Abstract
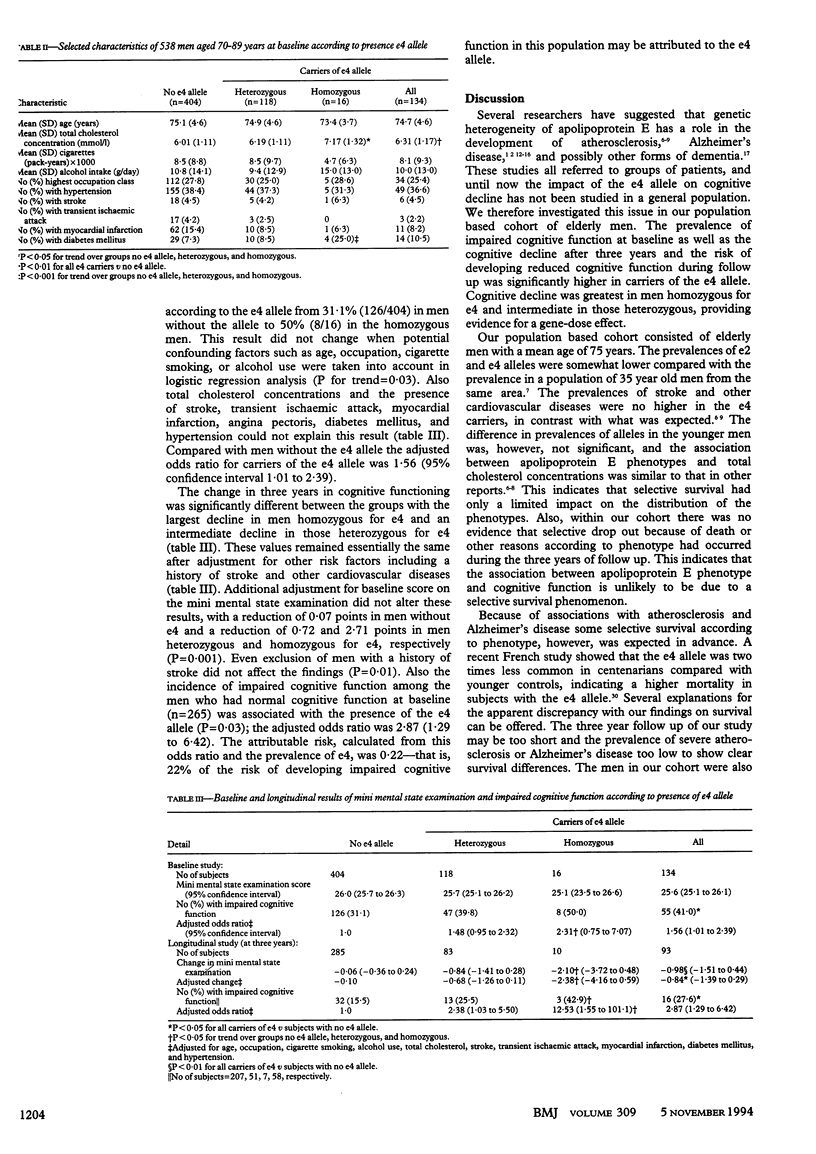
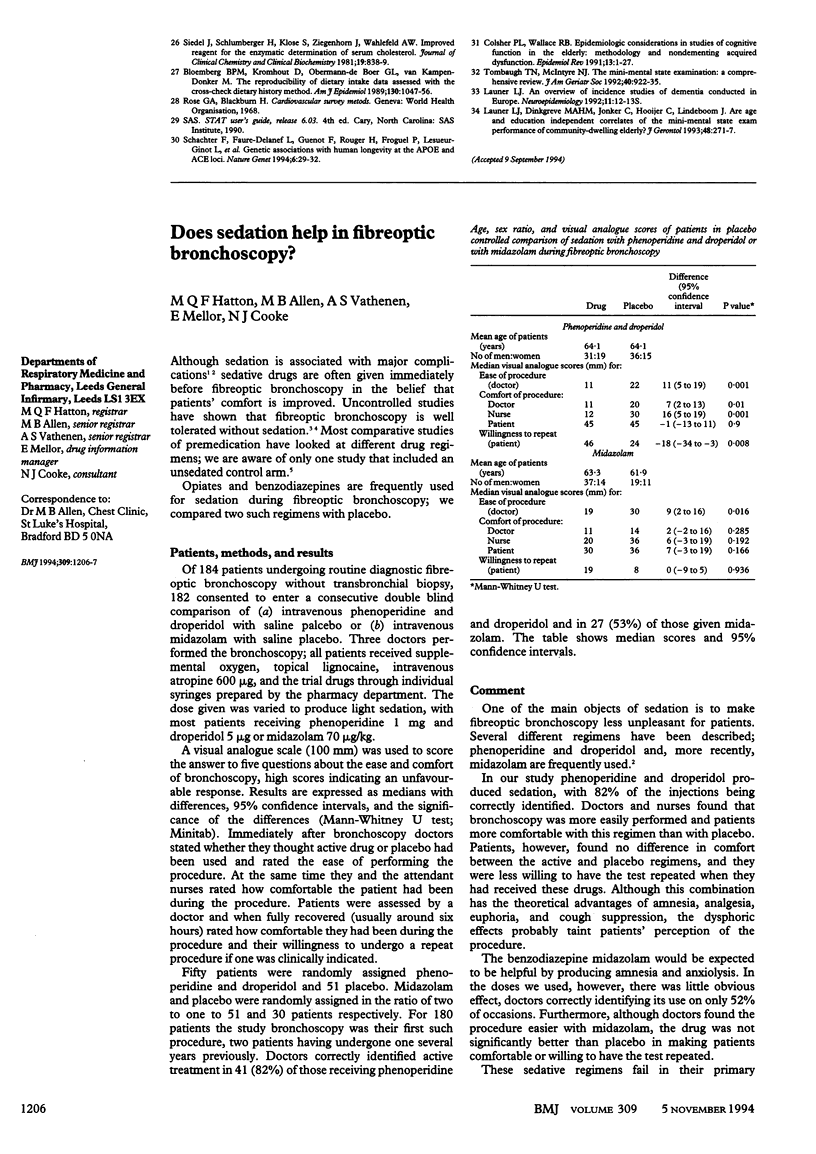
OBJECTIVES--To determine whether polymorphism of apolipoprotein E--notably, the e4 allele--predicts cognitive deterioration in the general population. DESIGN--Population based cohort investigated in 1990 and in 1993. SETTING--Zutphen, the Netherlands. SUBJECTS--Representative cohort of 538 Dutch men aged 70-89 at baseline. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES--Cognitive function assessed by mini mental state examination, change in cognitive function and incidence of impaired cognitive function at three years. RESULTS--The baseline prevalence of impaired cognitive function (mini mental state examination score < or = 25) was higher among carriers of the e4 allele compared with men without the allele (41.0% (55) v 31.1% (122) P = 0.03), and this result was still valid after adjustment for age, occupation, smoking, alcohol use, and cardiovascular diseases. The decline in cognitive function at three years was largest in men homozygous for e4 (-2.4 points), intermediate in those heterozygous for e4 (-0.7 points), and lowest in men without e4 (-0.1 points), and it was independent of other risk factors (P = 0.02). The risk of developing impaired cognitive function during follow up was significantly increased in allele carriers compared with non-carriers (27.6% (16/58) v 15.5% (32/207)). The adjusted odds ratio was 2.87 (95% confidence interval 1.29 to 6.42). Twenty two per cent of the risk of developing impaired cognitive function in this population may be attributable to the e4 allele. CONCLUSIONS--The apolipoprotein e4 allele predisposes to cognitive decline in a general population of elderly men.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloemberg B. P., Kromhout D., Obermann-De Boer G. L., Van Kampen-Donker M. The reproducibility of dietary intake data assessed with the cross-check dietary history method. Am J Epidemiol. 1989 Nov;130(5):1047–1056. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colsher P. L., Wallace R. B. Epidemiologic considerations in studies of cognitive function in the elderly: methodology and nondementing acquired dysfunction. Epidemiol Rev. 1991;13:1–27. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corder E. H., Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D. E., Gaskell P. C., Small G. W., Roses A. D., Haines J. L., Pericak-Vance M. A. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science. 