Abstract
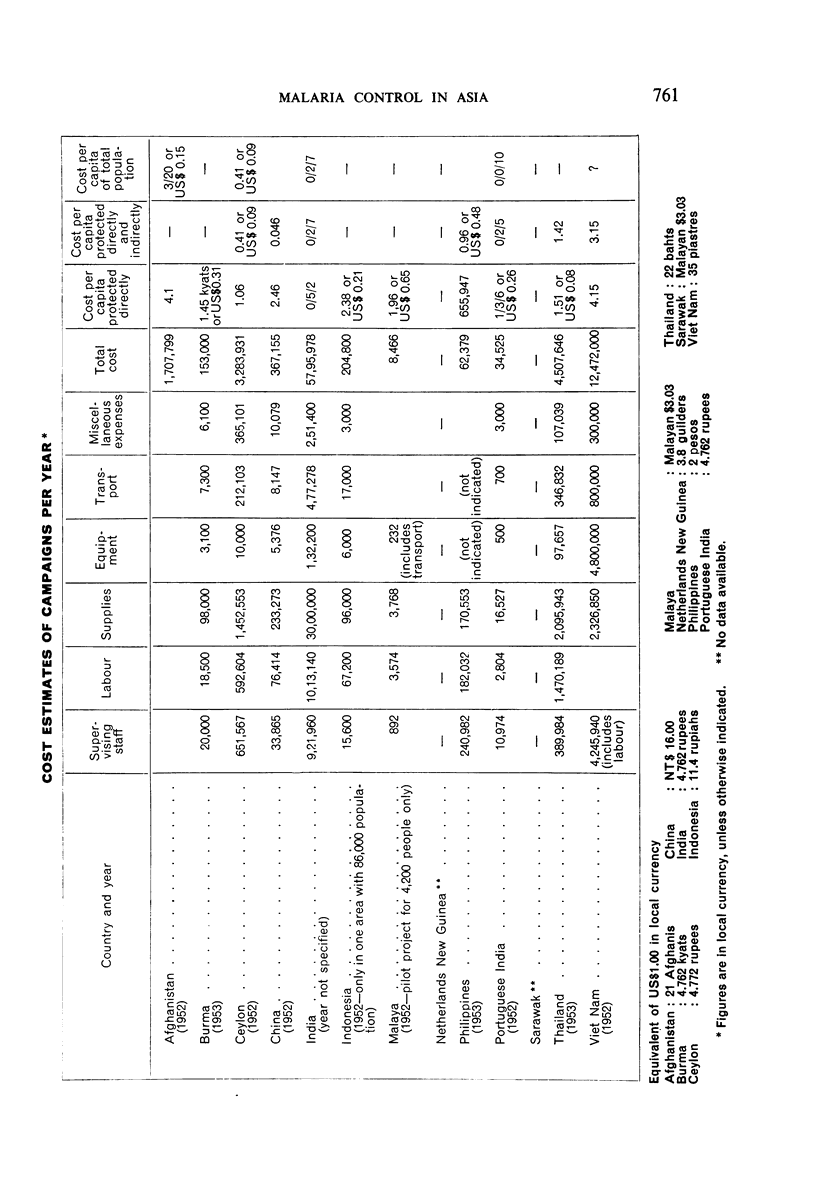
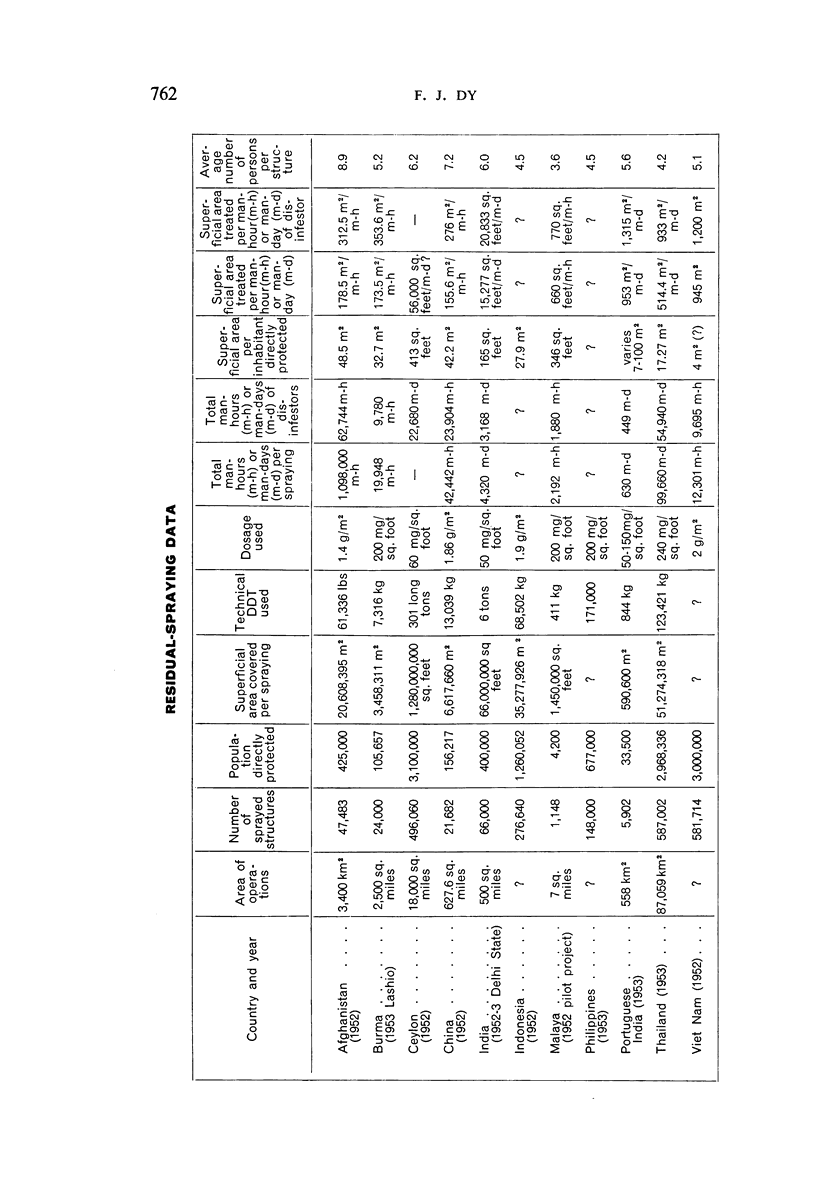
The author summarizes the information given by 13 governments—Afghanistan, Burma, Ceylon, China, India, Indonesia, Malaya, Netherlands New Guinea, Philippines, Portuguese