Abstract
This report presents the results of serological analyses made by the laboratory of the Treponematoses Control Project, Indonesia, from its establishment in April 1951 until April 1953. All sera were tested quantitatively with the VDRL and Kline slide-tests or the Kahn test, or with all three.
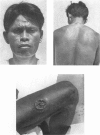
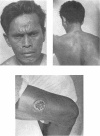
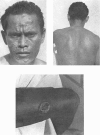
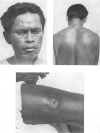
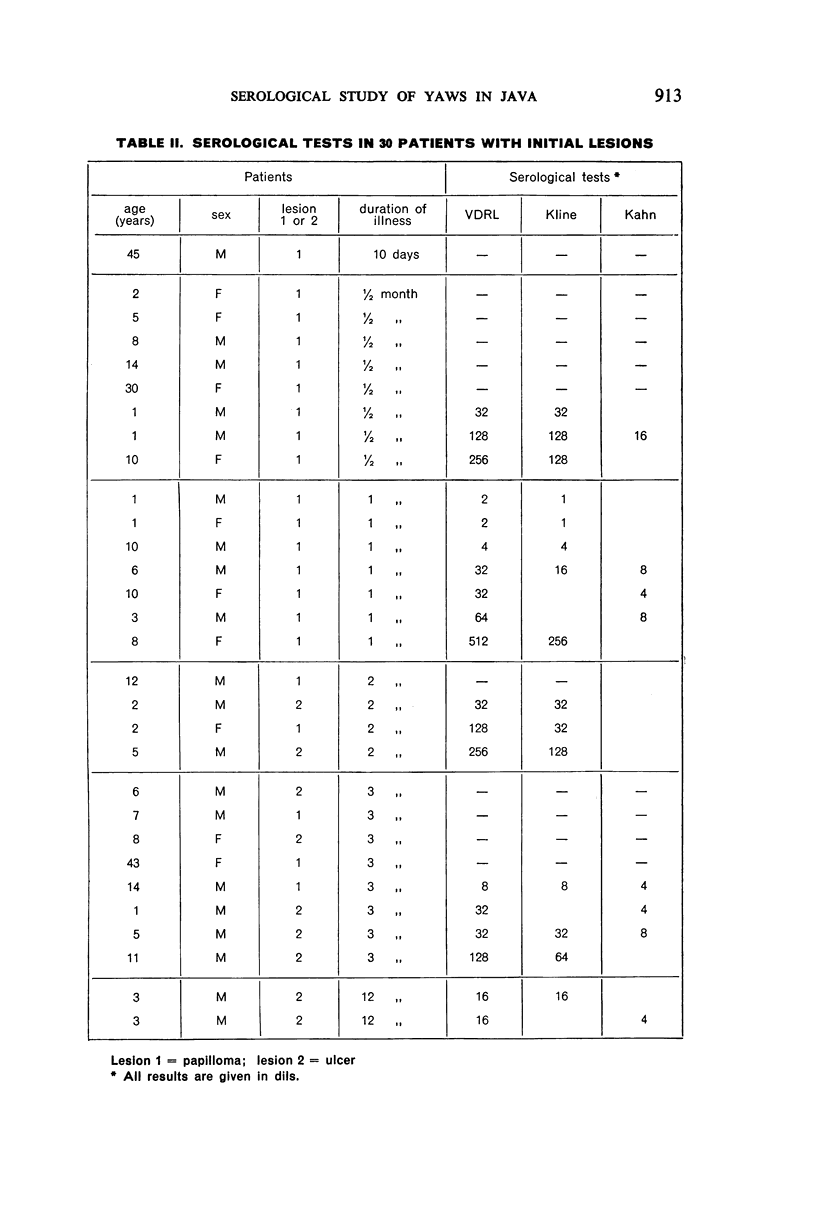
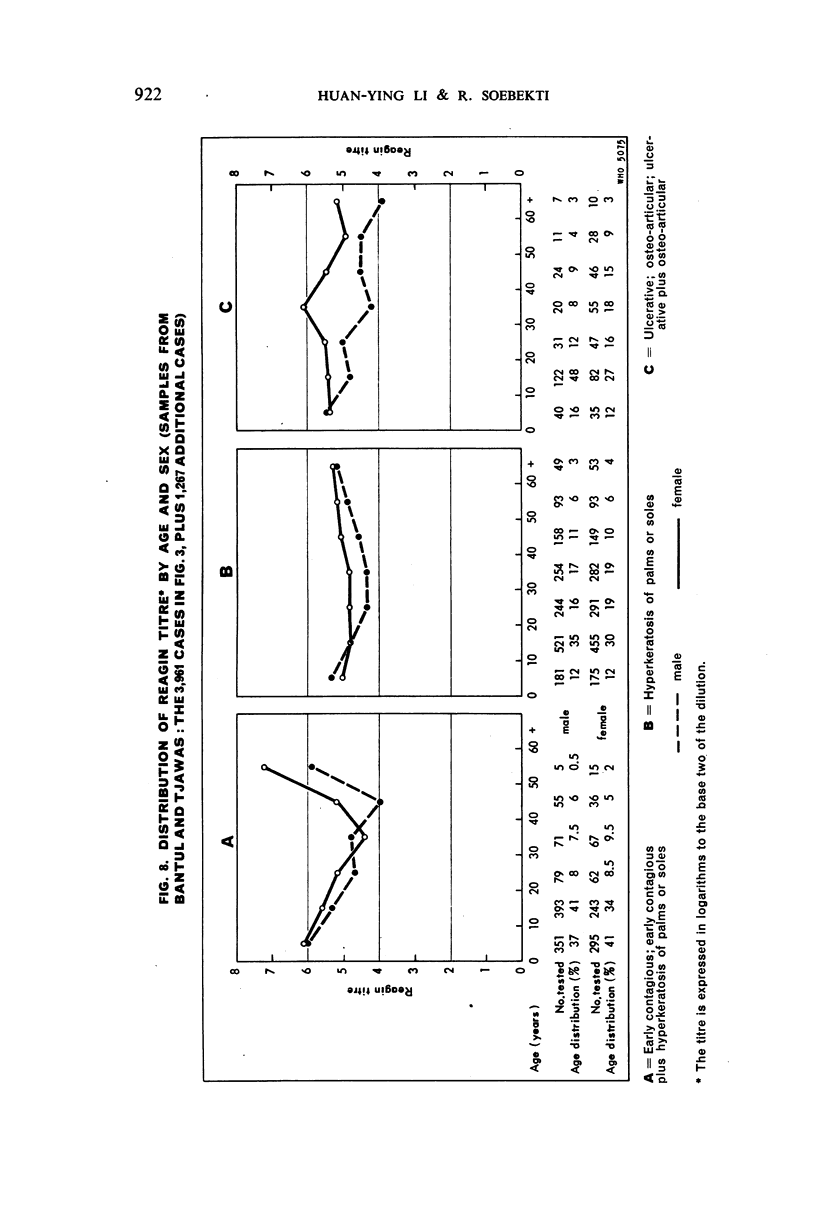
A study of the mean reagin titre in untreated yaws cases showed that the percentage of seronegative reactors among clinically positive cases was low. Less seronegativity was observed among females than males.
