Abstract
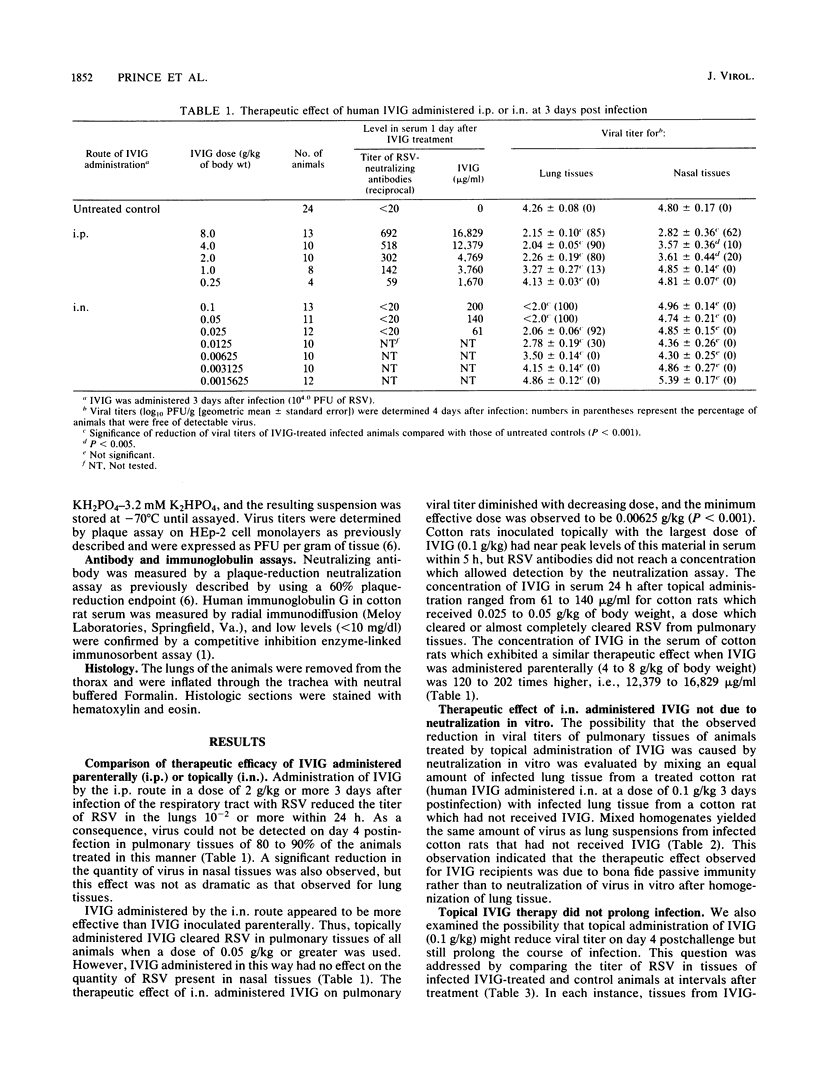
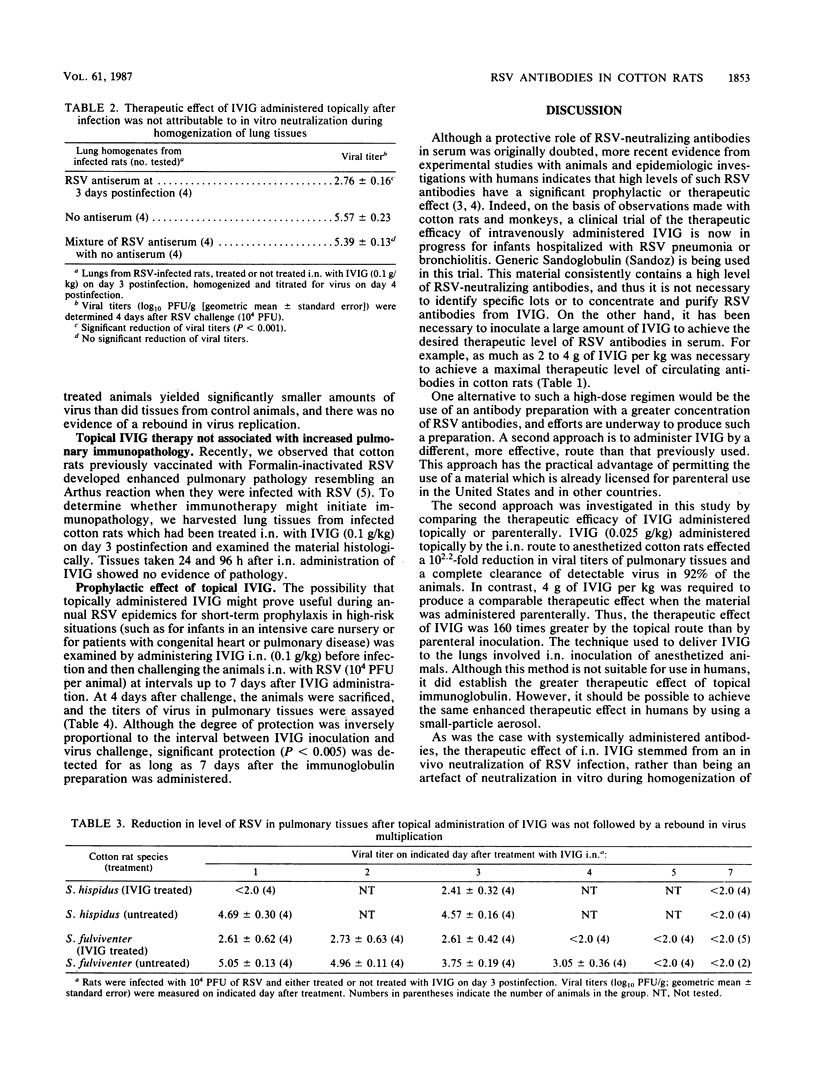
Initial studies of the prophylactic effect of parenterally administered respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)-neutralizing antibodies in cotton rats indicated that virus replication in lung tissues was restricted when animals with preexisting antibody titers in serum of 1:100 or more (as measured by plaque reduction) were challenged intranasally with 10(4) PFU of virus. Subsequently, a therapeutic effect of parenterally administered RSV antibodies (present in human gamma globulin) was demonstrated in both cotton rats and owl monkeys. Parenteral inoculation of RSV-infected cotton rats or owl monkeys with purified human immunoglobulin licensed for intravenous administration in humans (IVIG) effected a 10(-1.7) to 10(-2.7) reduction in the level of pulmonary virus at the height of infection. Because of these encouraging results, we examined topical administration of IVIG to determine whether it was also effective and whether it offered an advantage over the parenteral route with regard to simplicity and the dose required for full therapeutic effect. IVIG (0.025 g/kg) administered topically by the intranasal route to anesthetized cotton rats at the height of RSV infection effected a 10(2.2)-fold reduction in viral titers of pulmonary tissues and a complete clearance of detectable virus in 92% of the animals within 24 h. In contrast, 4 g of IVIG per kg was required to produce a comparable therapeutic effect when the material was administered parenterally. Thus, the therapeutic effect of IVIG was 160 times greater by the topical route than by parenteral inoculation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bosworth J. M., Jr, Brimfield A. A., Naylor J. A., Hunter K. W., Jr Measurement of monoclonal antibody concentrations in hybridoma cultures: comparison of competitive inhibition and antigen capture enzyme immunoassays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Sep 16;62(3):331–336. