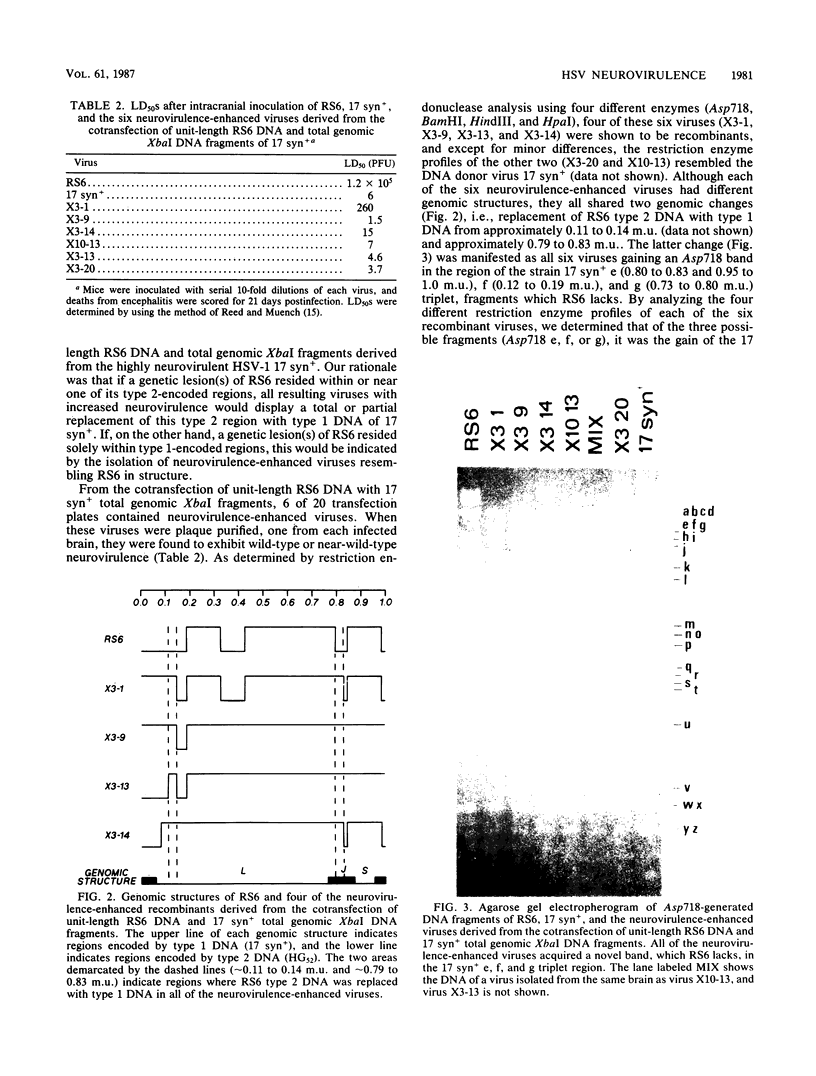
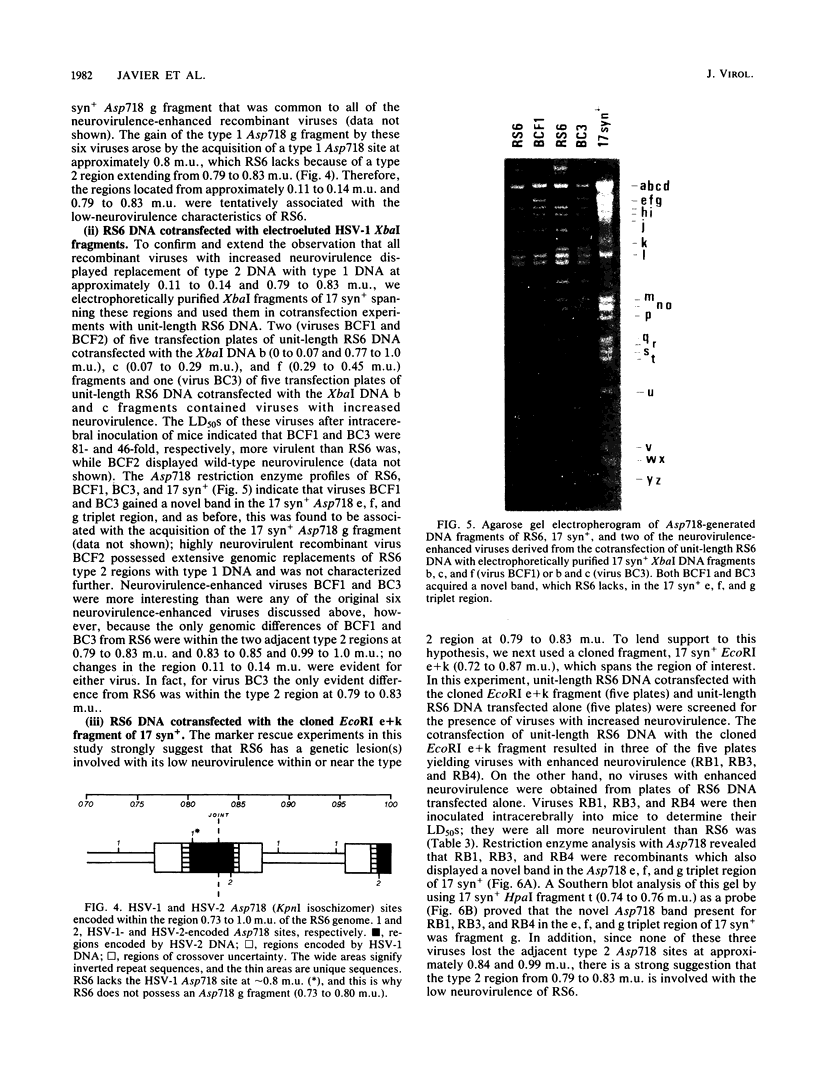
Abstract
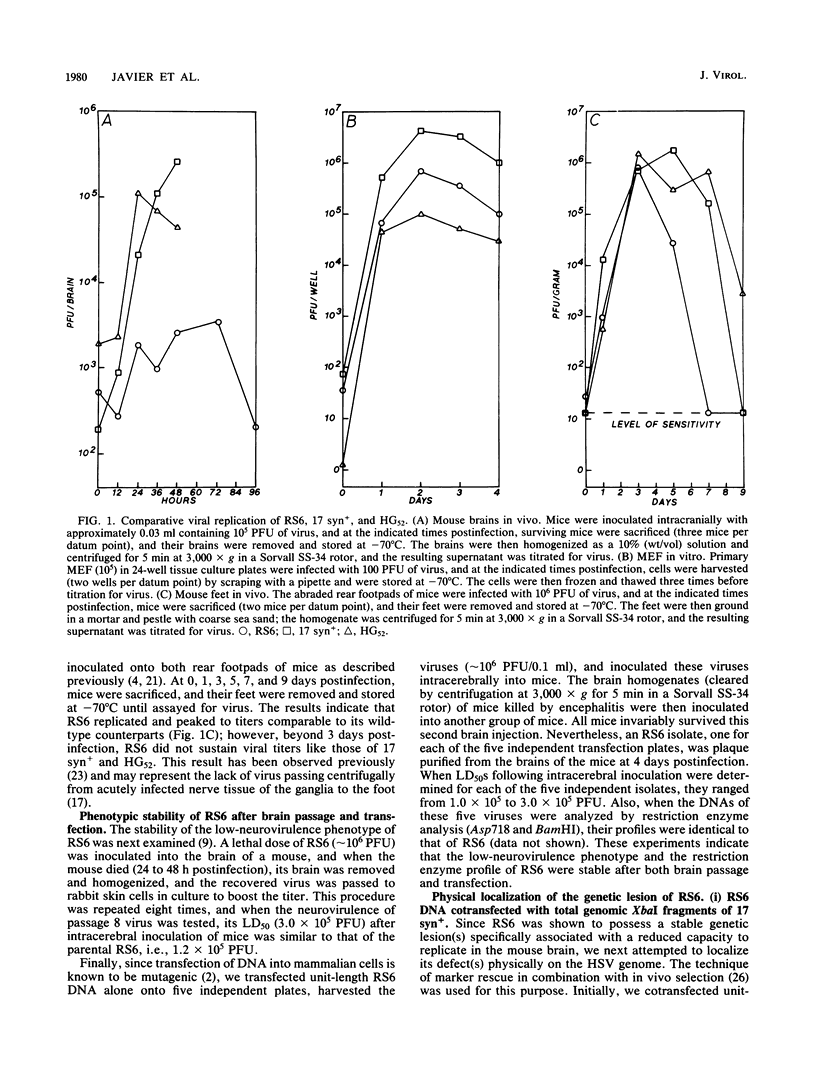
RS6 is a herpes simplex virus intertypic recombinant derived from type 1 strain 17 syn+ and type 2 strain HG52. With a 50% lethal dose of about 10(5) PFU after intracerebral inoculation of mice, RS6 was approximately 100,000 times less neurovirulent than either of its wild-type parental viruses were. When compared with strains 17 syn+ and HG52, RS6 replicated intermediately in primary mouse embryo fibroblasts in vitro at 38.5 degrees C (mouse temperature) and to wild-type peak titers in mouse feet in vivo. In contrast, following intracranial inoculation of mice, RS6 replicated significantly less well than did either of its parental viruses in brains. The genetic defect(s) responsible for the reduced neurovirulence of RS6 was stable after in vitro and in vivo serial passage, was not manifested as temperature-sensitive plaquing in vitro, and did not affect thymidine kinase expression. These data indicate that RS6 has a genetic defect(s) specifically affecting its ability to replicate in the mouse brain. Using marker rescue technologies, we increased the neurovirulence of RS6 and localized one genetic determinant(s) involved with the reduced neurovirulence of this agent to 0.72 to 0.87 map units (and, tentatively, to 0.79 to 0.83 map units) of the herpes simplex virus genome. When coupled with the work suggesting that thymidine kinase expression is essential for efficient replication in nerve tissues and earlier reports from this laboratory and others, the results presented in this study indicate that more than one herpes simplex virus gene is involved with neurovirulence.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker Y., Hadar J., Tabor E., Ben-Hur T., Raibstein I., Rösen A., Darai G. A sequence in HpaI-P fragment of herpes simplex virus-1 DNA determines intraperitoneal virulence in mice. Virology. 1986 Mar;149(2):255–259. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90128-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calos M. P., Lebkowski J. S., Botchan M. R. High mutation frequency in DNA transfected into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3015–3019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centifanto-Fitzgerald Y. M., Yamaguchi T., Kaufman H. E., Tognon M., Roizman B. Ocular disease pattern induced by herpes simplex virus is genetically determined by a specific region of viral DNA. J Exp Med. 1982 Feb 1;155(2):475–489. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.2.