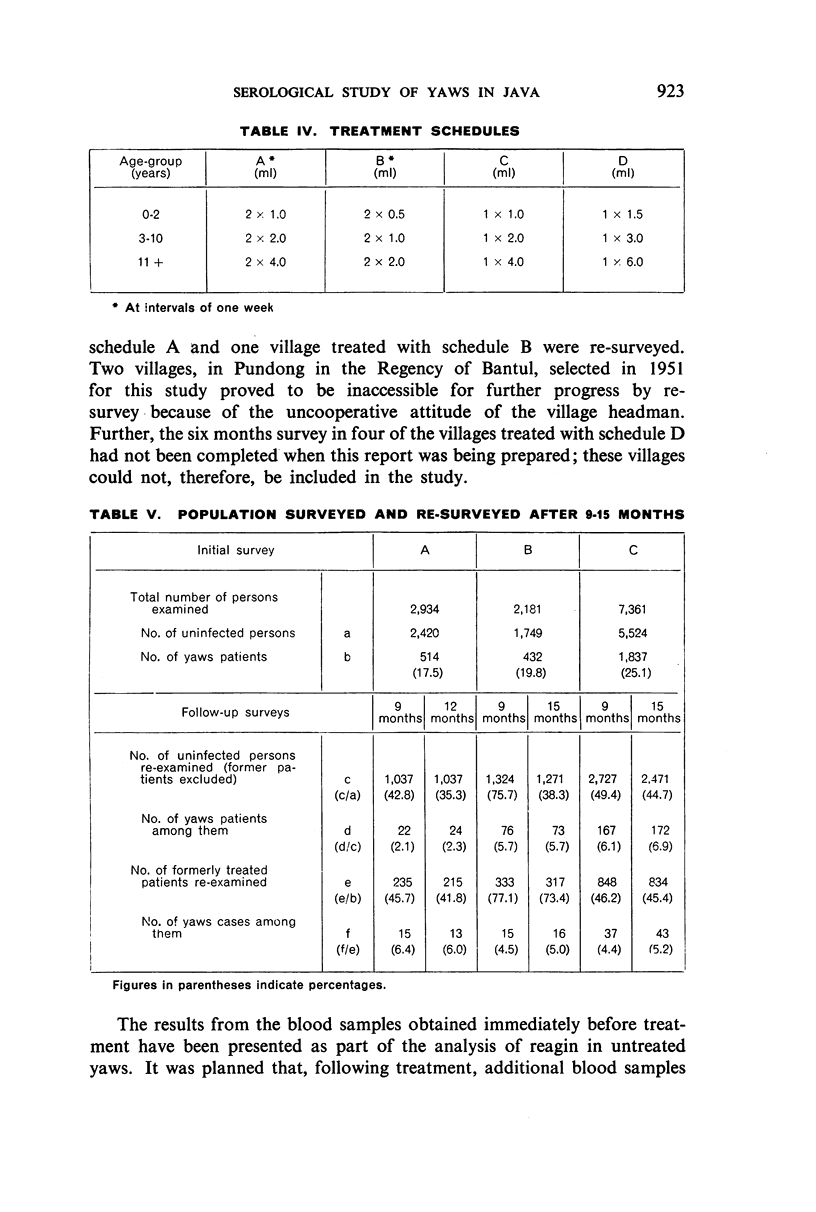
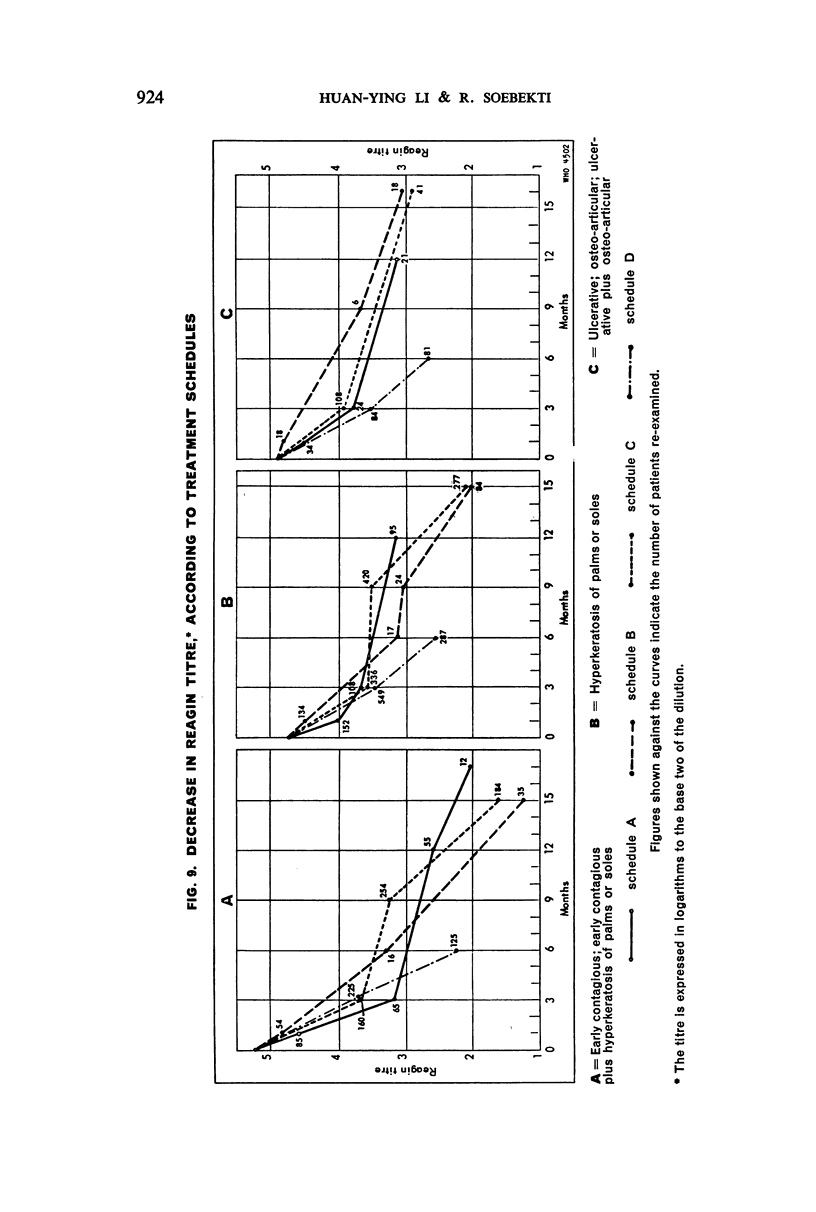
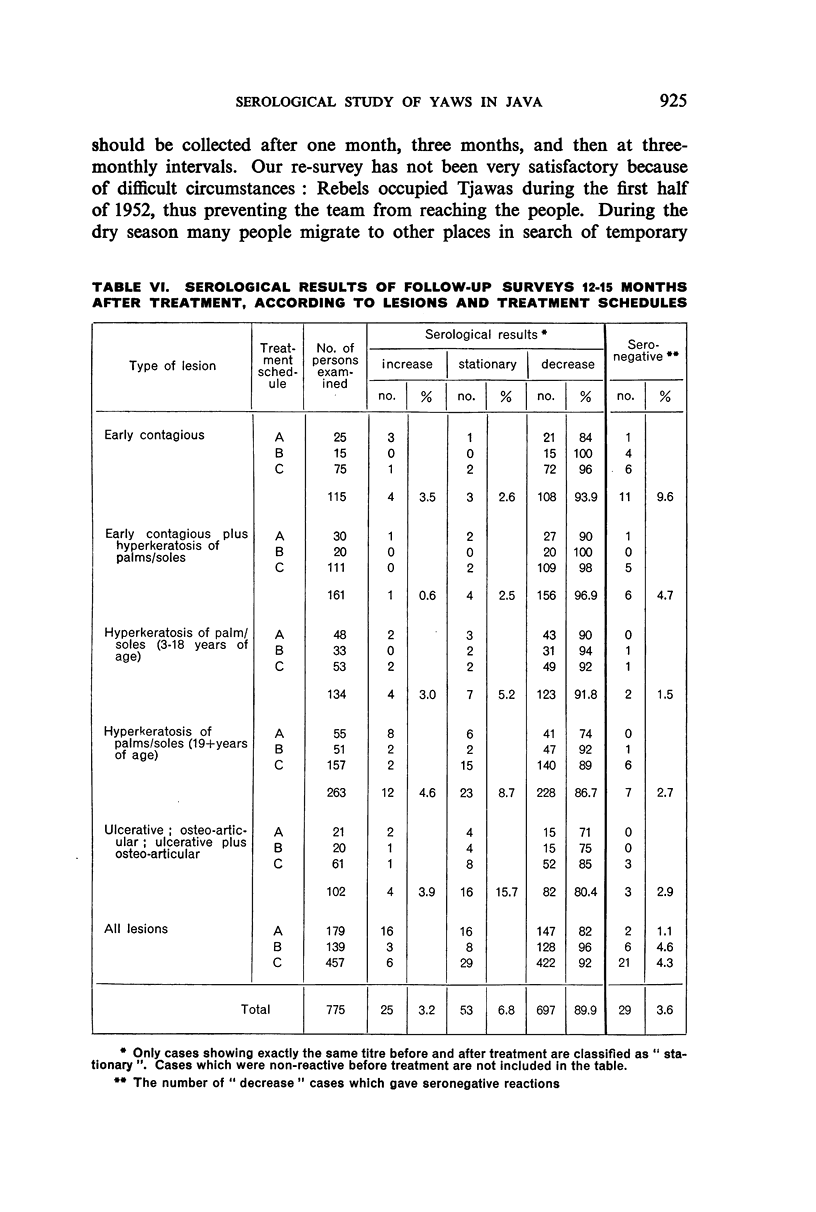
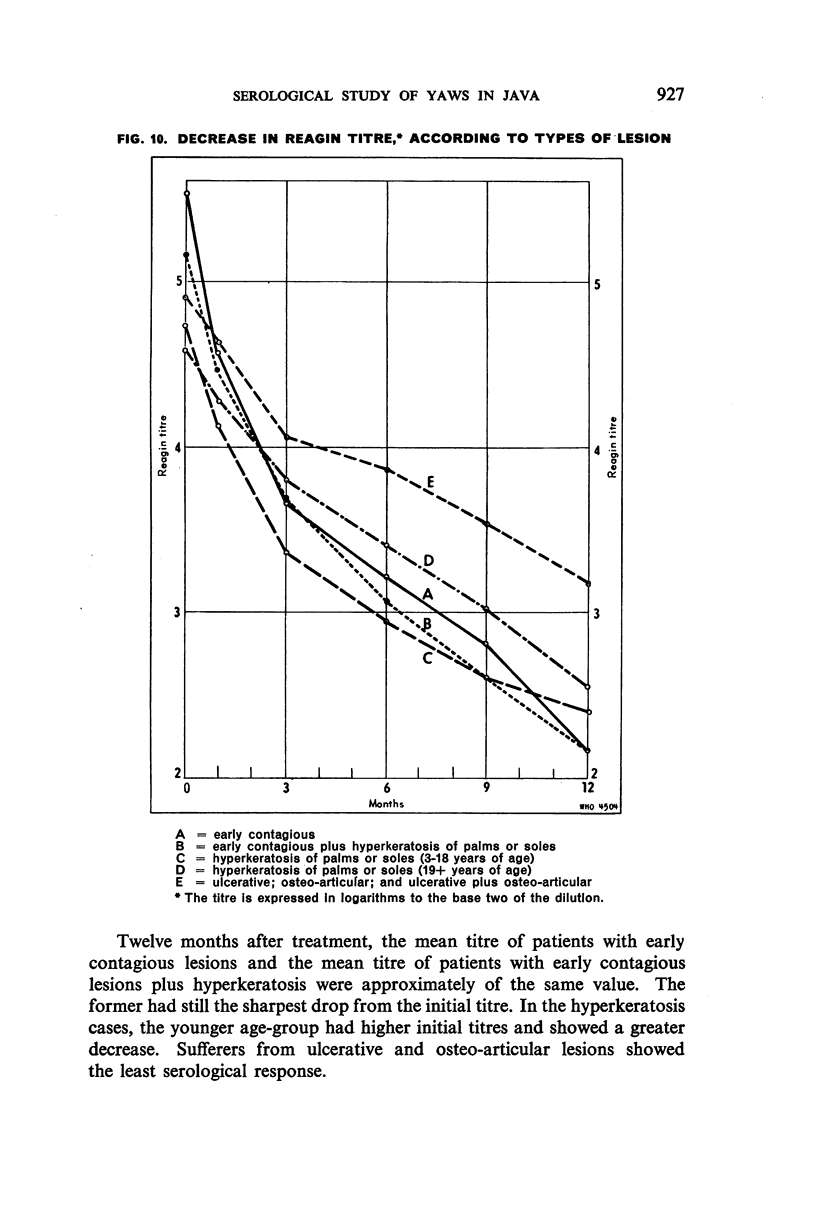
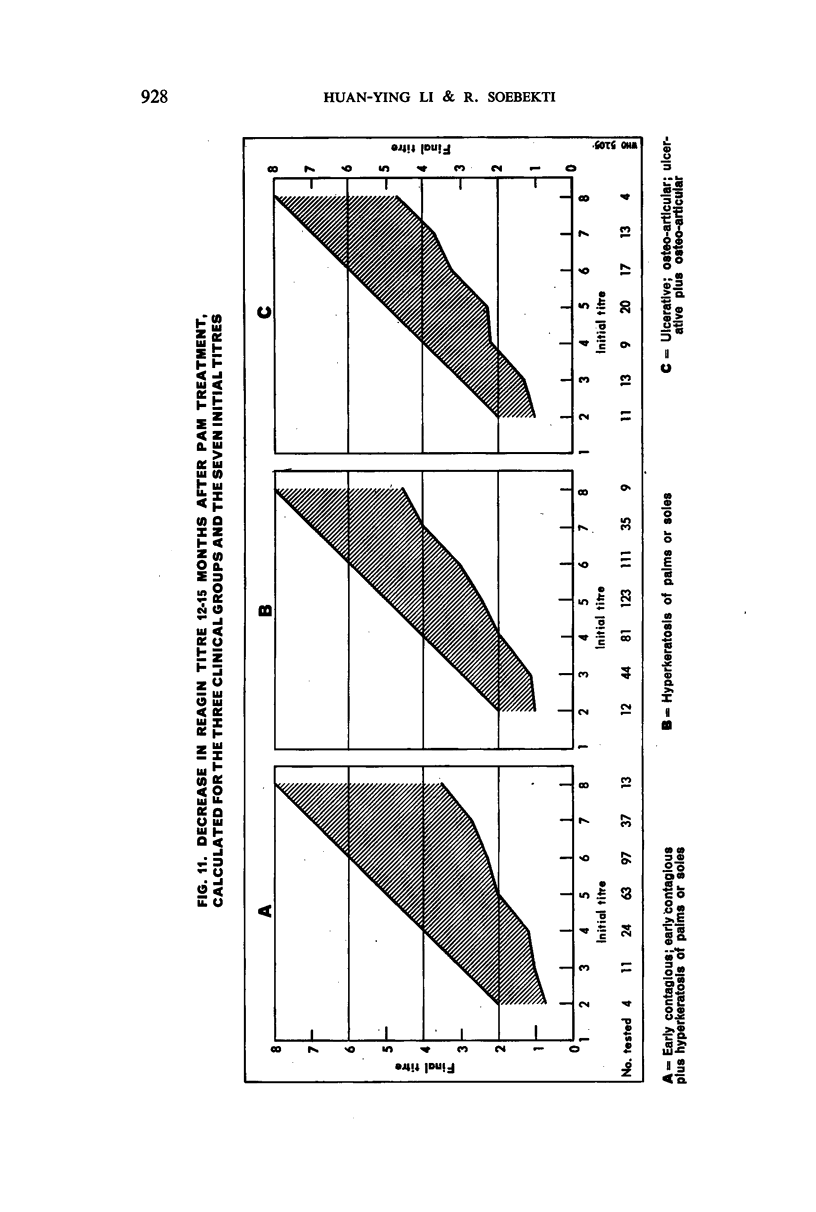
