Abstract
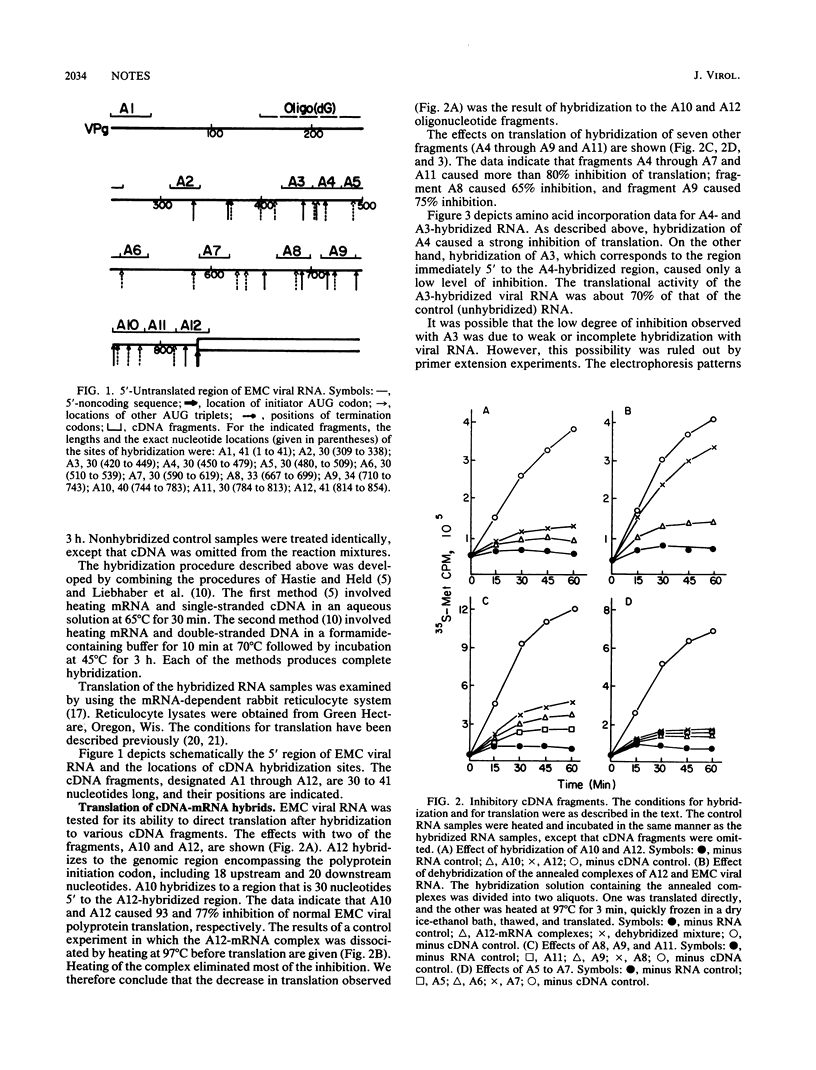
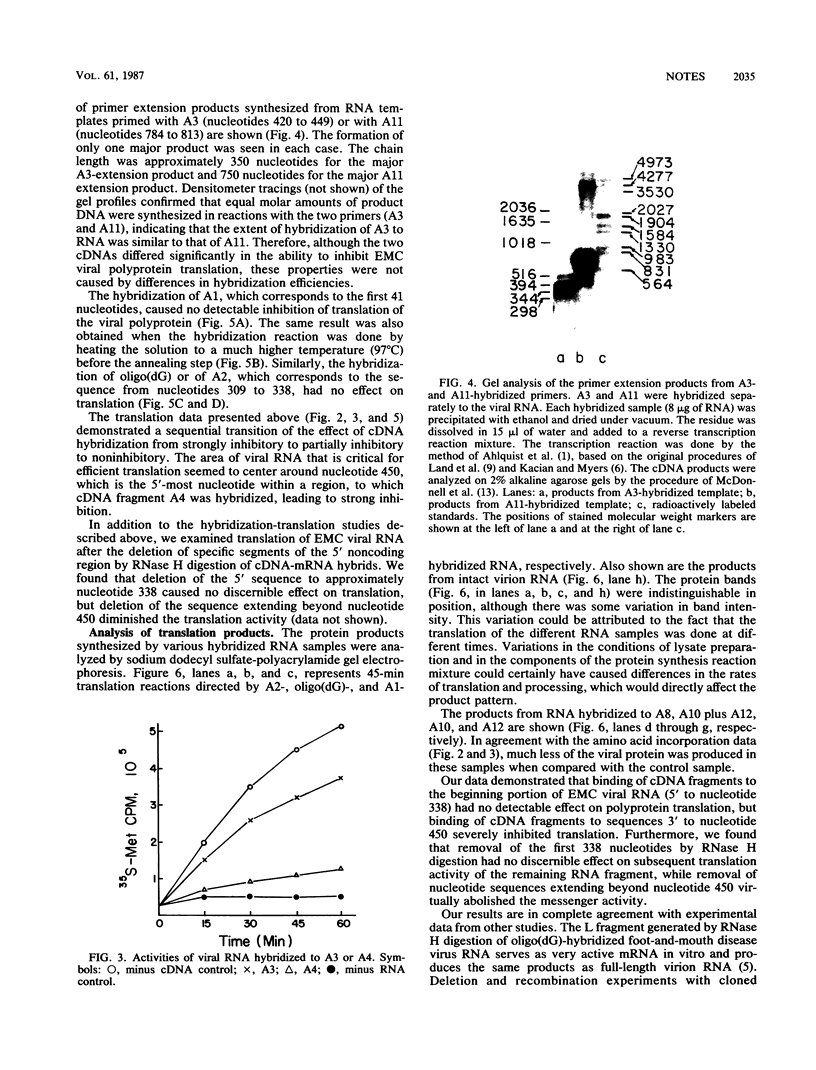
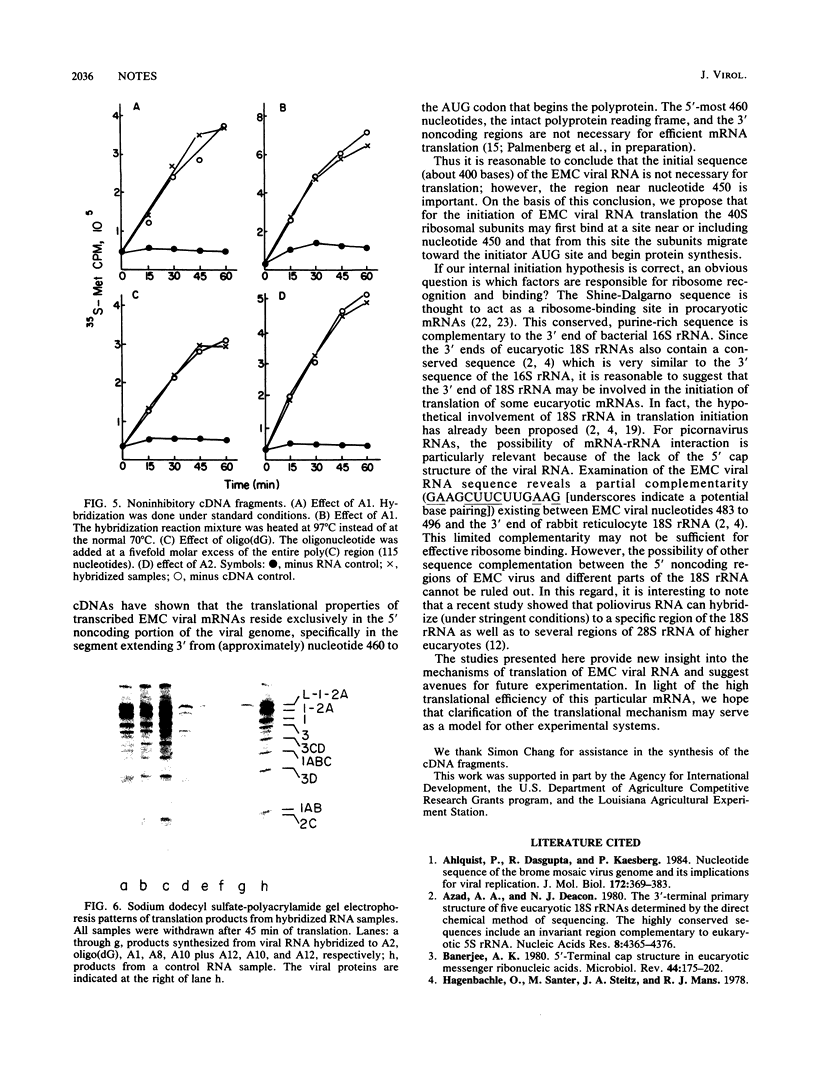
Cell-free translation of the RNA of encephalomyocarditis virus was examined after hybridization of chemically synthesized cDNA fragments to different sites of the 5' noncoding region of the viral RNA. The following results were obtained. The binding of cDNA fragments to the first 41 nucleotides, to the poly(C) tract (between nucleotides 149 and 263), and to the sequence between nucleotides 309 and 338 did not affect translation of the viral RNA; the binding of cDNA fragments to the sequence between nucleotides 420 and 449 caused a slight inhibition; and the binding of fragments to eight different sites between nucleotides 450 and the initiator AUG codon (nucleotide 834) caused high degrees of inhibition. The results suggest that the first part of the 5' untranslated region, at least to nucleotide 338, may not be required for encephalomyocarditis viral RNA translation; however, the region near nucleotide 450 is important for translation of the viral RNA. The possibility that initiation occurs at an internal site is discussed.
