Abstract
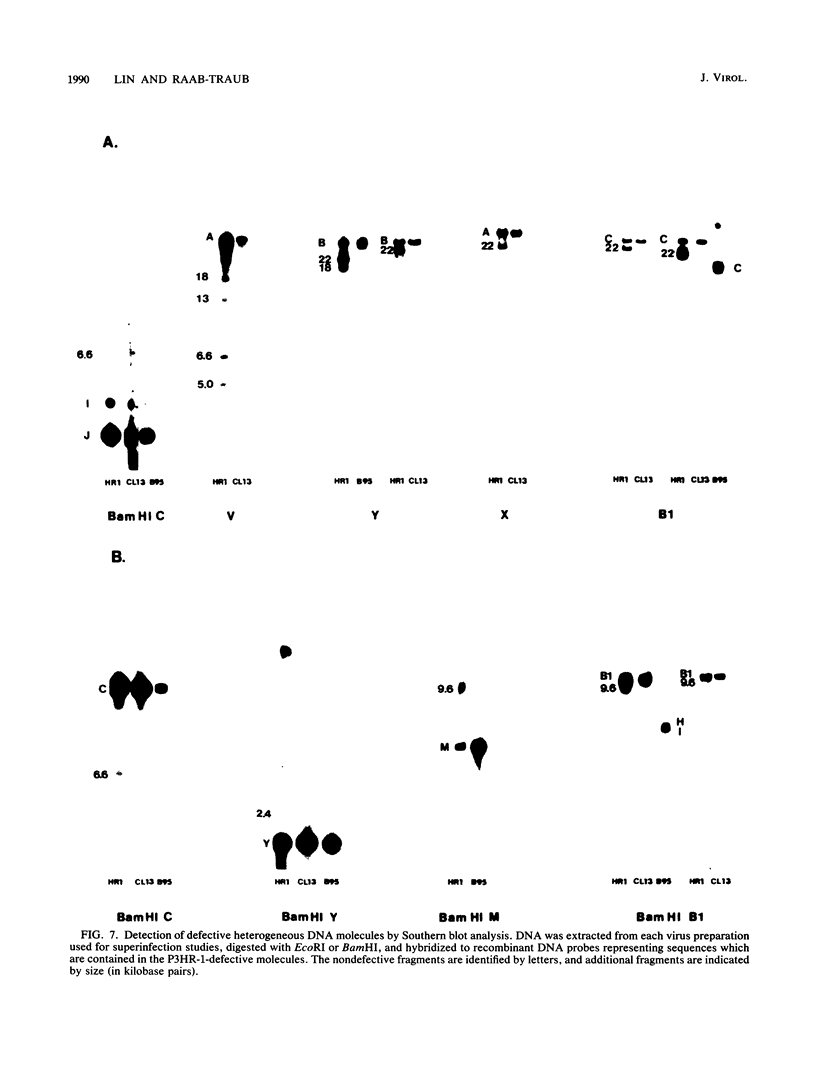
The heterogeneity of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) obtained from P3HR-1 cells has permitted derivation of a distinct subclone of P3HR-1 (L. Heston, M. Rabson, N. Brown, and G. Miller, Nature (London) 295:160-163, 1982). We have analyzed the biologic properties and genomic structure of this subclonal virus (clone 13) compared with those of parental P3HR-1 and B95-8 viruses. Synthesis of EBV compared with those of parental P3HR-1 and B95-8 viruses. Synthesis of EBV proteins in Raji cells superinfected with virus derived from P3HR-1, clone 13, and B95-8 was analyzed both by fluorography of radiolabeled proteins and by immunoblotting. Highly concentrated preparations of clone 13 and B95-8 virus induced most of the spectrum of EBV proteins in Raji cells with the exception of the 145,000-, 140,000-, and 110,000-molecular-weight proteins, which were either undetectable or reduced. Moreover, both clone 13 and B95-8 viruses also induced the same patterns of early antigen diffuse components as the parental P3HR-1 virus did. However, only P3HR-1 virus could induce EBV DNA synthesis in superinfected Raji cells, as determined both by buoyant density centrifugation and by in situ cytohybridization with biotinylated recombinant EBV DNA probes. Defective heterogeneous molecules present in P3HR-1 virus have been implicated in early antigen induction after superinfection of Raji cells. Therefore, Southern blots of clone 13, P3HR-1, and B95-8 viruses were hybridized to recombinant EBV fragments representing the sequences contained within the defective molecules in P3HR-1. The parental P3HR-1 contained the previously described defective molecules. No evidence for defective molecules was found in clone 13 or B95-8 viruses. These data indicate that concentrated preparations of both clone 13 and B95-8 viruses can induce abortive infection in Raji cells, but while the defective molecules are not needed for induction of early antigen diffuse components, they may be required for the induction of viral DNA synthesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen B., Steinberg J., Laemmli U. K., Weintraub H. The detection of DNA-binding proteins by protein blotting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):1–20. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. E., Palfreyman J. W., Preston C. M. Identification of herpes simplex virus DNA sequences which encode a trans-acting polypeptide responsible for stimulation of immediate early transcription. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho M. S., Bornkamm G. W., zur Hausen H. Structure of defective DNA molecules in Epstein-Barr virus preparations from P3HR-1 cells. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):199–207. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.199-207.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Countryman J., Miller G. Activation of expression of latent Epstein-Barr herpesvirus after gene transfer with a small cloned subfragment of heterogeneous viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4085–4089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delius H., Bornkamm G. W. Heterogeneity of Epstein-Barr virus. III. Comparison of a transforming and a nontransforming virus by partial denaturation mapping of their DNAs. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):81–89. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.81-89.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fresen K. O., Cho M. S., zur Hausen H. Recovery of transforming EBV from non-producer cells after superinfection with non-transforming P3HR-1 EBV. Int J Cancer. 1978 Oct 15;22(4):378–383. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910220403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fresen K. O., Merkt B., Bornkamm G. W., Hausen H. Heterogeneity of Epstein-Barr virus originating from P3HR-1 cells. I. Studies on EBNA induction. Int J Cancer. 1977 Mar 15;19(3):317–323. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller M., Dambaugh T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus DNA. IX. Variation among viral DNAs from producer and nonproducer infected cells. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):632–648. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.632-648.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heston L., Rabson M., Brown N., Miller G. New Epstein-Barr virus variants from cellular subclones of P3J-HR-1 Burkitt lymphoma. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):160–163. doi: 10.1038/295160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer P. R., Waldrop A. A., Ward D. C. Enzymatic synthesis of biotin-labeled polynucleotides: novel nucleic acid affinity probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6633–6637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. C., Choi E. I., Pagano J. S. Qualitative and quantitative analyses of Epstein-Barr virus early antigen diffuse component by western blotting enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with a monoclonal antibody. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):793–799. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.793-799.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. C., Pagano J. S. Sequential detection of different antigens induced by Epstein-Barr virus and herpes simplex virus in the same Western blot by using dual antibody probes. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):522–524. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.522-524.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. C., Shaw J. E., Smith M. C., Pagano J. S. Effect of 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate on the replication of Epstein-Barr virus. I. Characterization of viral DNA. Virology. 1979 Nov;99(1):183–187. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90052-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. C., Smith M. C., Pagano J. S. Activation of latent Epstein-Barr virus genomes: selective stimulation of synthesis of chromosomal proteins by a tumor promoter. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):985–991. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.985-991.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. C., Smith M. C., Pagano J. S. Effects of 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate on cell proliferation and Epstein-Barr virus DNA replication. Virology. 1982 Feb;117(1):186–194. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90518-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. C., Smith M. C., Pagano J. S. Prolonged inhibitory effect of 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine against replication of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):50–55. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.50-55.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Heston L., Countryman J. P3HR-1 Epstein-Barr virus with heterogeneous DNA is an independent replicon maintained by cell-to-cell spread. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):45–52. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.45-52.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Rabson M., Heston L. Epstein-Barr virus with heterogeneous DNA disrupts latency. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):174–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.174-182.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Robinson J., Heston L., Lipman M. Differences between laboratory strains of Epstein-Barr virus based on immortalization, abortive infection, and interference. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4006–4010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. R., Vroman B., Chase B., Sculley T., Hummel M., Kieff E. Identification of polypeptide components of the Epstein-Barr virus early antigen complex with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):193–201. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.193-201.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellett P. E., McKnight J. L., Jenkins F. J., Roizman B. Nucleotide sequence and predicted amino acid sequence of a protein encoded in a small herpes simplex virus DNA fragment capable of trans-inducing alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5870–5874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raab-Traub N., Dambaugh T., Kieff E. DNA of Epstein-Barr virus VIII: B95-8, the previous prototype, is an unusual deletion derivative. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):257–267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabson M., Heston L., Miller G. Identification of a rare Epstein-Barr virus variant that enhances early antigen expression in Raji cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2762–2766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Summers W. C., Klein G. Nucleic acid renaturation and restriction endonuclease cleavage analyses show that the DNAs of a transforming and a nontransforming strain of Epstein-Barr virus share approximately 90% of their nucleotide sequences. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):765–775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.765-775.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yajima Y., Marczynska B., Nonoyama M. Transforming activity of Epstein-Barr virus obtained by superinfection of Raji cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):2008–2010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]