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheresh D. A., Haines H. Blocked herpes simplex virus type 2-specific DNA synthesis in simian virus 40-transformed hamster cells permissive for herpes simplex virus type 1. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):584–590. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.584-590.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook M. L., Stevens J. G. Pathogenesis of herpetic neuritis and ganglionitis in mice: evidence for intra-axonal transport of infection. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):272–288. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.272-288.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Wilkie N. M. Inversion of the two segments of the herpes simplex virus genome in intertypic recombinants. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jan;64(Pt 1):1–18. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field H. J., Wildy P. The pathogenicity of thymidine kinase-deficient mutants of herpes simplex virus in mice. J Hyg (Lond) 1978 Oct;81(2):267–277. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400025109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIT S., PIEKARSKI L. J., DUBBS D. R. Induction of thymidine kinase by vaccinia-infected mouse fibroblasts. J Mol Biol. 1963 Jan;6:22–33. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80078-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaerner H. C., Schröder C. H., Ott-Hartmann A., Kümel G., Kirchner H. Genetic variability of herpes simplex virus: development of a pathogenic variant during passaging of a nonpathogenic herpes simplex virus type 1 virus strain in mouse brain. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):83–93. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.83-93.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leary J. J., Brigati D. J., Ward D. C. Rapid and sensitive colorimetric method for visualizing biotin-labeled DNA probes hybridized to DNA or RNA immobilized on nitrocellulose: Bio-blots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Stow N. D., Preston V. G., Timbury M. C., Wilkie N. M. Physical mapping of herpes simplex virus-induced polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):624–642. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.624-642.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer G., Waner J. L., Phuangsab A., Goodheart C. R. Type 1 and type 2 herpes simplex viruses: serological and biological differences. J Virol. 1970 Jan;5(1):51–59. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.1.51-59.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanberry L. R., Kern E. R., Richards J. T., Abbott T. M., Overall J. C., Jr Genital herpes in guinea pigs: pathogenesis of the primary infection and description of recurrent disease. J Infect Dis. 1982 Sep;146(3):397–404. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.3.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G., Cook M. L. Restriction of herpes simplex virus by macrophages. An analysis of the cell-virus interaction. J Exp Med. 1971 Jan 1;133(1):19–38. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Wilkie N. M. An improved technique for obtaining enhanced infectivity with herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. J Gen Virol. 1976 Dec;33(3):447–458. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-3-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Wilkie N. M. Physical mapping of temperature-sensitive mutations of herpes simplex virus type 1 by intertypic marker rescue. Virology. 1978 Oct 1;90(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90327-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subak-Sharpe J. H., Brown S. M., Ritchie D. A., Timbury M. C., Macnab J. C., Marsden H. S., Hay J. Genetic and biochemical studies with herpesvirus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):717–730. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenser R. B., Miller R. L., Rapp F. Trigeminal ganglion infection by thymidine kinase-negative mutants of herpes simplex virus. Science. 1979 Aug 31;205(4409):915–917. doi: 10.1126/science.224454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. L., Cook M. L., Devi-Rao G. B., Wagner E. K., Stevens J. G. Functional and molecular analyses of the avirulent wild-type herpes simplex virus type 1 strain KOS. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):203–211. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.203-211.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. L., Devi-Rao G. V., Stevens J. G., Wagner E. K. Rescue of a herpes simplex virus type 1 neurovirulence function with a cloned DNA fragment. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):504–508. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.504-508.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. L., Stevens J. G. Biological characterization of a herpes simplex virus intertypic recombinant which is completely and specifically non-neurovirulent. Virology. 1983 Nov;131(1):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90543-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. L., Wagner E. K., Stevens J. G. Physical location of a herpes simplex virus type-1 gene function(s) specifically associated with a 10 million-fold increase in HSV neurovirulence. Virology. 1983 Nov;131(1):180–192. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]