1993 Aug 13;261(5123):921–923. doi: 10.1126/science.8346443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallongeville J., Lussier-Cacan S., Davignon J. Modulation of plasma triglyceride levels by apoE phenotype: a meta-analysis. J Lipid Res. 1992 Apr;33(4):447–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das H. K., McPherson J., Bruns G. A., Karathanasis S. K., Breslow J. L. Isolation, characterization, and mapping to chromosome 19 of the human apolipoprotein E gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6240–6247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davignon J., Gregg R. E., Sing C. F. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis. 1988 Jan-Feb;8(1):1–21. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.8.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folstein M. F., Folstein S. E., McHugh P. R. "Mini-mental state". A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975 Nov;12(3):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertog M. G., Feskens E. J., Hollman P. C., Katan M. B., Kromhout D. Dietary antioxidant flavonoids and risk of coronary heart disease: the Zutphen Elderly Study. Lancet. 1993 Oct 23;342(8878):1007–1011. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)92876-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keys A., Aravanis C., Blackburn H. W., Van Buchem F. S., Buzina R., Djordjević B. D., Dontas A. S., Fidanza F., Karvonen M. J., Kimura N. Epidemiological studies related to coronary heart disease: characteristics of men aged 40-59 in seven countries. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1966;460:1–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba Y., Tomonaga M., Kawasaki H., Otomo E., Ikeda K. Apolipoprotein E immunoreactivity in cerebral amyloid deposits and neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease and kuru plaque amyloid in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Brain Res. 1991 Feb 8;541(1):163–166. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91092-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi S., Murakami K., Yamada N. Apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1993 Sep 18;342(8873):737–737. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91728-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olaisen B., Teisberg P., Gedde-Dahl T., Jr The locus for apolipoprotein E (apoE) is linked to the complement component C3 (C3) locus on chromosome 19 in man. Hum Genet. 1982;62(3):233–236. doi: 10.1007/BF00333526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pericak-Vance M. A., Bebout J. L., Gaskell P. C., Jr, Yamaoka L. H., Hung W. Y., Alberts M. J., Walker A. P., Bartlett R. J., Haynes C. A., Welsh K. A. Linkage studies in familial Alzheimer disease: evidence for chromosome 19 linkage. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jun;48(6):1034–1050. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier J., Davignon J., Bouthillier D., Kogan S., Bertrand P., Gauthier S. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1993 Sep 18;342(8873):697–699. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91705-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebeck G. W., Reiter J. S., Strickland D. K., Hyman B. T. Apolipoprotein E in sporadic Alzheimer's disease: allelic variation and receptor interactions. Neuron. 1993 Oct;11(4):575–580. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders A. M., Schmader K., Breitner J. C., Benson M. D., Brown W. T., Goldfarb L., Goldgaber D., Manwaring M. G., Szymanski M. H., McCown N. Apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 allele distributions in late-onset Alzheimer's disease and in other amyloid-forming diseases. Lancet. 1993 Sep 18;342(8873):710–711. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91709-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schächter F., Faure-Delanef L., Guénot F., Rouger H., Froguel P., Lesueur-Ginot L., Cohen D. Genetic associations with human longevity at the APOE and ACE loci. Nat Genet. 1994 Jan;6(1):29–32. doi: 10.1038/ng0194-29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrill B. C., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Rapid hepatic clearance of the canine lipoproteins containing only the E apoprotein by a high affinity receptor. Identity with the chylomicron remnant transport process. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1804–1807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit M., de Knijff P., Rosseneu M., Bury J., Klasen E., Frants R., Havekes L. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism in The Netherlands and its effect on plasma lipid and apolipoprotein levels. Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;80(3):287–292. doi: 10.1007/BF01790099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter W. J., Saunders A. M., Schmechel D., Pericak-Vance M., Enghild J., Salvesen G. S., Roses A. D. Apolipoprotein E: high-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1977–1981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tombaugh T. N., McIntyre N. J. The mini-mental state examination: a comprehensive review. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1992 Sep;40(9):922–935. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1992.tb01992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Bockxmeer F. M., Mamotte C. D. Apolipoprotein epsilon 4 homozygosity in young men with coronary heart disease. Lancet. 1992 Oct 10;340(8824):879–880. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)93288-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duijn C. M., de Knijff P., Cruts M., Wehnert A., Havekes L. M., Hofman A., Van Broeckhoven C. Apolipoprotein E4 allele in a population-based study of early-onset Alzheimer's disease. Nat Genet. 1994 May;7(1):74–78. doi: 10.1038/ng0594-74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


