Abstract
A chemokine receptor from the seven-transmembrane-domain G-protein-coupled receptor superfamily is an essential coreceptor for the cellular entry of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) and simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) strains. To investigate nonhuman primate CC-chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5) homologue structure and function, we amplified CCR5 DNA sequences from peripheral blood cells obtained from 24 representative species and subspecies of the primate suborders Prosimii (family Lemuridae) and Anthropoidea (families Cebidae, Callitrichidae, Cercopithecidae, Hylobatidae, and Pongidae) by PCR with primers flanking the coding region of the gene. Full-length CCR5 was inserted into pCDNA3.1, and multiple clones were sequenced to permit discrimination of both alleles. Compared to the human CCR5 sequence, the CCR5 sequences of the Lemuridae, Cebidae, and Cercopithecidae shared 87, 91 to 92, and 96 to 99% amino acid sequence homology, respectively. Amino acid substitutions tended to cluster in the amino and carboxy termini, the first transmembrane domain, and the second extracellular loop, with a pattern of species-specific changes that characterized CCR5 homologues from primates within a given family. At variance with humans, all primate species examined from the suborder Anthropoidea had amino acid substitutions at positions 13 (N to D) and 129 (V to I); the former change is critical for CD4-independent binding of SIV to CCR5. Within the Cebidae, Cercopithecidae, and Pongidae (including humans), CCR5 nucleotide similarities were 95.2 to 97.4, 98.0 to 99.5, and 98.3 to 99.3%, respectively. Despite this low genetic diversity, the phylogeny of the selected primate CCR5 homologue sequences agrees with present primate systematics, apart from some intermingling of species of the Cebidae and Cercopithecidae. Constructed HOS.CD4 cell lines expressing the entire CCR5 homologue protein from each of the Anthropoidea species and subspecies were tested for their ability to support HIV-1 and SIV entry and membrane fusion. Other than that of Cercopithecus pygerythrus, all CCR5 homologues tested were able to support both SIV and HIV-1 entry. Our results suggest that the shared structure and function of primate CCR5 homologue proteins would not impede the movement of primate immunodeficiency viruses between species.
The entry of primate immunodeficiency virus into a host target cell is mediated on the cell surface through sequential interactions of viral envelope glycoproteins with CD4 (10, 25, 44) and a chemokine receptor from the seven-transmembrane-domain G-protein-coupled receptor superfamily (1, 3, 6, 7, 11, 13, 14, 19, 40). Isolates of primate immunodeficiency virus that have different biological phenotypes use different subsets of chemokine receptors as cofactors for entry. Among the seven-transmembrane-domain G-protein-coupled receptors used for virus entry, the most physiologically relevant are CXC-chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) and CC-chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5), used by laboratory-adapted strains (X4 strains) and primary isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) (R5 and R5X4 strains), respectively (1, 2, 6, 8, 9, 39, 41, 45, 47). Unlike those of HIV-1, laboratory-adapted strains of simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) do not use CXCR4 for virus entry, although CXCR4 derived from nonhuman primates is a functional coreceptor for X4 strains and some pathogenic simian-human immunodeficiency virus constructs (4, 5, 16, 32, 50, 51). Some SIV and human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (HIV-2) strains are not dependent on CD4 for virus entry and therefore can infect cells that lack CD4 but express CCR5 or CXCR4 (2, 17).