Examination of decrease in mean reagin titre after treatment by clinical group showed maximum to minimum decrease in the following sequence: early contagious, early contagious plus hyperkeratosis, ulcerative plus osteo-articular, ulcerative, hyperkeratosis, and osteo-articular lesions. The decrease tended to be greater in females than males and in patients with high than with low titre; it also varied with the age of the patient. No significant variation in decrease was noted when four different PAM treatment schedules were tested comparatively. The percentage of serological cure and improvement with all schedules was highest in the cases with early lesions, and in the younger age-groups.
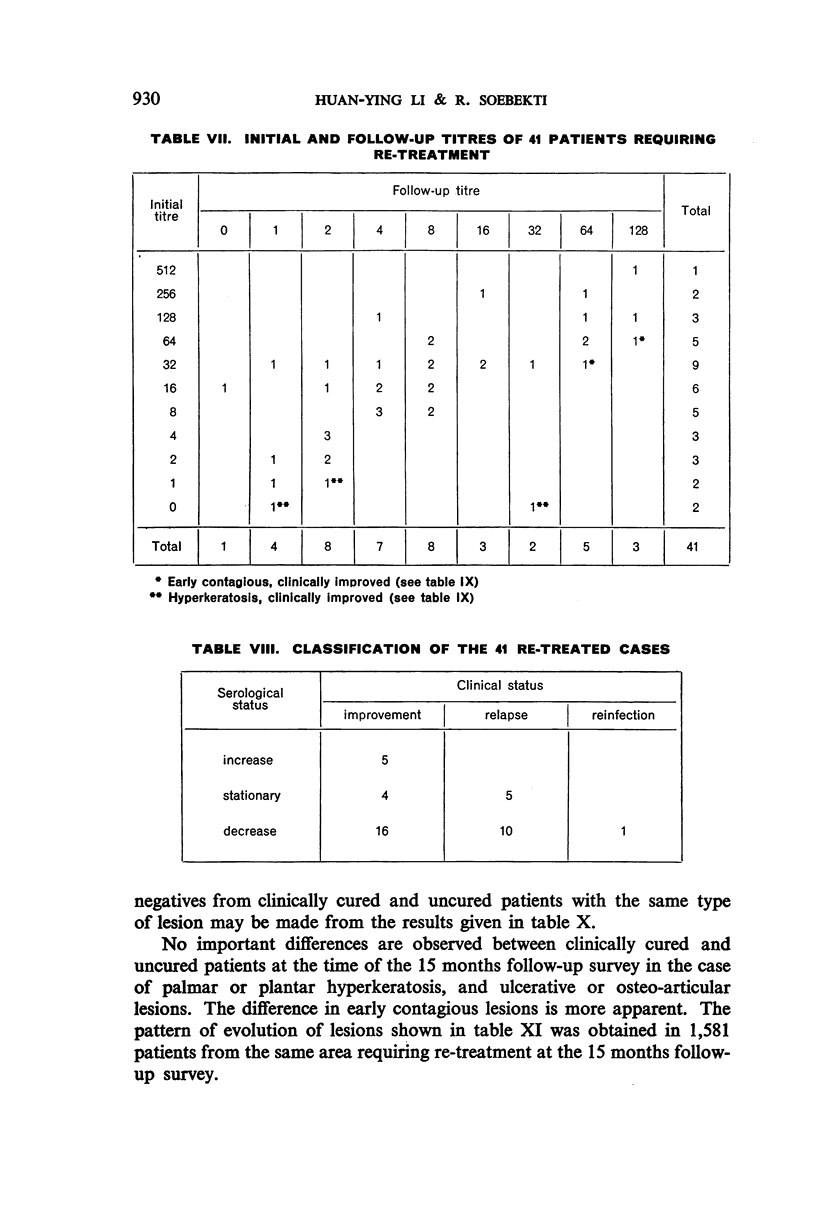
