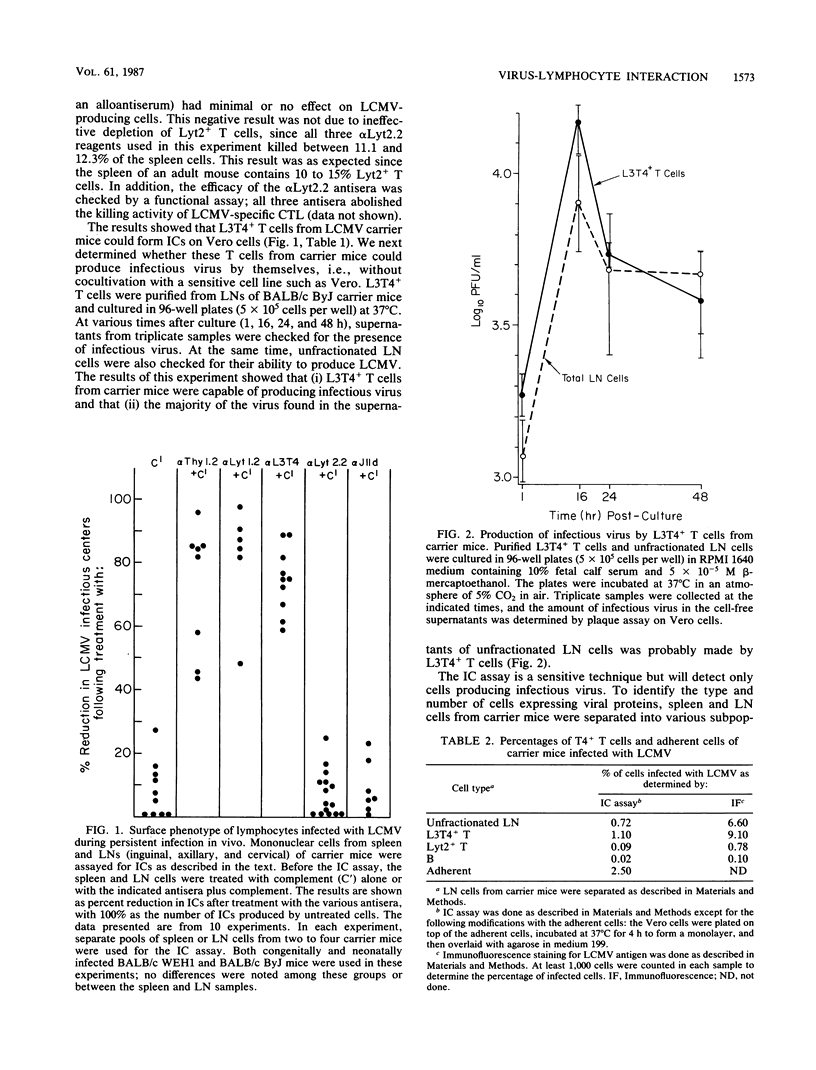
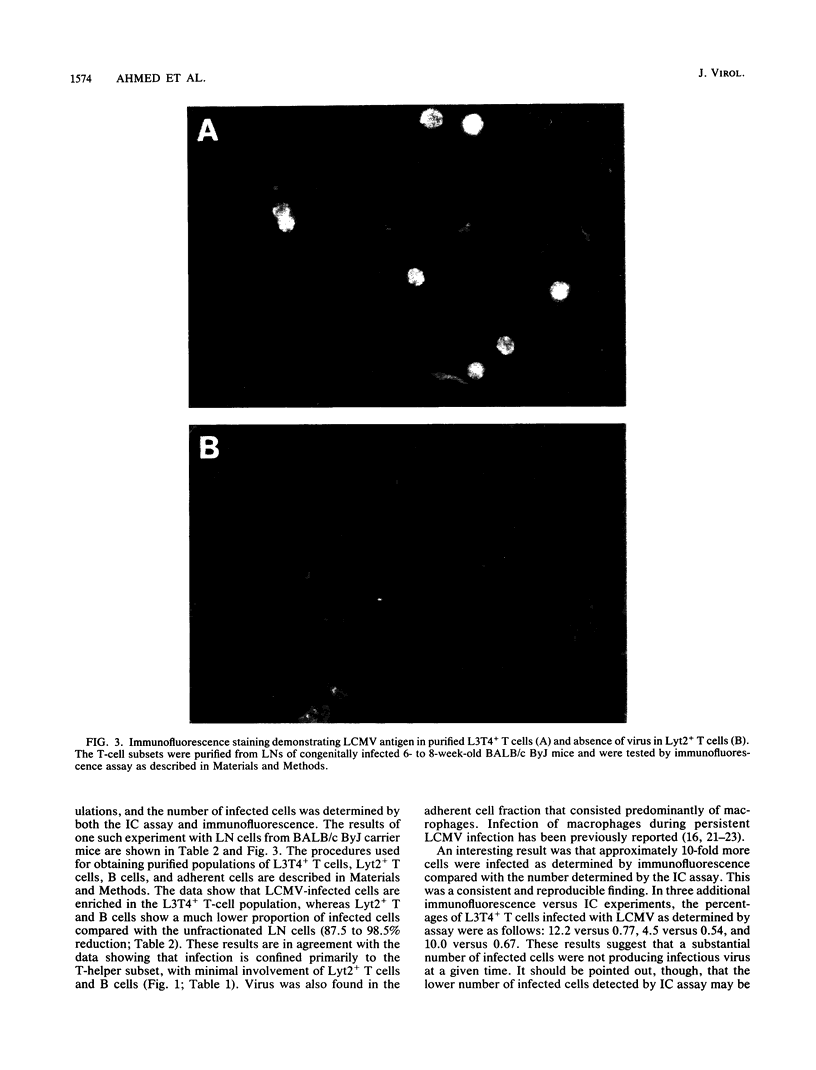
The lifelong persistence of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) in neonatally or congenitally infected mice is accompanied by a suppression of virus-specific T-cell responses. In this study, we identified the subset of T cells infected with LCMV during persistent infection in vivo. Using specific monoclonal antibodies to separate the different lymphocyte cell populations and employing both an infectious center assay and immunofluorescence to detect the virus, we found that infection is confined primarily to T cells of the helper subset (L3T4+ Lyt2-), with minimal involvement of cytotoxic T cells (Lyt2+ L3T4-) and mature B cells. About 0.54 to 1.1% of L3T4+ T cells were producing the virus, as determined by the infectious center assay. In contrast, 9.1 to 12.2% of these L3T4+ T cells contained viral antigen, as shown by immunofluorescence studies. This finding suggested that, at any given time, a substantial number of infected T cells were not producing infectious virus. This infection of T helper cells may be involved in the suppression of LCMV-specific T-cell responses observed in persistently infected mice.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed R., Salmi A., Butler L. D., Chiller J. M., Oldstone M. B. Selection of genetic variants of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus in spleens of persistently infected mice. Role in suppression of cytotoxic T lymphocyte response and viral persistence. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):521–540. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce J., Symington F. W., McKearn T. J., Sprent J. A monoclonal antibody discriminating between subsets of T and B cells. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2496–2501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier M. J., Welsh R. M., Dutko F. J., Oldstone M. B. The virology and immunobiology of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. Adv Immunol. 1980;30:275–331. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Boyse E. A. Functional subclasses of T-lymphocytes bearing different Ly antigens. I. The generation of functionally distinct T-cell subclasses is a differentiative process independent of antigen. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1376–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceredig R., Lowenthal J. W., Nabholz M., MacDonald H. R. Expression of interleukin-2 receptors as a differentiation marker on intrathymic stem cells. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):98–100. doi: 10.1038/314098a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dialynas D. P., Wilde D. B., Marrack P., Pierres A., Wall K. A., Havran W., Otten G., Loken M. R., Pierres M., Kappler J. Characterization of the murine antigenic determinant, designated L3T4a, recognized by monoclonal antibody GK1.5: expression of L3T4a by functional T cell clones appears to correlate primarily with class II MHC antigen-reactivity. Immunol Rev. 1983;74:29–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle M. V., Oldstone M. B. Interactions between viruses and lymphocytes. I. In vivo replication of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus in mononuclear cells during both chronic and acute viral infections. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1262–1269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Macher A. M., Longo D. L., Lane H. C., Rook A. H., Masur H., Gelmann E. P. NIH conference. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: epidemiologic, clinical, immunologic, and therapeutic considerations. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Jan;100(1):92–106. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-1-92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner S., Markovits P., Markovitz D. M., Kaplan M. H., Gallo R. C., Popovic M. The role of mononuclear phagocytes in HTLV-III/LAV infection. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):215–219. doi: 10.1126/science.3014648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb M. S., Schroff R., Schanker H. M., Weisman J. D., Fan P. T., Wolf R. A., Saxon A. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia and mucosal candidiasis in previously healthy homosexual men: evidence of a new acquired cellular immunodeficiency. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1425–1431. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Barré-Sinoussi F., Nugeyre M. T., Danquet C., Vilmer E., Griscelli C., Brun-Veziret F., Rouzioux C., Gluckman J. C., Chermann J. C. Selective tropism of lymphadenopathy associated virus (LAV) for helper-inducer T lymphocytes. Science. 1984 Jul 6;225(4657):59–63. doi: 10.1126/science.6328660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark C., Figueroa F., Nagy Z. A., Klein J. Cytotoxic monoclonal antibody specific for the Lyt-1.2 antigen. Immunogenetics. 1982;16(1):95–97. doi: 10.1007/BF00364447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshak-Rothstein A., Fink P., Gridley T., Raulet D. H., Bevan M. J., Gefter M. L. Properties and applications of monoclonal antibodies directed against determinants of the Thy-1 locus. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2491–2497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mims C. A., Subrahmanyan T. P. Immunofluorescence study of the mechanism of resistance to superinfection in mice carrying the lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(2):403–415. doi: 10.1002/path.1700910215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Ahmed R., Byrne J., Buchmeier M. J., Riviere Y., Southern P. Virus and immune responses: lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus as a prototype model of viral pathogenesis. Br Med Bull. 1985 Jan;41(1):70–74. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popescu M., Löhler J., Lehmann-Grube F. Infectious lymphocytes in lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus carrier mice. J Gen Virol. 1979 Mar;42(3):481–492. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-42-3-481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raulet D. H., Gottlieb P. D., Bevan M. J. Fractionation of lymphocyte populations with monoclonal antibodies specific for LYT-2.2 and LYT-3.1. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1136–1143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R., Löhler J., Lehmann-Grube F. Infection of cultivated mouse peritoneal macrophages with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jun;39(3):565–570. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-39-3-565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seamer J. Mouse macrophages as host cells for murine viruses. (Brief report). Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1965;17(5):654–663. doi: 10.1007/BF01262241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Oldstone M. B. Inhibition of immunologic injury of cultured cells infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus: role of defective interfering virus in regulating viral antigenic expression. J Exp Med. 1977 Jun 1;145(6):1449–1468. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.6.1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. MHC-restricted cytotoxic T cells: studies on the biological role of polymorphic major transplantation antigens determining T-cell restriction-specificity, function, and responsiveness. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:51–177. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]