Abstract
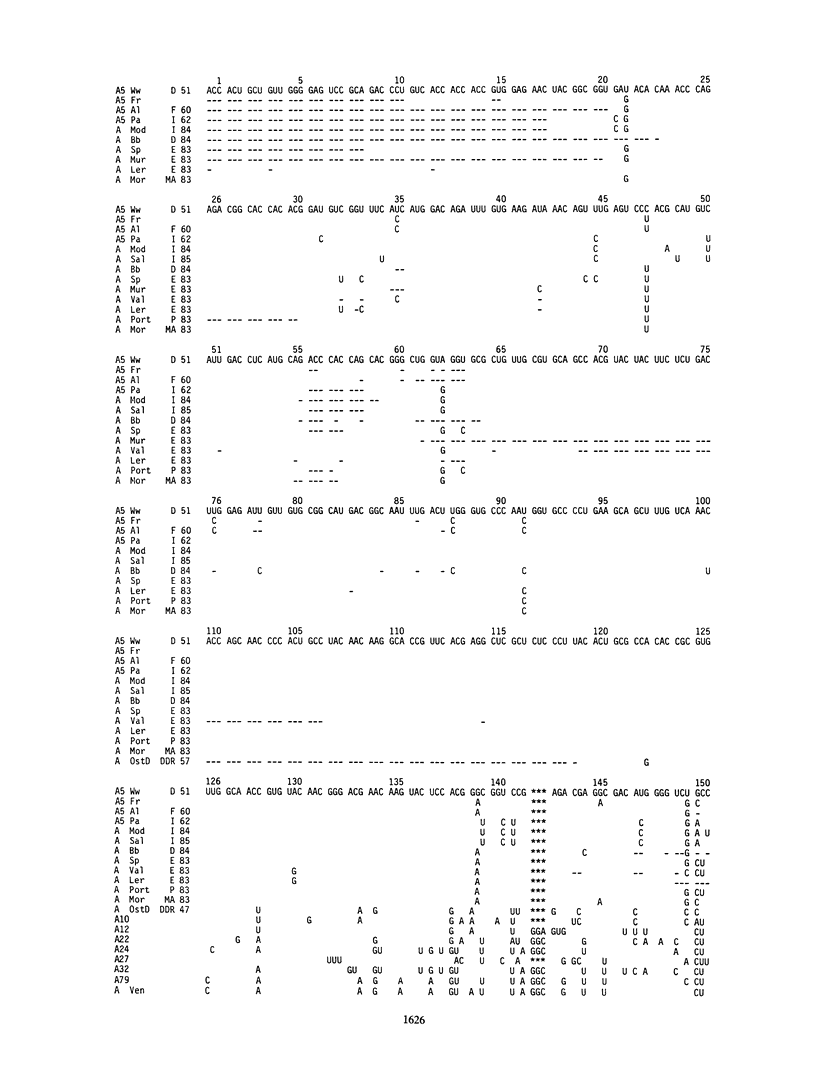
The VP1-coding regions of foot-and-mouth disease virus strains from 18 recent European outbreaks and of 9 strains isolated more than 20 years ago and used in part as vaccines were determined by direct cDNA sequencing. Comparison of the sequences revealed that most of the isolated outbreak viruses are closely related to the vaccine strains used. Isolates from the Italian epizootic of 1984 to 1985 correspond, for example, to the vaccine strain A5 Parma 62; the outbreak in 1984 in Bernbeuren, Federal Republic of Germany, was induced by A5 Allier 60; outbreaks in 1982 in Funen, Denmark, and in Murchin, German Democratic Republic, were caused by O1 Lausanne 65. Viruses isolated during the 1983 Iberian epizootic show a close relationship to the vaccine strain A5 Allier 60 but were probably derived from another not yet identified vaccine strain from Spain. Only two minor outbreaks in the Federal Republic of Germany, A Aachen in 1976 and O Wuppertal in 1982, did not correspond to the classical European strains but were obviously introduced from outside. We suggest that nucleotide sequence analysis should be used as a standard method of diagnosis, because when compared with other techniques it more clearly reveals the origin and course of epizootics and offers the possibility of preventing further outbreaks.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck E., Feil G., Strohmaier K. The molecular basis of the antigenic variation of foot-and-mouth disease virus. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):555–559. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01462.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhm H. O., Kaaden O. R. Untersuchungen zur Typenbestimmung eines Maul- und Klauenseuchestammes (Typ A). Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1978 Jul 1;91(13):256–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A., DeLamarter J., Weiss S., Küpper H. Comparison of the major antigenic determinants of different serotypes of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):451–459. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.451-459.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A., Whitehead P., Weiss S., Küpper H. Nucleotide sequence of the VP1 gene of the foot-and-mouth disease virus strain A Venceslau. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):241–245. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90127-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forss S., Strebel K., Beck E., Schaller H. Nucleotide sequence and genome organization of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6587–6601. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. M., Underwood B. O., McCahon D., Newman J. W., Brown F. Biochemical identification of viruses causing the 1981 outbreaks of foot and mouth disease in the UK. Nature. 1981 Oct 8;293(5832):479–480. doi: 10.1038/293479a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurz C., Forss S., Küpper H., Strohmaier K., Schaller H. Nucleotide sequence and corresponding amino acid sequence of the gene for the major antigen of foot and mouth disease virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 24;9(8):1919–1931. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.8.1919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makoff A. J., Paynter C. A., Rowlands D. J., Boothroyd J. C. Comparison of the amino acid sequence of the major immunogen from three serotypes of foot and mouth disease virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):8285–8295. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.8285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabholz A. Die Maul- und Klauenseuche 1965-1966 in der Schweiz. Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 1966 Dec;108(12):717–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterburg G., Glatting K. H., Sommer R. Computer programs for the analysis and the management of DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):207–216. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaff E., Mussgay M., Böhm H. O., Schulz G. E., Schaller H. Antibodies against a preselected peptide recognize and neutralize foot and mouth disease virus. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):869–874. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01262.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A., Jung R., Hunger H. D. Optimized conditions for solid-phase sequencing: simultaneous chemical cleavage of a series of long DNA fragments immobilized on CCS anion-exchange paper. Gene. 1986;42(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90144-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands D. J., Clarke B. E., Carroll A. R., Brown F., Nicholson B. H., Bittle J. L., Houghten R. A., Lerner R. A. Chemical basis of antigenic variation in foot-and-mouth disease virus. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):694–697. doi: 10.1038/306694a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rweyemamu M. M., Pay T. W., Parker M. J. Serological differentiation of foot-and-mouth disease virus strains in relation to selection of suitable vaccine viruses. Dev Biol Stand. 1976;35:205–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strohmaier K., Franze R., Adam K. H. Location and characterization of the antigenic portion of the FMDV immunizing protein. J Gen Virol. 1982 Apr;59(Pt 2):295–306. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-59-2-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weddell G. N., Yansura D. G., Dowbenko D. J., Hoatlin M. E., Grubman M. J., Moore D. M., Kleid D. G. Sequence variation in the gene for the immunogenic capsid protein VP1 of foot-and-mouth disease virus type A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2618–2622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann G. Die antigenen und immunologischen Eigenschaften und Beziehungen von A-Subtypen des Maul- und Klauenseuchevirus. I. Nach Impfung von Meerschweinchen mit aktivem Virus. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1966 Jun;13(3):225–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