India, Sarawak, Thailand, and Viet Nam—on their existing and proposed malaria-control programmes in response to a questionnaire prepared by WHO for discussion at the First Asian Malaria Conference, which was held in Bangkok in September 1953.
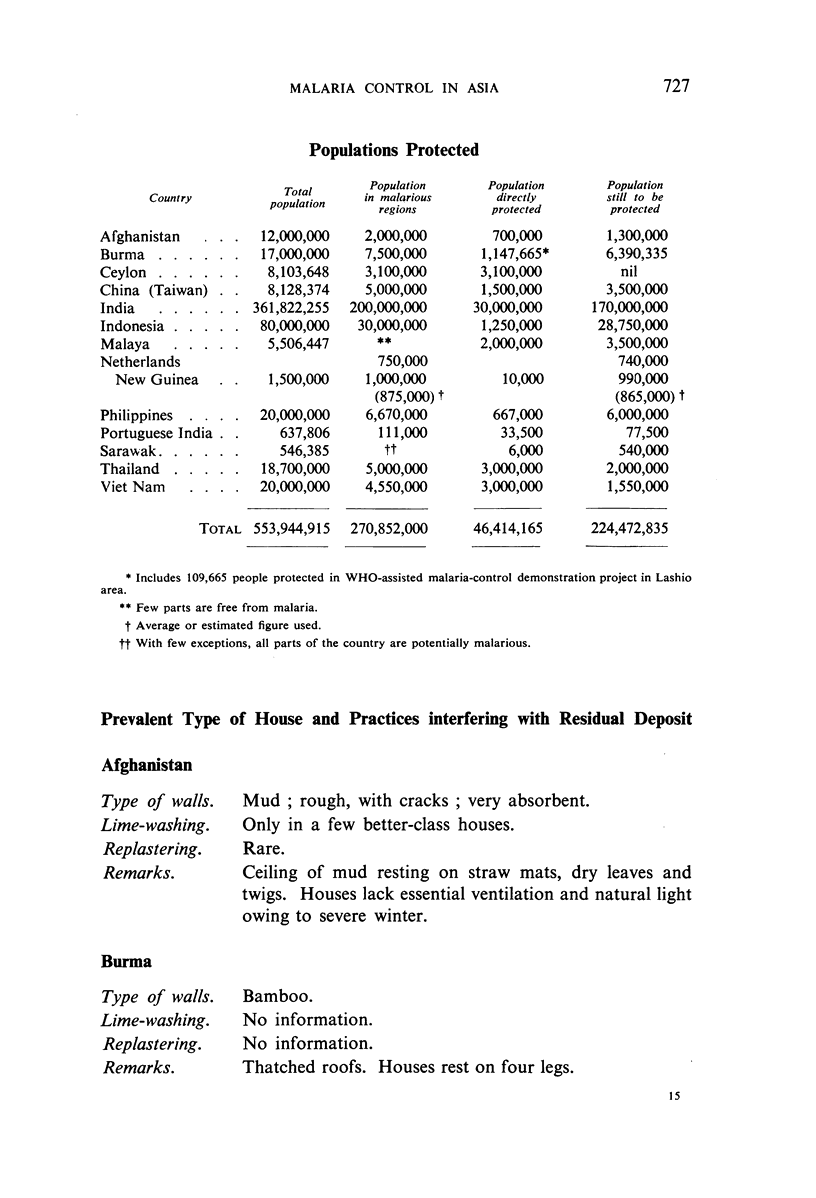
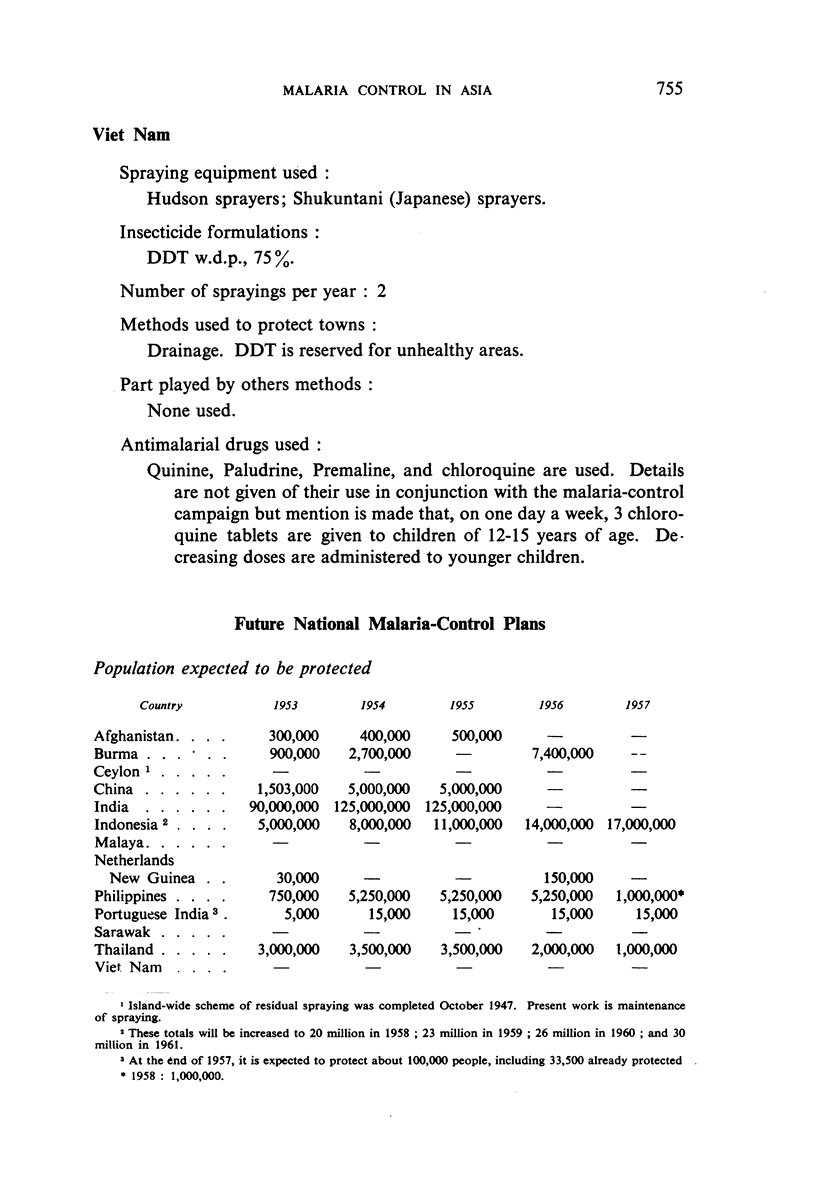
Although in late 1953 nearly 46.5 million of the 271 million people living in malarious regions were protected against the disease, more than 224 million others were still unprotected.