Whereas the envelope glycoproteins of the primate immunodeficiency viruses share many common features, including similar locations of cysteine residues, conserved and variable regions, and CD4 binding domains, significant differences exist, especially between SIV and HIV-1 envelope glycoproteins (29). The external envelope glycoproteins of SIV and HIV-2 have approximately 70% amino acid sequence similarity to each other, and their nucleotide sequences have less than 40% similarity to those of selected HIV-1 envelope genes (29). Nonetheless, the divergent strains of the distantly related primate lentiviruses use a chemokine receptor from the seven-transmembrane-domain G-protein-coupled receptor superfamily for virus entry, and CCR5 use is indeed almost universal (4, 28, 49). Knowledge of CCR5 use by SIV per se is restricted to receptors that were derived from humans and selected nonhuman primates, however (4, 15, 49). Therefore, we cloned and analyzed CCR5 sequences derived from 24 representative primate species and subspecies of the suborders Prosimii and Anthropoidea. Phylogenetic reconstruction of the nonhuman CCR5 homologue sequences by maximum-likelihood and neighbor-joining methods recapitulated the evolutionary relationships for these representative primate species and subspecies. Despite a number of amino acid substitutions in multiple extracellular domains of the primate CCR5 homologues, many of which were highly conserved in primates within a given species, the primate CCR5 homologues supported SIV and HIV-1 entry.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Peripheral blood cells from animals from representative species and subspecies of the primate suborders Prosimii and Anthropoidea.
We obtained peripheral blood from individual members of 24 species in 17 genera of primates: 2 prosimians (Lemur catta and Varecia variegata rubra, both in the family Lemuridae), 4 New World monkeys (Alouatta caraya and Aotus trivirgatus, both in the family Cebidae; Callithrix jacchus and Saguinus nigricollis, both in the family Callitrichidae), 13 Old World monkeys (Cercopithecus diana, C. sabaeus, C. pygerythrus, Macaca fascicularis, M. fuscata, M. mulatta, M. tonkeana, M. nemestrina, and Colobus guerza), and 5 apes [Papio cynocephalus papio and Mandrillus (Papio) sphinx, both in the family Cercopithecidae; Hylobates concolor, in the family Hylobatidae; Gorilla gorilla, Pan trogodytes, and Pongo pygmaeus, all in the family Pongidae]. In phylogenetic reconstructions, this last family includes humans. Our use of animals for research purposes complied with all relevant federal guidelines and institutional policies.
PCR amplification of nonhuman primate CCR5 homologues.
We isolated total cellular DNA by using a Puregene DNA isolation kit (Gentra Systems, Minneapolis, Minn.). DNA pellets were resuspended in water, the nucleic acid content was quantified, and the DNA was used directly for in vitro amplification. To amplify a functional CCR5 gene from each species, we designed primers based on the conserved 5′ (CCR5A; 5′-GGAGGGCAACTAAATACATTCTAGG-3′) and 3′ (CCR5B; 5′-GACTGGTCACCAGCCCACTTGAGTCC-3′) untranslated regions that flank the entire human CCR5 gene (GenBank accession number U57840). We were not able to amplify the entire CCR5 gene from cells obtained from primates of the families Lorisidae, Tarsiidae, and Lemuridae, a finding that suggests a nucleotide sequence mismatch within a region that flanks the gene. We were able to amplify the CCR5 DNA of the family Lorisidae by using PCR with oligonucleotide primer pairs located within the CCR5 5′ (ATGGATTATCAAGTGTCAAG) and 3′ (TCACAAGCCCACAGATATTT) sequences. Five hundred nanograms of input cell DNA was used in each reaction. PCR was performed as described previously (27) with a Perkin-Elmer Cetus 9600 automated thermal cycler programmed for 5 cycles at 98°C for 10 s, 55°C for 30 s, and 72°C for 45 s and then for 35 cycles at 98°C for 10 s, 60°C for 30 s, and 72°C for 45 s. Reagent controls were run in parallel. PCR product DNAs were resolved on a 1.0% agarose gel by electrophoresis. The appropriately sized band was excised, and the DNA was extracted by using the QIAquick gel extraction method (Qiagen, Valencia, Calif.). Purified PCR product DNA was inserted into vector pCR2.1 by the TA cloning method. All polynucleotide extractions and amplification reactions were done with appropriate negative controls to detect contamination at each step of the procedure.
DNA sequencing.
