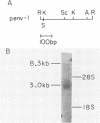
Abstract
We report the isolation and sequence of a cDNA clone containing part of the env message of the Moloney murine leukemia virus (MoMuLV). This clone was derived from a rat thymic lymphoma induced by MoMuLV. The AG acceptor site employed in this message is located at position 5490 in the MoMuLV genome. This splice site is detectable at the cDNA level by the creation of a novel SacI restriction site not present in the viral genome. In the -1 to -40 region, this AG acceptor site is preceded by four conserved heptanucleotides (PyXPyTPuAPy) that may function as acceptors for removal of the 5' end of the intron.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns A. J., Lai M. H., Bosselman R. A., McKennett M. A., Bacheler L. T., Fan H., Maandag E. C., van der Putten H. V., Verma I. M. Molecular cloning of unintegrated and a portion of integrated moloney murine leukemia viral DNA in bacteriophage lambda. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):254–263. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.254-263.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. L., Chabot B., Steitz J. A. U2 as well as U1 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins are involved in premessenger RNA splicing. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):737–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosselman R. A., van Straaten F., Van Beveren C., Verma I. M., Vogt M. Analysis of the env gene of a molecularly cloned and biologically active Moloney mink cell focus-forming proviral DNA. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):19–31. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.19-31.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. The generality of self-splicing RNA: relationship to nuclear mRNA splicing. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90751-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot B., Black D. L., LeMaster D. M., Steitz J. A. The 3' splice site of pre-messenger RNA is recognized by a small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1344–1349. doi: 10.1126/science.2933810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frendewey D., Keller W. Stepwise assembly of a pre-mRNA splicing complex requires U-snRNPs and specific intron sequences. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):355–367. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski P. J., Seiler S. R., Sharp P. A. A multicomponent complex is involved in the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):345–353. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski P. J., Sharp P. A. Affinity chromatography of splicing complexes: U2, U5, and U4 + U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in the spliceosome. Science. 1986 Sep 19;233(4770):1294–1299. doi: 10.1126/science.3638792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquier A., Rodriguez J. R., Rosbash M. A quantitative analysis of the effects of 5' junction and TACTAAC box mutants and mutant combinations on yeast mRNA splicing. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):423–430. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90172-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W. The RNA lariat: a new ring to the splicing of mRNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):423–425. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90449-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T. Multiple factors including the small nuclear ribonucleoproteins U1 and U2 are necessary for pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):725–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Baltimore D. Varying the position of a retrovirus packaging sequence results in the encapsidation of both unspliced and spliced RNAs. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):401–407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.401-407.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A. J., Lin R. J., Cheng S. C., Abelson J. Molecular consequences of specific intron mutations on yeast mRNA splicing in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):335–344. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R., Guthrie C. A point mutation in the conserved hexanucleotide at a yeast 5' splice junction uncouples recognition, cleavage, and ligation. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):107–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikielny C. W., Rosbash M. mRNA splicing efficiency in yeast and the contribution of nonconserved sequences. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. A role for exon sequences and splice-site proximity in splice-site selection. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):681–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. Intron sequences involved in lariat formation during pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Green M. R. Role of the 3' splice site consensus sequence in mammalian pre-mRNA splicing. Nature. 1985 Oct 24;317(6039):732–734. doi: 10.1038/317732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Green M. R. Specific and stable intron-factor interactions are established early during in vitro pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):131–142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Green M. R. Excision of an intact intron as a novel lariat structure during pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90553-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Strauss P. G., Hu L. F. A common region for proviral DNA integration in MoMuLV-induced rat thymic lymphomas. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):445–449. doi: 10.1038/302445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Strauss P. G., Lohse M. A. Concerted DNA rearrangements in Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced thymomas: a potential synergistic relationship in oncogenesis. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):258–267. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.258-267.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., Galleshaw J. A., Jonas V., Berns A. J., Doolittle R. F., Donoghue D. J., Verma I. M. Nucleotide sequence and formation of the transforming gene of a mouse sarcoma virus. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):258–262. doi: 10.1038/289258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]