Abstract
Cloned cDNA encoding the membrane glycoprotein E1 of the coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus strain A59 was expressed transiently in a monkey fibroblast cell line (COS) by using a simian virus 40-based vector. As determined by indirect immunofluorescence microscopy, the E1 protein accumulated intracellularly in a perinuclear region coincident with a Golgi marker. The same three species of E1 that occur in virus-infected cells were also found in transfected cells. These are one unglycosylated form and two apparently O-glycosylated forms that could be labeled in a tunicamycin-resistant fashion with [3H]glucosamine. Because O glycosylation occurs posttranslationally in the Golgi apparatus, we could show, by monitoring the rate of acquisition of oligosaccharides, that the transport of E1 from the rough endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus had a half time of between 15 and 30 min.
Full text
PDF
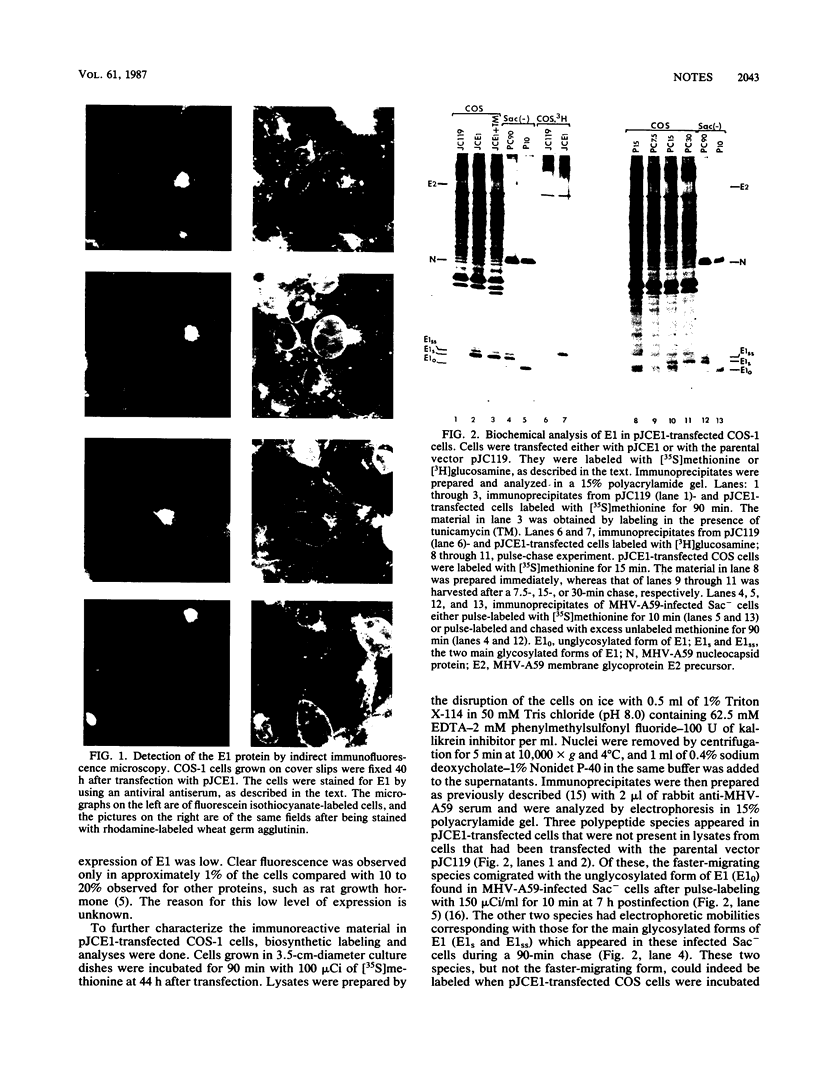


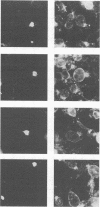
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J., Niemann H., Smeekens S., Rottier P., Warren G. Sequence and topology of a model intracellular membrane protein, E1 glycoprotein, from a coronavirus. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):751–752. doi: 10.1038/308751a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois-Dalcq M. E., Doller E. W., Haspel M. V., Holmes K. V. Cell tropism and expression of mouse hepatitis viruses (MHV) in mouse spinal cord cultures. Virology. 1982 Jun;119(2):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90092-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagerland J. A., Pohlenz J. F., Woode G. N. A morphological study of the replication of Breda virus (proposed family Toroviridae) in bovine intestinal cells. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jul;67(Pt 7):1293–1304. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-7-1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan J. L., Rose J. K. Conversion of a secretory protein into a transmembrane protein results in its transport to the Golgi complex but not to the cell surface. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):779–787. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90413-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. V., Doller E. W., Behnke J. N. Analysis of the functions of coronavirus glycoproteins by differential inhibition of synthesis with tunicamycin. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1981;142:133–142. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0456-3_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. V., Doller E. W., Sturman L. S. Tunicamycin resistant glycosylation of coronavirus glycoprotein: demonstration of a novel type of viral glycoprotein. Virology. 1981 Dec;115(2):334–344. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90115-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Spear P. G. O-linked oligosaccharides are acquired by herpes simplex virus glycoproteins in the Golgi apparatus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):987–997. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90083-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuismanen E., Bång B., Hurme M., Pettersson R. F. Uukuniemi virus maturation: immunofluorescence microscopy with monoclonal glycoprotein-specific antibodies. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):137–146. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.137-146.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuismanen E., Hedman K., Saraste J., Pettersson R. F. Uukuniemi virus maturation: accumulation of virus particles and viral antigens in the Golgi complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;2(11):1444–1458. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.11.1444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemann H., Boschek B., Evans D., Rosing M., Tamura T., Klenk H. D. Post-translational glycosylation of coronavirus glycoprotein E1: inhibition by monensin. