Abstract
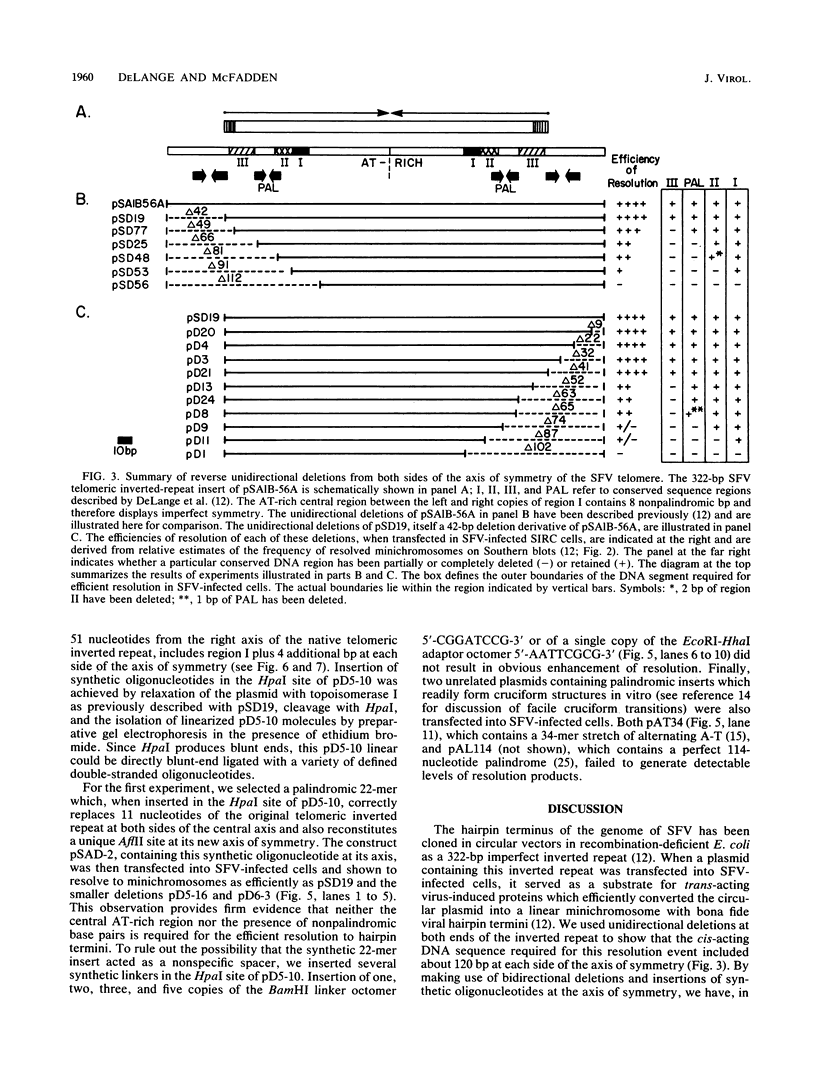
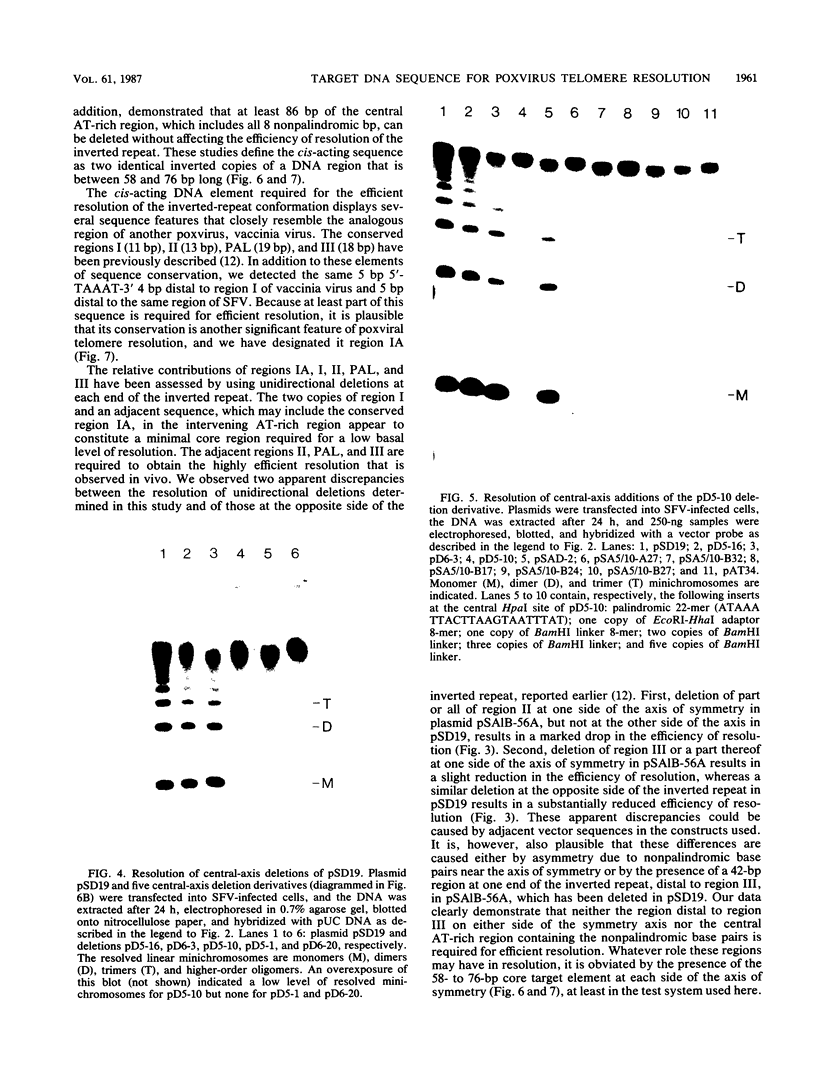
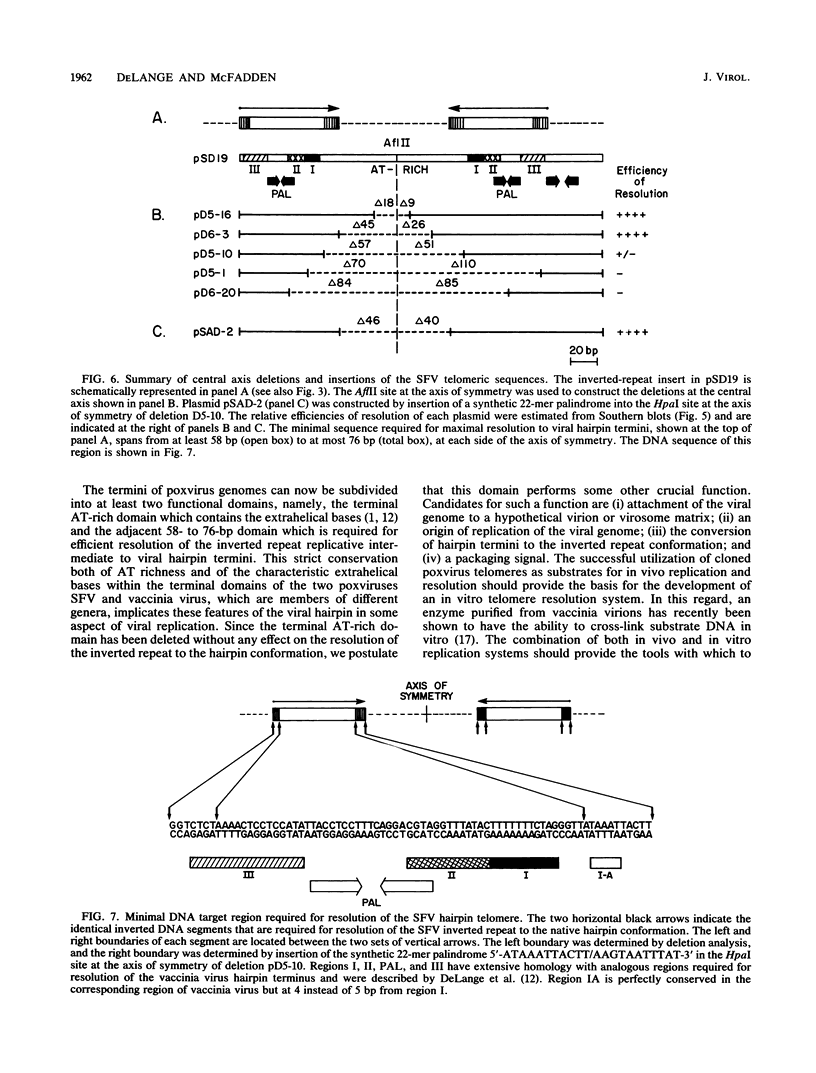
The terminal hairpin sequences of the linear double-stranded DNA genome of the leporipoxvirus Shope fibroma virus (SFV) has been cloned in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and in recombination-deficient Escherichia coli as a palindromic insert within circular plasmid vectors. This sequence configuration is equivalent to the inverted repeat structure detected as a telomeric replicative intermediate during poxvirus replication in vivo. Previously, it has been shown that when circular plasmids containing this palindromic insert were transfected into SFV-infected cells, efficient replication and resolution generated linear minichromosomes with bona fide viral hairpin termini (A. M. DeLange, M. Reddy, D. Scraba, C. Upton, and G. McFadden, J. Virol. 59:249-259, 1986). To localize the minimal target DNA sequence required for efficient resolution, a series of staggered unidirectional deletions were constructed at both ends of the inverted repeat. Analyses of the resolution efficiencies of the various clones indicate that up to 240 base pairs (bp) centered at the symmetry axis were required for maximal resolution to minichromosomes. To investigate the role of the AT-rich central axis sequences, which in SFV include 8 nonpalindromic bp, a unique AflII site at the symmetry axis was exploited. Bidirectional deletions extending from this AflII site and insertions of synthetic oligonucleotides into one of the deletion derivatives were constructed and tested in vivo. The efficiency with which these plasmids resolved to linear minichromosomes with hairpin termini has enabled us to define the minimal target DNA sequence as two inverted copies of an identical DNA sequence between 58 and 76 bp in length. The nonpalindromic nucleotides, which, after resolution, constitute the extrahelical residues characteristic of native poxviral telomeres, were not required for resolution. The close resemblance of the SFV core target sequence to the analogous region from the orthopoxvirus vaccinia virus is consistent with a conserved mechanism for poxviral telomere resolution.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baroudy B. M., Venkatesan S., Moss B. Incompletely base-paired flip-flop terminal loops link the two DNA strands of the vaccinia virus genome into one uninterrupted polynucleotide chain. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):315–324. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90349-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateman A. J. Letter: Simplification of palindromic telomere theory. Nature. 1975 Jan 31;253(5490):379–380. doi: 10.1038/253379a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H., Gall J. G. A tandemly repeated sequence at the termini of the extrachromosomal ribosomal RNA genes in Tetrahymena. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):33–53. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90294-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. Telomeres: do the ends justify the means? Cell. 1984 May;37(1):7–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90295-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. The molecular structure of centromeres and telomeres. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:163–194. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boissy R., Astell C. R. An Escherichia coli recBCsbcBrecF host permits the deletion-resistant propagation of plasmid clones containing the 5'-terminal palindrome of minute virus of mice. Gene. 1985;35(1-2):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90170-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalier-Smith T. Palindromic base sequences and replication of eukaryote chromosome ends. Nature. 1974 Aug 9;250(5466):467–470. doi: 10.1038/250467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLange A. M., Futcher B., Morgan R., McFadden G. Cloning of the vaccinia virus telomere in a yeast plasmid vector. Gene. 1984 Jan;27(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90234-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLange A. M., McFadden G. Sequence-nonspecific replication of transfected plasmid DNA in poxvirus-infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):614–618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLange A. M., Reddy M., Scraba D., Upton C., McFadden G. Replication and resolution of cloned poxvirus telomeres in vivo generates linear minichromosomes with intact viral hairpin termini. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):249–259. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.249-259.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geshelin P., Berns K. I. Characterization and localization of the naturally occurring cross-links in vaccinia virus DNA. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 5;88(4):785–796. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90399-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves D. R., Patient R. K., Lilley D. M. Facile cruciform formation by an (A-T)34 sequence from a Xenopus globin gene. J Mol Biol. 1985 Oct 5;185(3):461–478. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90064-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniford D. B., Pulleyblank D. E. Transition of a cloned d(AT)n-d(AT)n tract to a cruciform in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4343–4363. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., Hirai K., Gunge N., Hishinuma F. Hairpin plasmid--a novel linear DNA of perfect hairpin structure. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1881–1886. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03864.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakritz N., Foglesong P. D., Reddy M., Baum S., Hurwitz J., Bauer W. R. A vaccinia virus DNase preparation which cross-links superhelical DNA. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):935–943. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.935-943.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchlinsky M., Moss B. Resolution of linear minichromosomes with hairpin ends from circular plasmids containing vaccinia virus concatemer junctions. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):879–884. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90562-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer R. W., Graves R. L. The mechanism of cytoplasmic orthopoxvirus DNA replication. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):391–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90422-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickup D. J., Bastia D., Joklik W. K. Cloning of the terminal loop of vaccinia virus DNA. Virology. 1983 Jan 15;124(1):215–217. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90309-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard A. E., Cummings D. J. Replication of linear mitochondrial DNA from Paramecium: sequence and structure of the initiation-end crosslink. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7341–7345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G. J., Green R. L. Comparison of physical and genetic properties of palindromic DNA sequences. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1103–1111. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1103-1111.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winters E., Baroudy B. M., Moss B. Molecular cloning of the terminal hairpin of vaccinia virus DNA as an imperfect palindrome in an Escherichia coli plasmid. Gene. 1985;37(1-3):221–228. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90276-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]