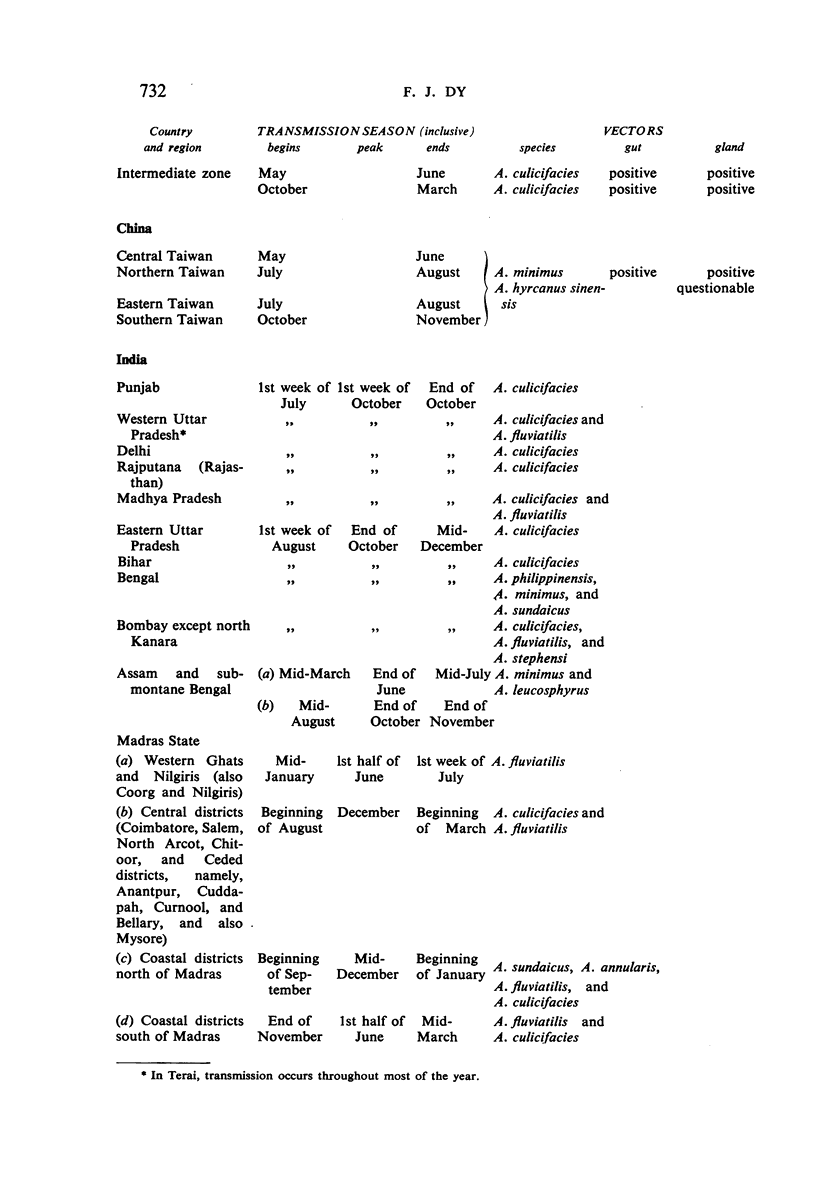
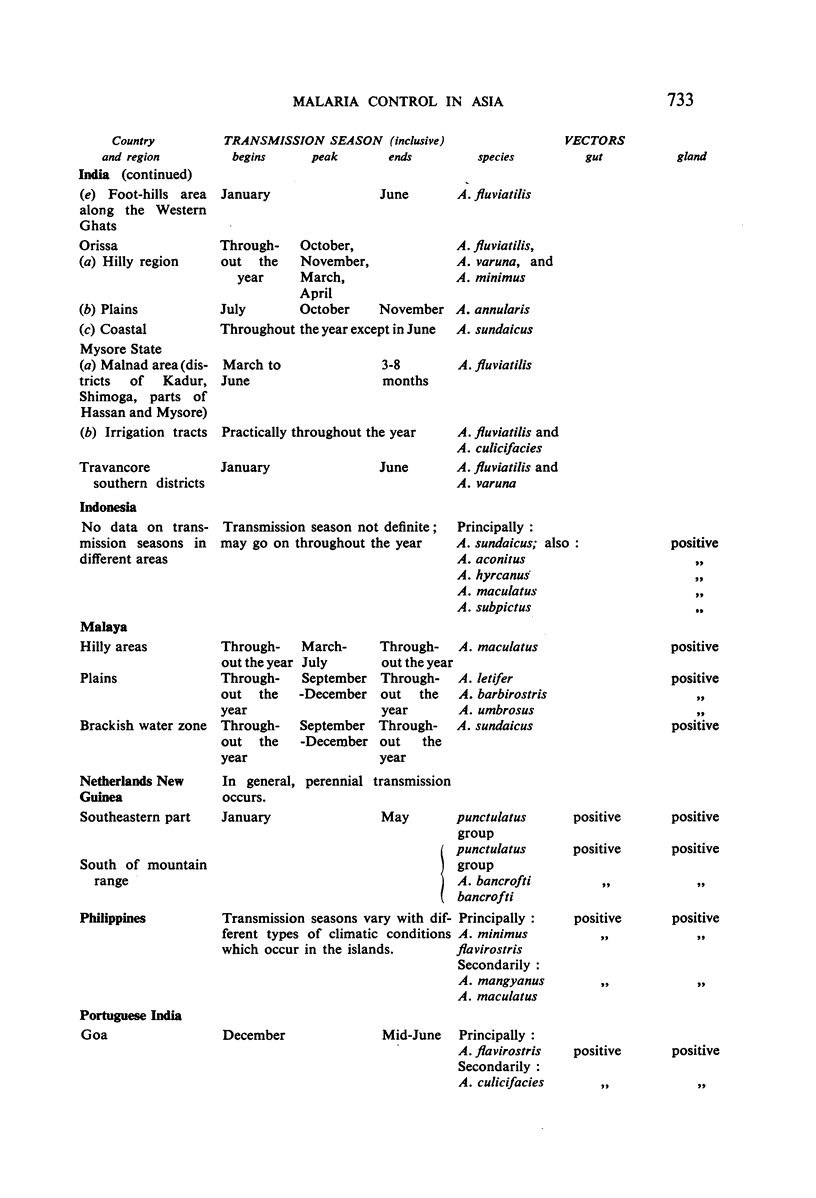
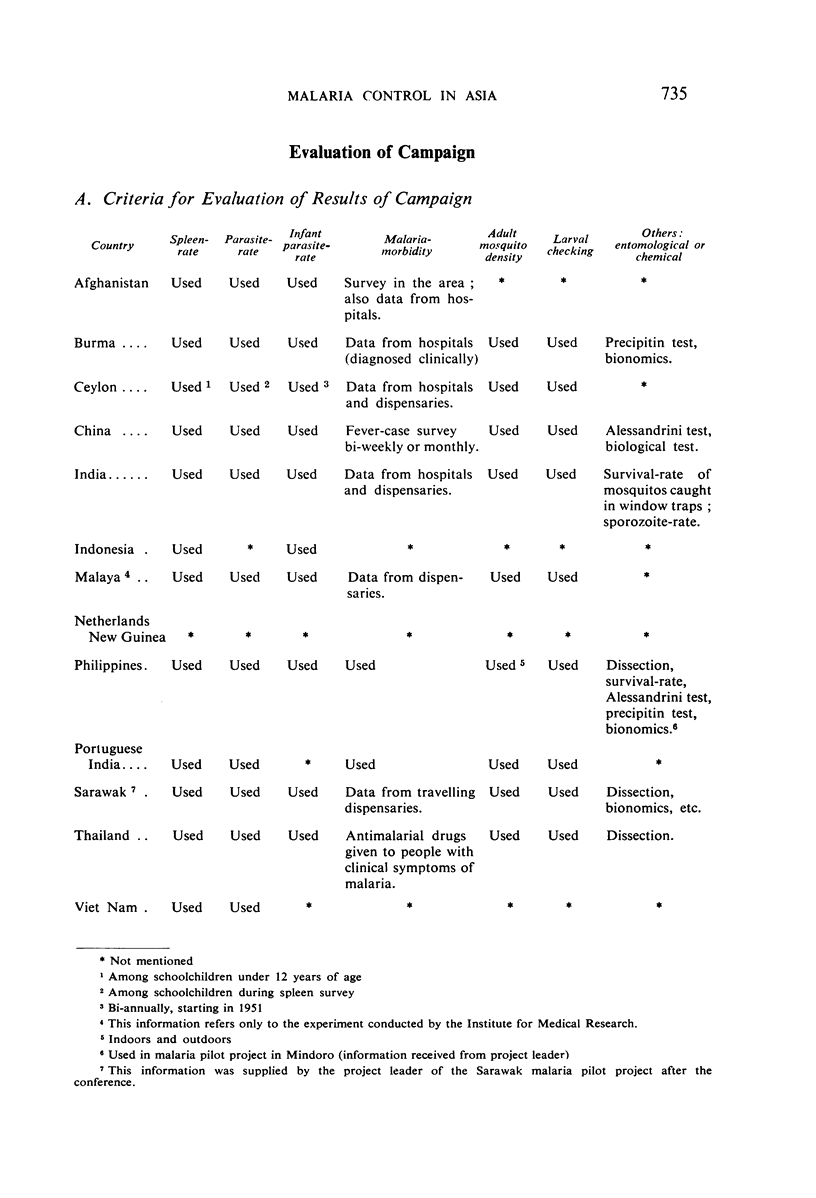
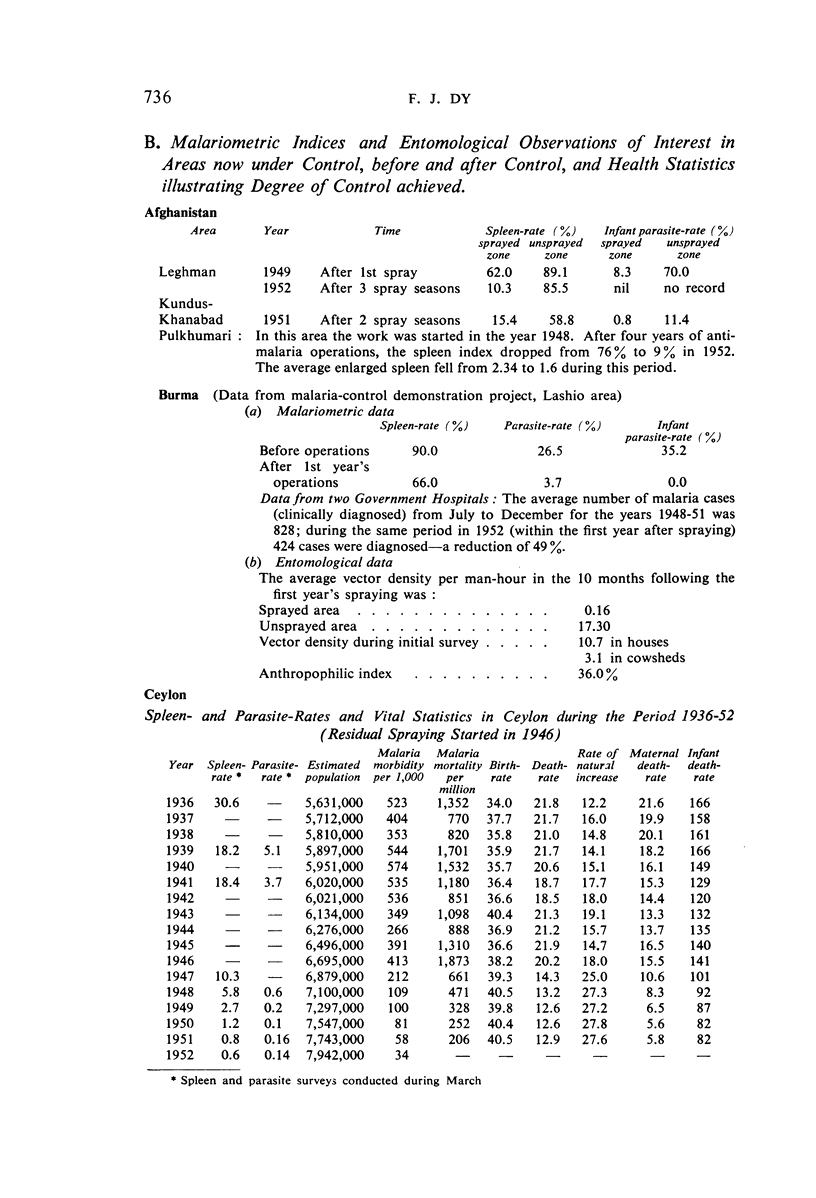
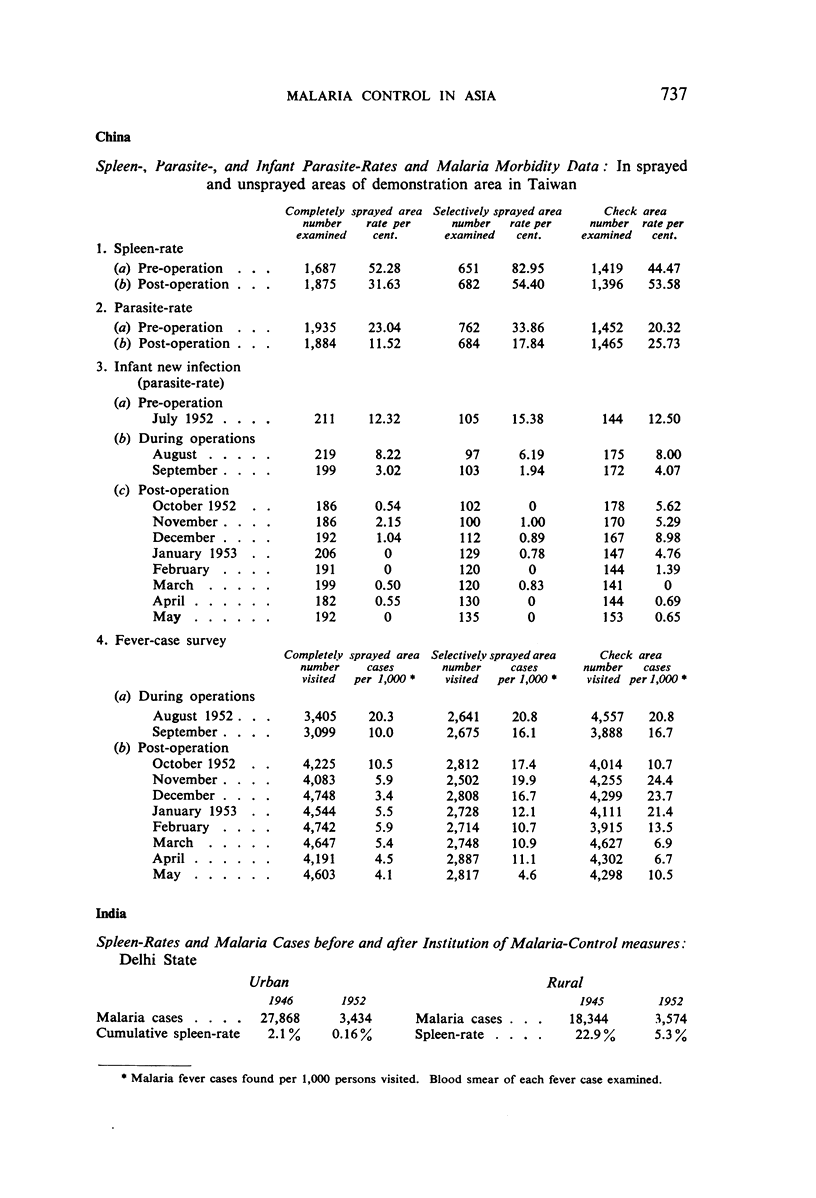