For each species, we obtained CCR5 sequences from at least one representative animal. Six clones containing the appropriately sized CCR5 homologue insert were randomly selected from each animal to ensure a 97% probability of analyzing both alleles [1 − 2(1 −n), where n is the number of independent clones]. The PCR product DNA inserts were sequenced in both directions by using ABI dye-terminator chemistry. Extension reactions were resolved on an ABI 377 automated sequencer, and the resulting chromatograms were assembled by using AutoAssembler (Applied BioSystems, Foster City, Calif.). Stop codons were found in two of the clones sequenced: 1 of 12 clones from two C. jacchus animals and 1 of 18 clones from six M. mulatta animals. Because these stop codons were not found in other clones, they likely represent PCR-associated errors. There were no frameshift mutations, in-frame insertions, or deletions in any of the clones sequenced. A consensus sequence was computed for each animal and was used in all DNA sequence analyses. We numbered the CCR5 homologue sequences according to the human CCR5 sequence under GenBank accession number U57840.
Phylogenetic sequence analysis of primate CCR5 homologue sequences.
Comparisons were based on various breakdowns of the available PCR product DNA sequence data. Both DNA and protein alignments were hand edited by using a multiple-alignment sequence editor (18). Analysis of the number of synonymous mutations per potential synonymous site and of the number of nonsynonymous mutations per potential nonsynonymous site was performed by using the formula of Nei and Gojobori (34). Because the CCR5 nucleotide sequences of primates in the same species proved to be very similar or identical to each other, we selected one representative CCR5 sequence for analysis. We were not able to amplify the full-length CCR5 homologue sequence from primates of the taxonomic suborder Prosimii; we therefore used the 1,019 nucleotides that we could evaluate for all nonhuman primates for all phylogenetic analyses.
The CCR5 sequence alignments were subjected to three different tree-building methods: maximum parsimony, neighbor joining (a distance method), and maximum likelihood. These methods were implemented with the computer programs PAUP, version 3.1.1 (48); neighbor in PHYLIP, version 3.5c (48); and RevDNArates, a modification of DNArates code that incorporates a general reversible base substitution model, and RevDNAml, a modification of fastDNAml code that also incorporates a reversible model for rapid implementation of PHYLIP maximum-likelihood code (26, 35). We used the exhaustive branch-and-bound search method to find all possible shortest trees under parsimony. We compared 57 models of nucleotide substitution for neighbor-joining distance by using hierarchical likelihood ratio tests (22, 23). Of these 57 models, 56 are implemented in Modeltest, version 3.06 (37). The general time-reversible model with site-specific rates is implemented in PAUP, RevDNAml, and RevDNArates; in Modeltest, it is computed by hand. We tested all 57 models by using a single neighbor-joining tree based on the assumptions and methods implemented in Modeltest. This strategy includes the Jukes-Cantor model (equal base frequencies, equal rates of substitution), minimum evolution, no invariant sites, negative branch lengths set to zero, and random breaking of ties. We used RevDNArates to optimize parameters for the model with the general time-reversible model with site-specific rates that include base frequencies, substitution rates, and four site-specific categories of rates. After determining the best model, we used RevDNAml to search for the best tree. For the final tree, we used PAUP with 500 neighbor-joining search replicates to compute bootstrap percentages for each branch.
Expression vector constructs.
We selected a representative CCR5 homologue insert from each species to transfer into mammalian expression vector pCDNA3.1. Briefly, clone pCR2.1 was digested with the appropriate flanking restriction enzymes to remove the CCR5 insert. The insert was inserted into pCDNA3.1 and then sequenced in its entirety to ensure that no mutations had been introduced in the cloning process. We performed in vitro transcription-translation reactions (Promega, Madison, Wis.) by using the subcloned genes to ensure that a protein product of the approximately correct molecular weight could be made from each clone. Translatable clones were used to assess the role of primate CCR5 genes as cofactors for virus entry. Luciferase reporter viruses were prepared by cotransfecting 293T cells with pNL-Luc-Env or pSIV-Luc-R-E and vectors expressing different SIV or HIV-1 envelopes as described previously (11, 14).
Primary SIV strains.
Primary SIV strains (SIVsmSL92b and SIVsmFNJ) were isolated from cells obtained from two sooty mangabeys by cocultivation with uninfected cells from the native host species as described previously (4).