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. B., McBride J. T., Walsh E. E., Bell D. M., Gala C. L., Hildreth S., Ten Eyck L. G., Hall W. J. Aerosolized ribavirin treatment of infants with respiratory syncytial viral infection. A randomized double-blind study. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jun 16;308(24):1443–1447. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198306163082403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemming V. G., Prince G. A., Horswood R. L., London W. J., Murphy B. R., Walsh E. E., Fischer G. W., Weisman L. E., Baron P. A., Chanock R. M. Studies of passive immunotherapy for infections of respiratory syncytial virus in the respiratory tract of a primate model. J Infect Dis. 1985 Nov;152(5):1083–1087. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.5.1083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince G. A., Hemming V. G., Horswood R. L., Chanock R. M. Immunoprophylaxis and immunotherapy of respiratory syncytial virus infection in the cotton rat. Virus Res. 1985 Oct;3(3):193–206. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince G. A., Jenson A. B., Hemming V. G., Murphy B. R., Walsh E. E., Horswood R. L., Chanock R. M. Enhancement of respiratory syncytial virus pulmonary pathology in cotton rats by prior intramuscular inoculation of formalin-inactiva ted virus. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):721–728. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.721-728.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince G. A., Jenson A. B., Horswood R. L., Camargo E., Chanock R. M. The pathogenesis of respiratory syncytial virus infection in cotton rats. Am J Pathol. 1978 Dec;93(3):771–791. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taber L. H., Knight V., Gilbert B. E., McClung H. W., Wilson S. Z., Norton H. J., Thurson J. M., Gordon W. H., Atmar R. L., Schlaudt W. R. Ribavirin aerosol treatment of bronchiolitis associated with respiratory syncytial virus infection in infants. Pediatrics. 1983 Nov;72(5):613–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



