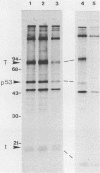
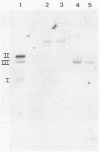
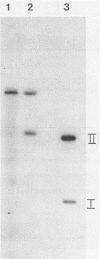
Abstract
T-antigen-positive transformation revertant cell lines were isolated from fully simian virus 40 (SV40)-transformed Fisher rat embryo fibroblast cells (REF 52 cells) by methionine starvation. Reversion of the transformed cells (SV-52 cells) was caused by a mutation within the cellular genome. To demonstrate this, we isolated SV40 DNA from the host genome, inserted it into plasmid pSPT18 DNA, cloned it in Escherichia coli, and microinjected it into the nuclei of the REF 52 cells. Fully transformed cells were obtained with the same efficiency (20 to 25%) as after microinjection of wild-type SV40 DNA I. Furthermore, the revertant cells were resistant to retransformation by SV40. Following microinjection of wild-type SV40 DNA I, 42 independent cell lines were isolated. Cells of all analyzed lines acquired additional SV40 DNA copies, but changes in the cell morphology or growth characteristic were not demonstrable. However, the revertants were retransformable with a high efficiency after polyomavirus and adenovirus type 2 infections or microinjection. Also, fusion of the revertant cells with the grandparental REF 52 cells led to restoration of the transformed state.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Deppert W., Hanke K., Henning R. Simian virus 40 T-antigen-related cell surface antigen: serological demonstration on simian virus 40-transformed monolayer cells in situ. J Virol. 1980 Aug;35(2):505–518. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.2.505-518.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Raz A., Gruss P., Givol D., Oren M. Participation of p53 cellular tumour antigen in transformation of normal embryonic cells. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):646–649. doi: 10.1038/312646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann A., Graessmann M., Mueller C. Fused cells are suited for microinjection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 28;88(2):428–432. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann A., Graessmann M., Mueller C. Regulation of SV40 gene expression. Adv Cancer Res. 1981;35:111–149. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60910-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann A., Graessmann M., Tjian R., Topp W. C. Simian virus 40 small-t protein is required for loss of actin cable networks in rat cells. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1182–1191. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1182-1191.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann A., Graessmann M., Topp W. C., Botchan M. Retransformation of a simian virus 40 revertant cell line, which is resistant to viral and DNA infections, by microinjection of viral DNA. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):989–994. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.989-994.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann M., Graessmann A. Microinjection of tissue culture cells. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:482–492. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann M., Guhl E., Bumke-Vogt C., Graessmann A. The second large simian virus 40 T-antigen exon contains the information for maximal cell transformation. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):111–129. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90433-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris H. Malignant tumours generated by recessive mutations. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):582–583. doi: 10.1038/323582a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jat P. S., Cepko C. L., Mulligan R. C., Sharp P. A. Recombinant retroviruses encoding simian virus 40 large T antigen and polyomavirus large and middle T antigens. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1204–1217. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jat P. S., Sharp P. A. Large T antigens of simian virus 40 and polyomavirus efficiently establish primary fibroblasts. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):746–750. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.746-750.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. A short amino acid sequence able to specify nuclear location. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., Butel J. S. Intracellular transport of SV40 large tumor antigen: a mutation which abolishes migration to the nucleus does not prevent association with the cell surface. Virology. 1982 May;119(1):169–184. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., Wong C., Butel J. S. Differential ability of a T-antigen transport-defective mutant of simian virus 40 to transform primary and established rodent cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1043–1050. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Levine A. J. Characterization of a 54K dalton cellular SV40 tumor antigen present in SV40-transformed cells and uninfected embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G., Chou J. Y. Simian virus 40 functions required for the establishment and maintenance of malignant transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):599–612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.599-612.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller C., Graessmann A., Graessmann M. Mapping of early SV40-specific functions by microinjection of different early viral DNA fragments. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):579–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. Simian virus 40 gene A function and maintenance of transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):636–644. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.636-644.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Germ-line transformation of mice. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:465–499. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parada L. F., Land H., Weinberg R. A., Wolf D., Rotter V. Cooperation between gene encoding p53 tumour antigen and ras in cellular transformation. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):649–651. doi: 10.1038/312649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan K. W., Christensen J. B., Imperiale M. J., Brockman W. W. Isolation of a simian virus 40 T-antigen-positive, transformation-resistant cell line by indirect selection. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3577–3582. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Function of simian virus 40 gene A in transforming infection. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):613–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.613-618.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vass-Marengo J., Ratiarson A., Asselin C., Bastin M. Ability of a T-antigen transport-defective mutant of simian virus 40 to immortalize primary cells and to complement polyomavirus middle T in tumorigenesis. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):655–659. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.655-659.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel A., Pollack R. Isolation and characterization of revertant cell lines. IV. Direct selection of serum-revertant sublines of SV40-transformed 3T3 mouse cells. J Cell Physiol. 1973 Oct;82(2):189–198. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040820207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel A., Risser R., Pollack R. Isolation and characterization of revertant cell lines. 3. Isolation of density-revertants of SV40-transformed 3T3 cells using colchicine. J Cell Physiol. 1973 Oct;82(2):181–188. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040820206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J. D., Swimmer C., Cocke T., Shenk T. A second domain of simian virus 40 T antigen in which mutations can alter the cellular localization of the antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2207–2212. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]