Virus entry assay.
HOS.CD4 cells were transiently transfected with pcDNA3.1-CCR5 constructs containing the CCR5 homologues of the various primate species by using a CellPhect kit (Pharmacia Biotech). To test for virus entry, cells (2 × 104 per well) in culture medium (Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium containing 10% fetal calf serum and 1.0 μg of puromycin/ml) were seeded in 24-well plates 24 h posttransfection. After an additional 24 h of culturing, cells were infected with luciferase reporter viruses (40 ng of p24 or p27) in a total of 300 μl of culture medium containing 1 ng of Polybrene/ml. The medium from the reporter virus-infected cells was replaced with fresh medium (1 ml per well) after overnight incubation. After an additional 3 days of culturing, we prepared 100 μl of cell lysate and measured the luciferase activity in 20 μl by using commercial reagents (Promega).
Cell-cell fusion assay.
The cell-cell fusion assay has been described in detail elsewhere (41). Briefly, effector QT6 cells were infected with vaccinia virus expressing T7 polymerase (vTF1.1) and then transfected with plasmid pcDNA3.1 containing the designated envelope gene via the calcium phosphate transfection method. Target QT6 quail cells were transfected with plasmids expressing CD4, coreceptor, and T7 luciferase. At 24 h after infection or transfection, effector cells were added to target cells, and fusion was quantified 8 h after mixing by lysing cells with 0.5% Triton X-100. An aliquot of the lysate was mixed with an equal volume of luciferase assay reagent (Promega), and luminescence was read in a Luminometer (42).
Nucleotide sequence accession numbers.
After rigorous quality control testing (30), the 169 human and nonhuman CCR5 homologue sequences were submitted to GenBank under accession numbers AF161887 to AF162055.
RESULTS
Phylogenetic analysis of primate CCR5 sequences.
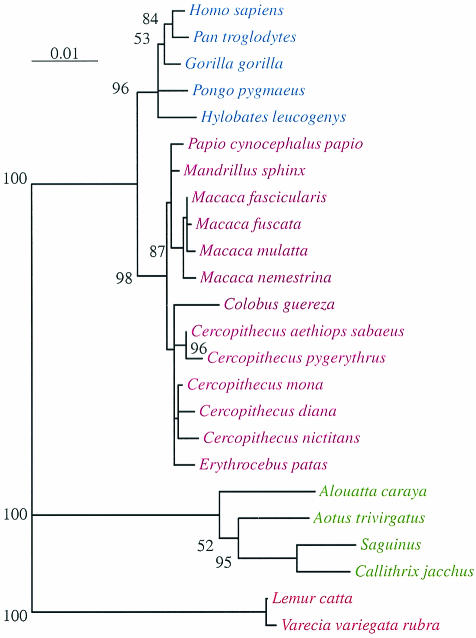
Figure 1 shows a representative phylogenetic tree for the primate CCR5 homologues created by using the maximum-likelihood method with the F84 model and 10 jumble replicates. One representative nucleotide sequence for each primate species (Table 1) was used to generate the maximum-likelihood tree. The only difference between the phylogenetic reconstructions created by using the maximum-likelihood and neighbor-joining methods was the location of C. guerza, which was located basal to the C. aethiops cluster in the maximum-likelihood tree but basal to all cercopithecines in the neighbor-joining tree (data not shown). Since bootstrapping a maximum-likelihood tree with 25 taxa was not computationally feasible, we bootstrapped the equivalent neighbor-joining tree, which yielded approximately the same branching order, 500 times. Values greater than or equal to 50% are shown on the maximum-likelihood tree. Despite the inherent limitations of this approach, it does provide some indication of the stability of the tree. The full sequence alignment has 31 taxa and 1,019 nucleotide sites in the CCR5 homologues from all nonhuman primates that we could evaluate with no missing data, gaps, or ambiguous nucleotides. Of the 1,019 sites, 776 are constant and (under parsimony) 81 are uninformative and 162 are informative. For this alignment, there are 588 shortest parsimony trees, each 330 steps long (data available on request). The large number of shortest trees reflects poor resolution in a few parts of the tree, primarily within species and between closely related species. This result is to be expected. Of the 57 models of nucleotide substitutions that we tested, 8 models include a parameter to estimate the transition/transversion ratio, which ranged from 3.7 to 4.2.