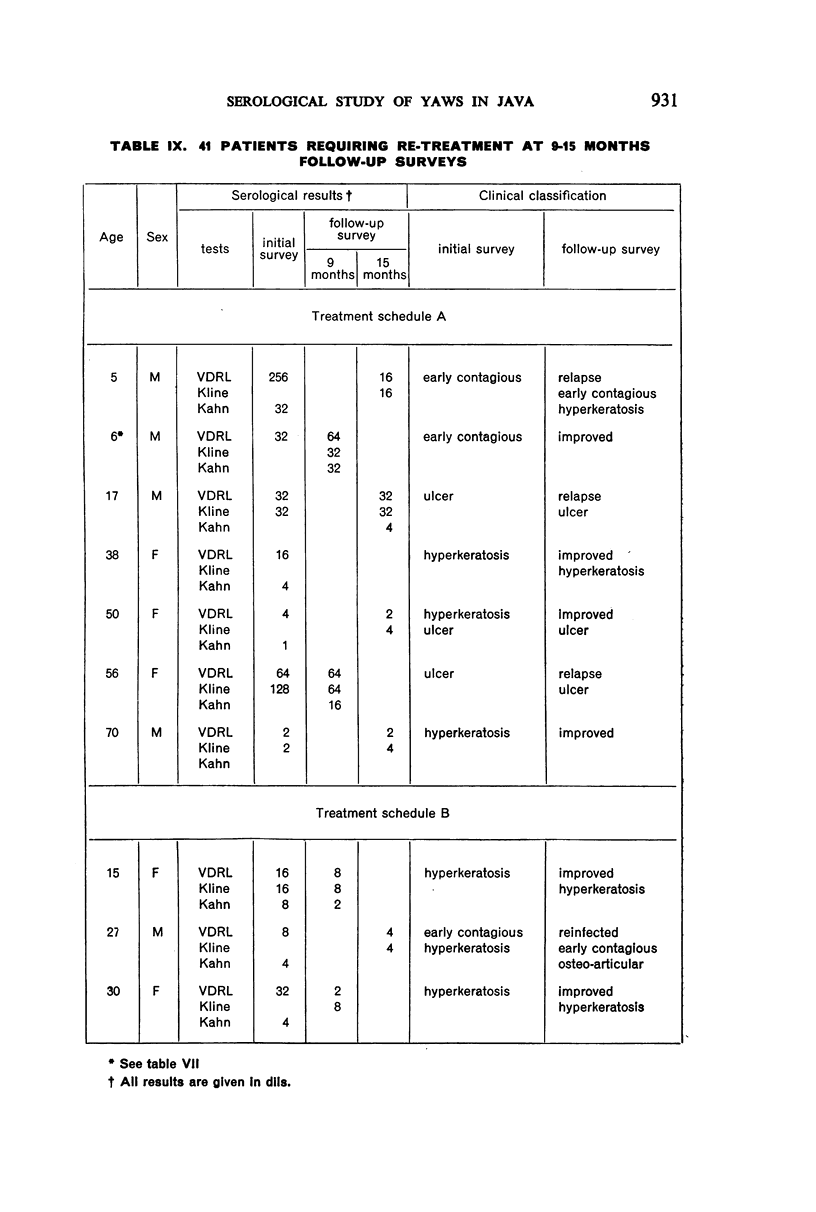
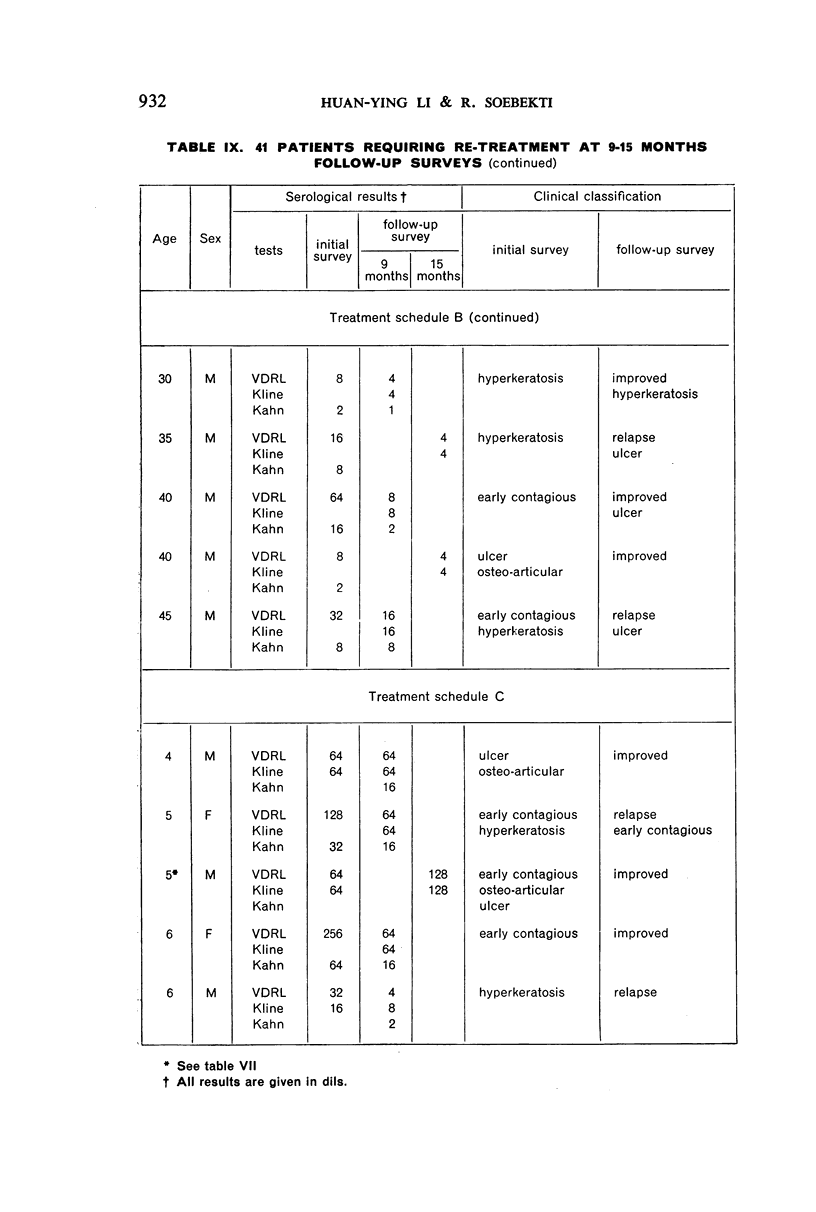
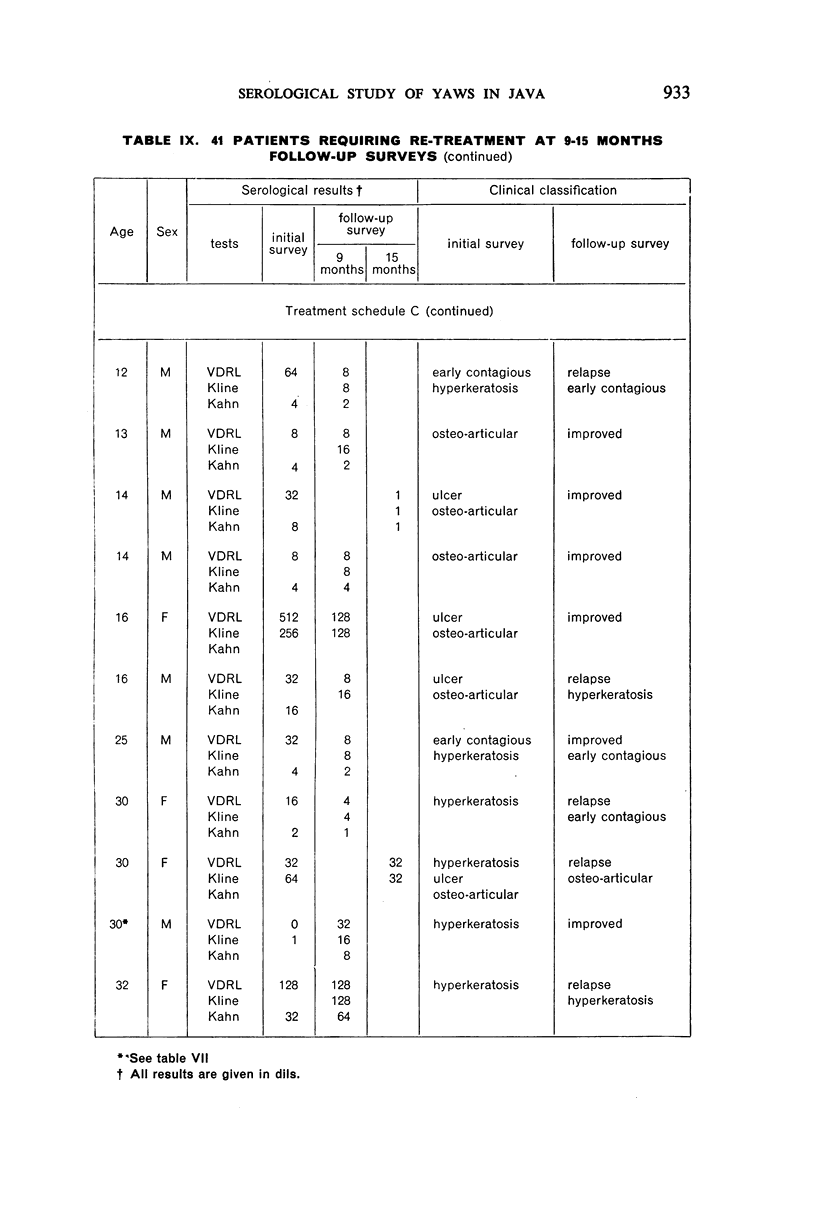
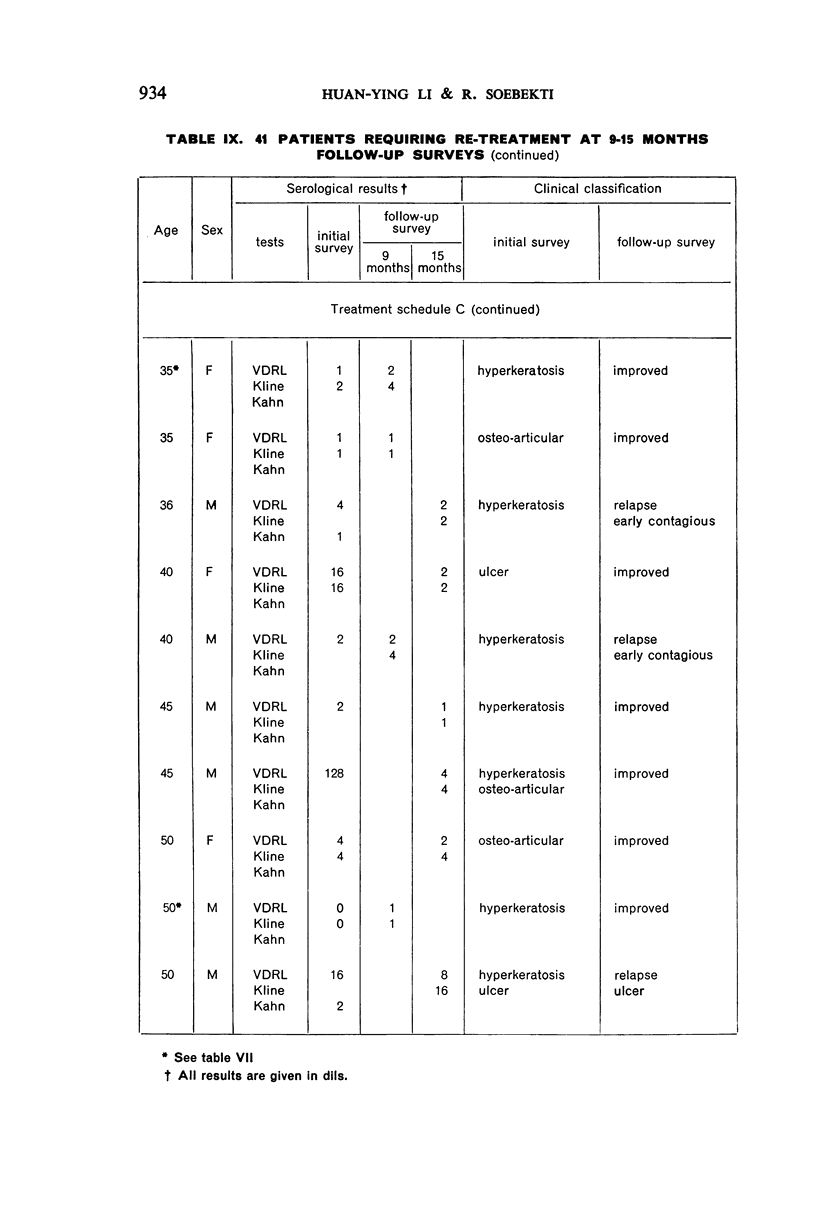
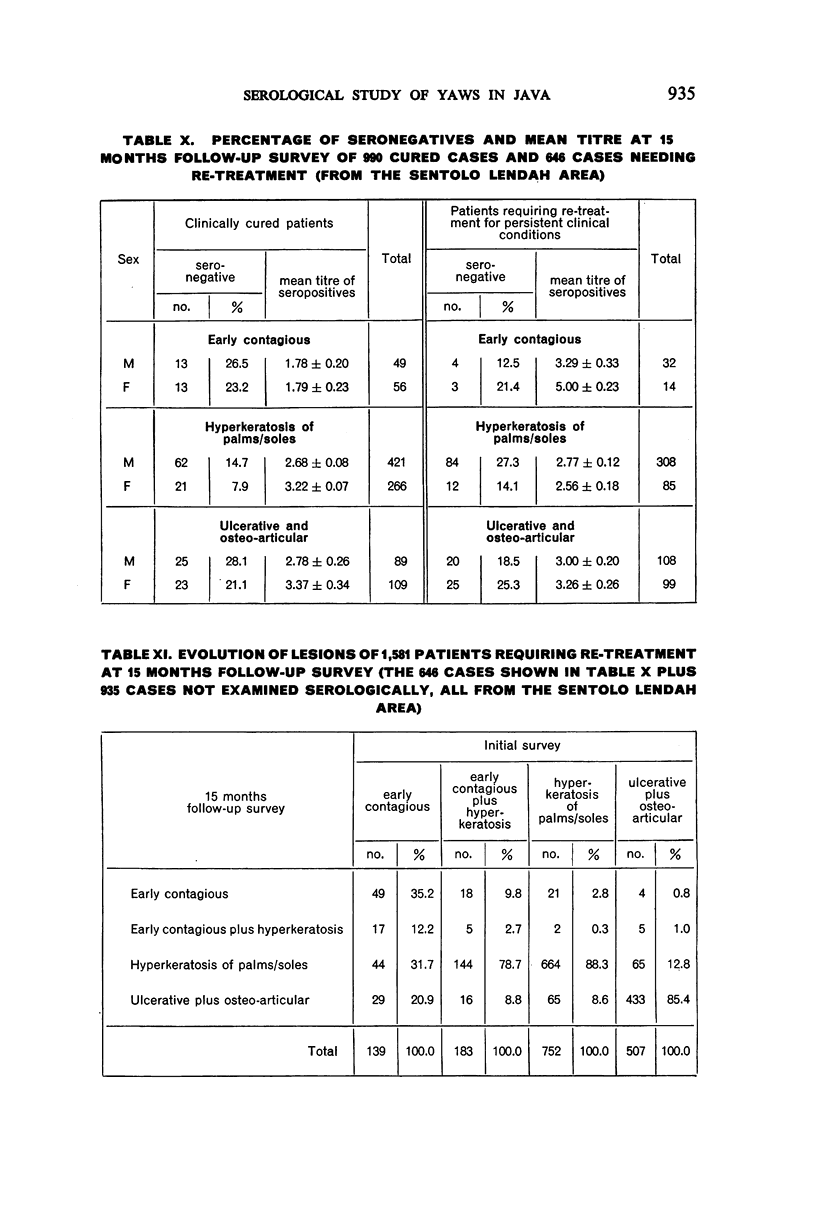
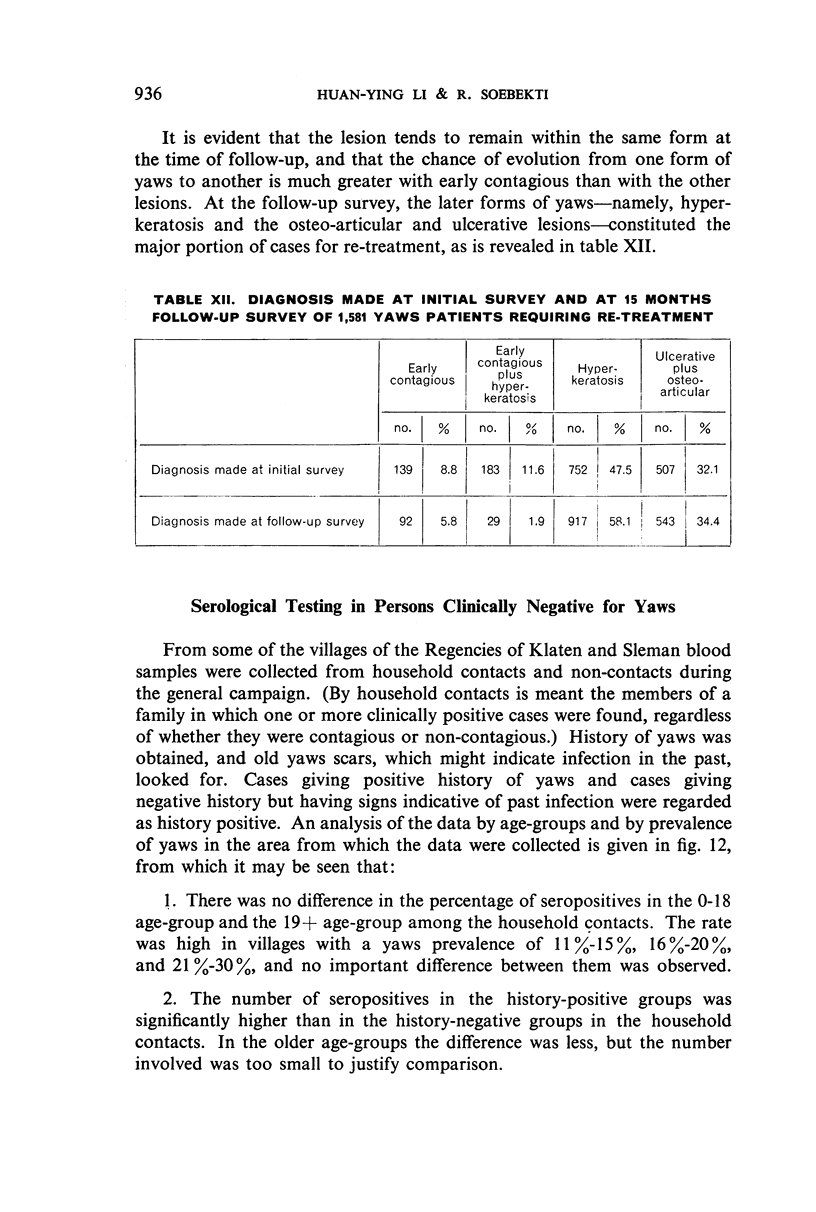
A study of patients requiring re-treatment at the time of resurvey showed no important difference in mean reagin titre between clinically cured and uncured patients suffering from palmar or plantar hyperkeratosis and ulcerative or osteo-articular lesions.