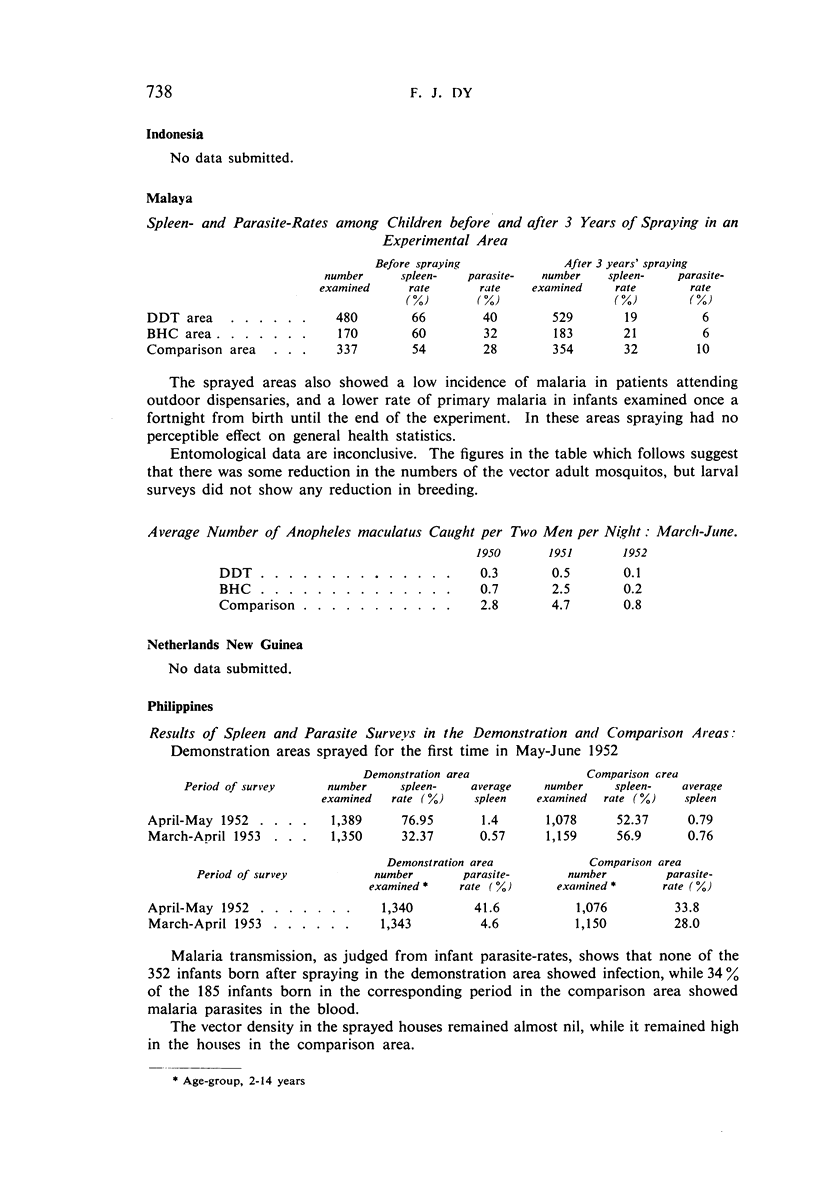
It is noted that residual-insecticide spraying—the basis of most campaigns—has significantly reduced spleen- and parasite-rates; that the minor opposition to spraying initially encountered in some places quickly disappeared as the benefits became apparent; that malaria control has resulted in general improvements in public health and has promoted socio-economic development; that anopheline resistance to the insecticides used has not been observed; that ten governments voiced the need for indoctrination of public officials concerning malaria control; and that there is a trend among governments to make financial provision for long-term malaria-control schemes.
Full text
PDF