Full text
PDF

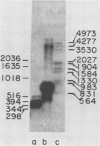
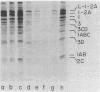
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlquist P., Dasgupta R., Kaesberg P. Nucleotide sequence of the brome mosaic virus genome and its implications for viral replication. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 5;172(4):369–383. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azad A. A., Deacon N. J. The 3'-terminal primary structure of five eukaryotic 18S rRNAs determined by the direct chemical method of sequencing. The highly conserved sequences include an invariant region complementary to eukaryotic 5S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 10;8(19):4365–4376. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.19.4365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A. K. 5'-terminal cap structure in eucaryotic messenger ribonucleic acids. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):175–205. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.175-205.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Santer M., Steitz J. A., Mans R. J. Conservation of the primary structure at the 3' end of 18S rRNA from eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):551–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90328-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastie N. D., Held W. A. Analysis of mRNA populations by cDNA.mRNA hybrid-mediated inhibition of cell-free protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1217–1221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kacian D. L., Myers J. C. Synthesis of extensive, possibly complete, DNA copies of poliovirus RNA in high yields and at high specific activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2191–2195. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. How do eucaryotic ribosomes select initiation regions in messenger RNA? Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1109–1123. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Grez M., Hauser H., Lindenmaier W., Schütz G. 5'-Terminal sequences of eucaryotic mRNA can be cloned with high efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2251–2266. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebhaber S. A., Cash F. E., Shakin S. H. Translationally associated helix-destabilizing activity in rabbit reticulocyte lysate. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15597–15602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo K. M., Jones S. S., Hackett N. R., Khorana H. G. Specific amino acid substitutions in bacterioopsin: Replacement of a restriction fragment in the structural gene by synthetic DNA fragments containing altered codons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2285–2289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure M. A., Perrault J. Poliovirus genome RNA hybridizes specifically to higher eukaryotic rRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 11;13(19):6797–6816. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.19.6797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonell M. W., Simon M. N., Studier F. W. Analysis of restriction fragments of T7 DNA and determination of molecular weights by electrophoresis in neutral and alkaline gels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):119–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A. C., Kirby E. M., Janda M. R., Drake N. L., Duke G. M., Potratz K. F., Collett M. S. The nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of the encephalomyocarditis viral polyprotein coding region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2969–2985. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks G. D., Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C. Encephalomyocarditis virus 3C protease: efficient cell-free expression from clones which link viral 5' noncoding sequences to the P3 region. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):376–384. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.376-384.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in vitro yields an active proteolytic processing enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):457–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sangar D. V., Black D. N., Rowlands D. J., Harris T. J., Brown F. Location of the initiation site for protein synthesis on foot-and-mouth disease virus RNA by in vitro translation of defined fragments of the RNA. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):59–68. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.59-68.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargan D. R., Gregory S. P., Butterworth P. H. A possible novel interaction between the 3'-end of 18 S ribosomal RNA and the 5'-leader sequence of many eukaryotic messenger RNAs. FEBS Lett. 1982 Oct 18;147(2):133–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)81026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih D. S., Shih C. T., Kew O., Pallansch M., Rueckert R., Kaesberg P. Cell-free synthesis and processing of the proteins of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5807–5811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih D. S., Shih C. T., Zimmern D., Rueckert R. R., Kaesberg P. Translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in reticulocyte lysates: kinetic analysis of the formation of virion proteins and a protein required for processing. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):472–480. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.472-480.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A., Jakes K. How ribosomes select initiator regions in mRNA: base pair formation between the 3' terminus of 16S rRNA and the mRNA during initiation of protein synthesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4734–4738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svitkin Y. V., Agol V. I. Complete translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA and faithful cleavage of virus-specific proteins in a cell-free system from Krebs-2 cells. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):7–11. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vartapetian A. B., Mankin A. S., Skripkin E. A., Chumakov K. M., Smirnov V. D., Bogdanov A. A. The primary and secondary structure of the 5'-end region of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA. A novel approach to sequencing long RNA molecules. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):189–195. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90189-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimmer E. Genome-linked proteins of viruses. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):199–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90335-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]