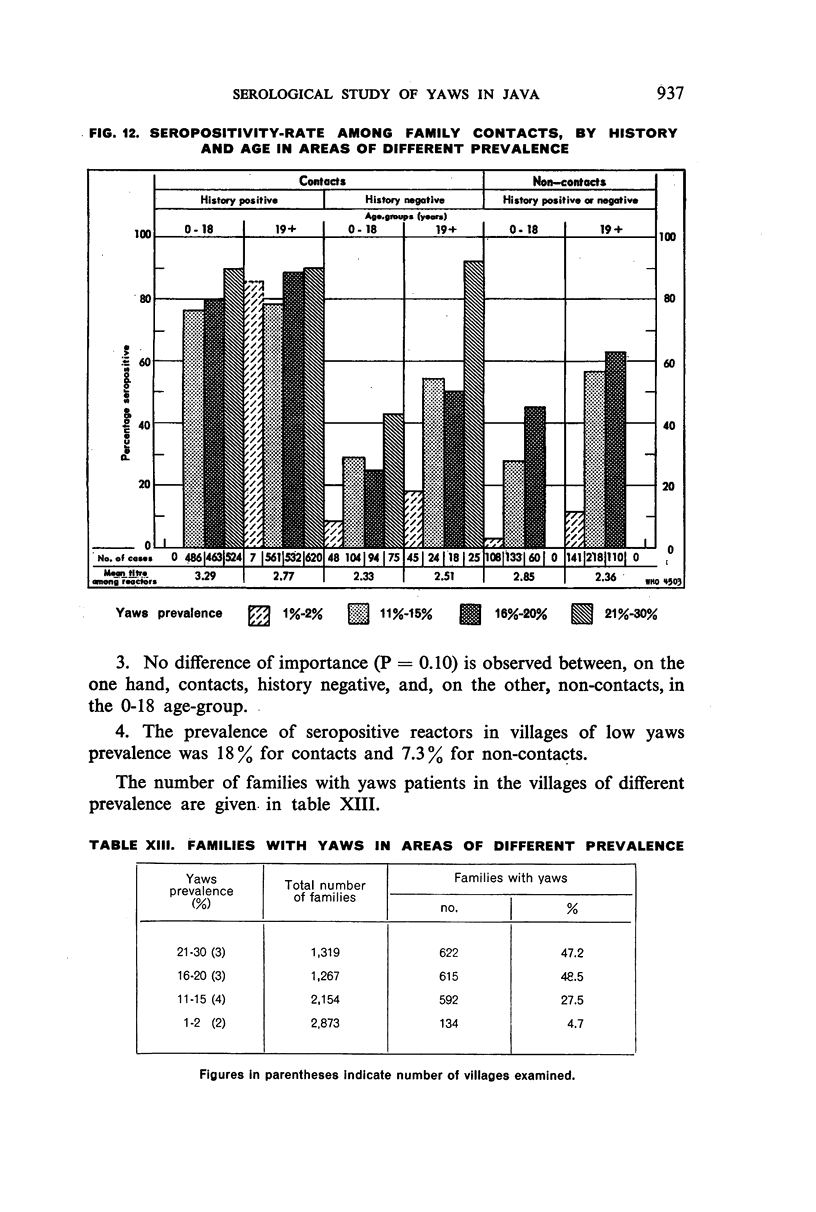
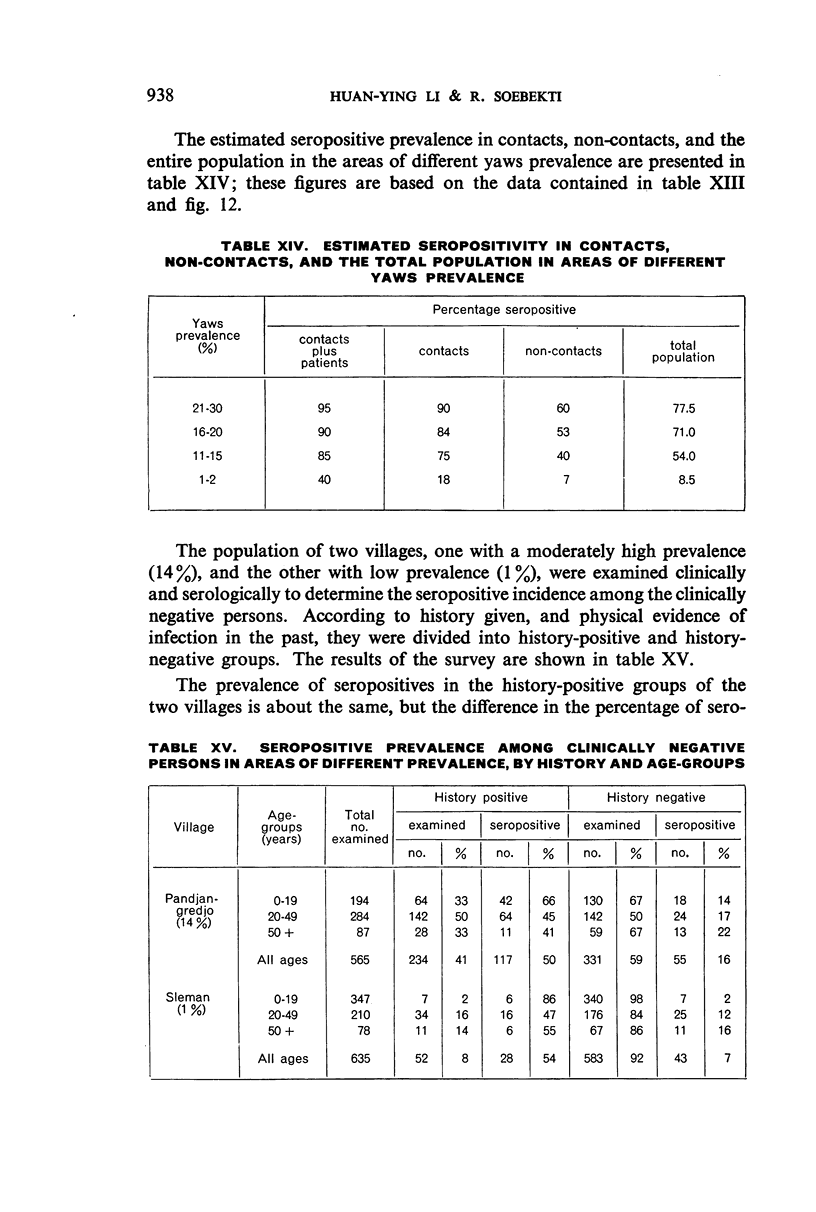
Serological testing of sera from clinically negative household contacts and non-contacts, with or without previous history of yaws, gave the following results: Among the household contacts, the number of seronegative reactors, while not affected by age-distribution, was significantly higher in the history-positive than in the history-negative groups. The percentage of seropositive reactors was in direct proportion to the prevalence of yaws, the seropositivity-rate being high in villages with a yaws incidence of 11%-30%.
The report also contains suggestions for improving the conduct of the anti-yaws campaign.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- REIN C. R., STERNBERG T. H. Penicillin therapy of yaws and serologic results. Arch Derm Syphilol. 1948 Jun;57(6):942–952. doi: 10.1001/archderm.1948.01520190021004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]