Abstract
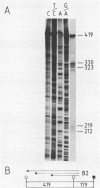
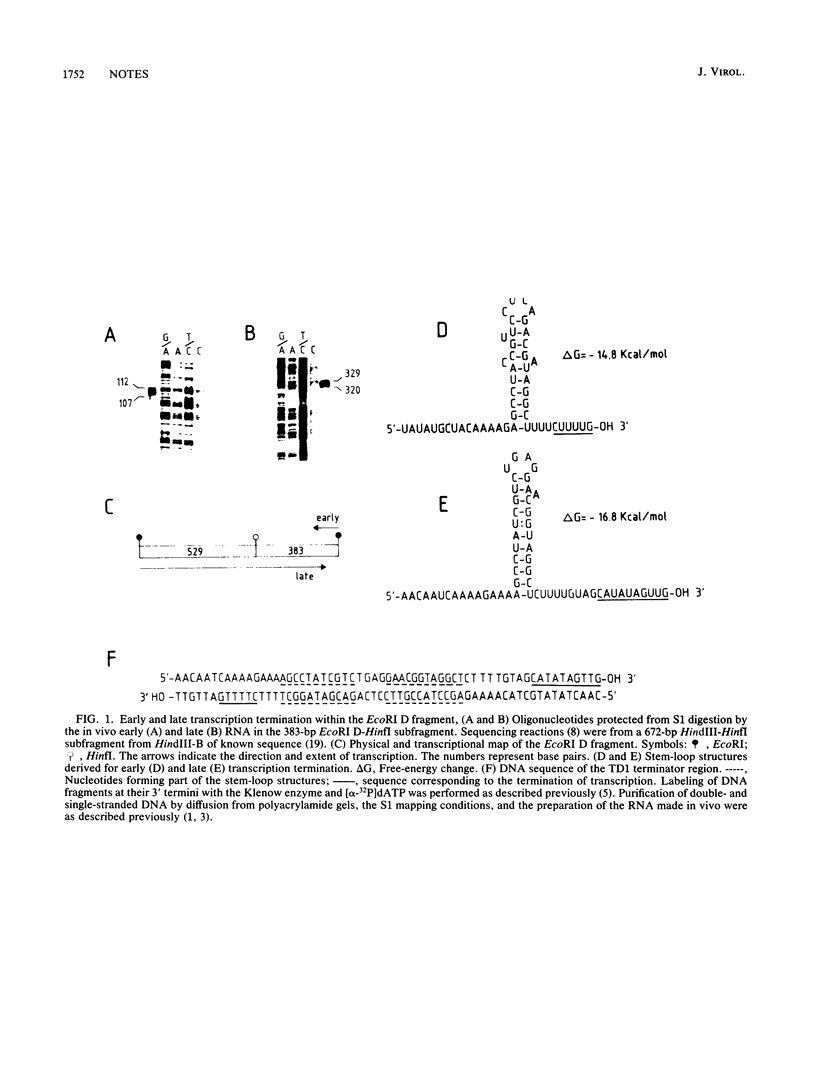
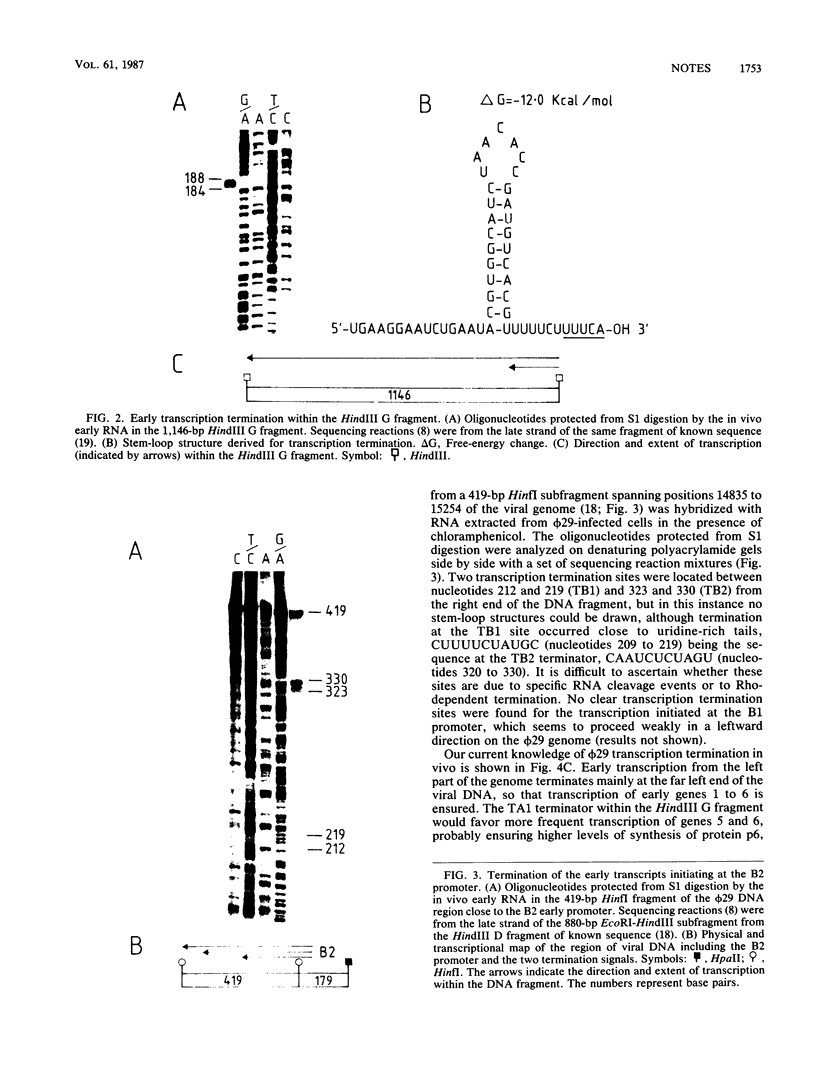
The main early and late transcription termination sites in vivo in bacteriophage phi 29 DNA were determined by nuclease S1 mapping. Transcription of the phi 29 early genes located at the left end of the viral genome terminated at the very end of the DNA molecule and within the HindIII G fragment of the viral DNA. Transcription termination of the early genes located at the right end of the genome and that of the late viral genes overlapped in a specific region of the phi 29 DNA within the EcoRI D fragment. Stem-loop structures followed by uridine-rich tails could be derived close to the 3' ends of early and late mRNAs, suggesting Rho-independent transcription termination in phi 29 DNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barthelemy I., Salas M., Mellado R. P. In vivo transcription of bacteriophage phi 29 DNA: transcription initiation sites. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):874–879. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.874-879.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa J. L., Camacho A., Moreno F., Jiménez F., Mellado R. P., Viñuela E., Salas M. Bacillus subtilis phage phi29. Characterization of gene products and functions. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jul 1;66(2):229–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie G. E., Calendar R. Bacteriophage P2 late promoters. Transcription initiation sites for two late mRNAs. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 15;167(4):773–790. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80110-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Murray C. L., Rabinowitz J. C. Specificity of promoter site utilization in vitro by bacterial RNA polymerases on Bacillus phage phi 29 DNA. Transcription mapping with exonuclease III. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8819–8830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escarmís C., Salas M. Nucleotide sequence at the termini of the DNA of Bacillus subtilis phage phi 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1446–1450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey K. J., Saedi M. S., Ito J. The complete sequence of Bacillus phage phi 29 gene 16: a protein required for the genome encapsidation reaction. Gene. 1985;40(2-3):311–316. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes W. M., Platt T., Rosenberg M. Termination of transcription in E. coli. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1029–1032. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellado R. P., Barthelemy I., Salas M. In vitro transcription of bacteriophage phi 29 DNA. Correlation between in vitro and in vivo promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 25;14(12):4731–4741. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.12.4731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellado R. P., Barthelemy I., Salas M. In vivo transcription of bacteriophage phi 29 DNA early and late promoter sequences. J Mol Biol. 1986 Sep 20;191(2):191–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90256-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellado R. P., Moreno F., Viñuela E., Salas M., Reilly B. E., Anderson D. L. Genetic analysis of bacteriophage phi 29 of Bacillus subtilis: integration and mapping of reference mutants of two collections. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):495–500. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.495-500.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellado R. P., Peñalva M. A., Inciarte M. R., Salas M. The protein covalently linked to the 5' termini of the DNA of Bacillus subtilis phage phi 29 is involved in the initiation of DNA replication. Virology. 1980 Jul 15;104(1):84–96. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90367-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogo J. M., Inciarte M. R., Corral J., Viñuela E., Salas M. RNA polymerase binding sites and transcription map of the DNA of Bacillus subtilis phage phi29. J Mol Biol. 1979 Feb 5;127(4):411–436. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90230-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villanueva N., Salas M. Adsorption of bacteriophage phi 29 to Bacillus subtilis through the neck appendages of the viral particle. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):15–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.15-19.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa H., Ito J. Nucleotide sequence of the major early region of bacteriophage phi 29. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):323–335. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90149-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]