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1499–1504. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01346.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemann H., Heisterberg-Moutsis G., Geyer R., Klenk H. D., Wirth M. Glycoprotein E1 of MHV-A59: structure of the O-linked carbohydrates and construction of full length recombinant cDNA clones. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1984;173:201–213. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9373-7_20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemann H., Klenk H. D. Coronavirus glycoprotein E1, a new type of viral glycoprotein. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 25;153(4):993–1010. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90463-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottier P. J., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A. Viral protein synthesis in mouse hepatitis virus strain A59-infected cells: effect of tunicamycin. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):350–357. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.350-357.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottier P. J., Spaan W. J., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A. Translation of three mouse hepatitis virus strain A59 subgenomic RNAs in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):20–26. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.20-26.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottier P. J., Welling G. W., Welling-Wester S., Niesters H. G., Lenstra J. A., Van der Zeijst B. A. Predicted membrane topology of the coronavirus protein E1. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 25;25(6):1335–1339. doi: 10.1021/bi00354a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottier P., Armstrong J., Meyer D. I. Signal recognition particle-dependent insertion of coronavirus E1, an intracellular membrane glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4648–4652. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)89119-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottier P., Brandenburg D., Armstrong J., van der Zeijst B., Warren G. Assembly in vitro of a spanning membrane protein of the endoplasmic reticulum: the E1 glycoprotein of coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus A59. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1421–1425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague J., Condra J. H., Arnheiter H., Lazzarini R. A. Expression of a recombinant DNA gene coding for the vesicular stomatitis virus nucleocapsid protein. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):773–781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.773-781.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S., Holmes K. V. The molecular biology of coronaviruses. Adv Virus Res. 1983;28:35–112. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60721-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tooze J., Tooze S. A. Infection of AtT20 murine pituitary tumour cells by mouse hepatitis virus strain A59: virus budding is restricted to the Golgi region. Eur J Cell Biol. 1985 May;37:203–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tooze J., Tooze S. A., Warren G. Laminated cisternae of the rough endoplasmic reticulum induced by coronavirus MHV-A59 infection. Eur J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;36(1):108–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tooze J., Tooze S., Warren G. Replication of coronavirus MHV-A59 in sac- cells: determination of the first site of budding of progeny virions. Eur J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;33(2):281–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M., Horzinek M. C. Morphogenesis of Berne virus (proposed family Toroviridae). J Gen Virol. 1986 Jul;67(Pt 7):1305–1314. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-7-1305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]