FIG. 1.
Phylogenetic reconstruction of human and nonhuman primate CCR5 homologue sequences by using the neighbor-joining algorithm. We used one representative CCR5 sequence per species (Table 1). The numbers are bootstrap values (percentages); each value refers to the branch to its right or left. Branches with no bootstrap values had either a bootstrap value not greater than 50% (rare) or a branch length near or equal to zero (common). Apes are highlighted in blue, Old World monkeys are highlighted in magenta, New World monkeys are highlighted in green, and prosimians are highlighted in red.
TABLE 1.
List of species (or subspecies which taxonomists may treat as species) studied
| Zoological name | Common name | na | GenBank accession no.
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shownb | Not shown | |||
| Homo sapiens | Human | 13 | AF161909 | AF161910-AF161921 |
| Pan troglodytes | Chimpanzee | 8 | AF161898 | AF161899-AF161905 |
| Gorilla gorilla | Gorilla | 7 | AF161891 | AF161892-AF161897 |
| Pongo pygmaeus | Orangutan | 3 | AF161907 | AF161906, AF161908 |
| Hylobates concolor | Crested gibbon | 5 | AF161889 | AF161887, AF161888, AF161890, AF162024 |
| Papio cynocephalus papio | Yellow baboon | 11 | AF161988 | AF161987, AF161989-AF161997 |
| Mandrillus sphinx | Mandrill | 3 | AF161998 | AF161999, AF162032 |
| Macaca fascicularis | Crab-eating macaque | 5 | AF161950 | AF161951-AF161954 |
| Macaca fuscata | Japanese macaque | 3 | AF161957 | AF161955, AF161956 |
| Macaca mulatta | Thesus macaque | 18 | AF161959 | AF161958, AF161960-AF161975 |
| Macaca nemestrina | Pigtailed macaque | 11 | AF161982 | AF161976-AF161981, AF161983-AF161986 |
| Colobus guereza | Guereza | 6 | AF162000 | AF162001-AF162005 |
| Cercopithecus diana | Diana monkey | 2 | AF161949 | AF161948 |
| Cercopithecus aethiops sabaeus | Sabaeus monkey, grivet monkey | 12 | AF162018 | AF162006, AF162007, AF162016, AF162017, AF162019, AF162022, AF162023, AF162027, AF162029-AF162031 |
| Cercopithecus pygerythrus | Green monkey | 3 | AF162020 | AF162025, AF162026 |
| Cercopithecus mona | Mona monkey | 5 | AF162037 | AF162038-AF162041 |
| Cercopithecus nictitans | Greater white-nosed monkey | 6 | AF162042 | AF162043-AF162047 |
| Erythrocebus patas | Patas monkey | 12 | AF162033 | AF162034-AF162036, AF162048-AF162055 |
| Alouatta caraya | Black howler monkey | 2 | AF161945 | AF162028 |
| Aotus trivirgatus | Owl monkey, night monkey | 2 | AF161946 | AF161947 |
| Saguinus sp. | Tamarin | 13 | AF161926 | AF161922-AF161925, AF161927-AF161933, AF162015 |
| Callithrix jacchus | Common marmoset | 12 | AF161934 | AF161935-AF161944, AF162021 |
| Lemur catta | Ring-tailed lemur | 4 | AF162008 | AF162010-AF162012 |
| Varecia variegata rubra | Red-ruffed lemur | 3 | AF162009 | AF162013, AF162014 |
Number of sequences reported for each species out of a total of 169 sequences; each sequence is the consensus sequence from six sequenced clones obtained from a single animal.
Shown in alignments and trees.
Deduced amino acid sequences of primate CCR5 homologues.
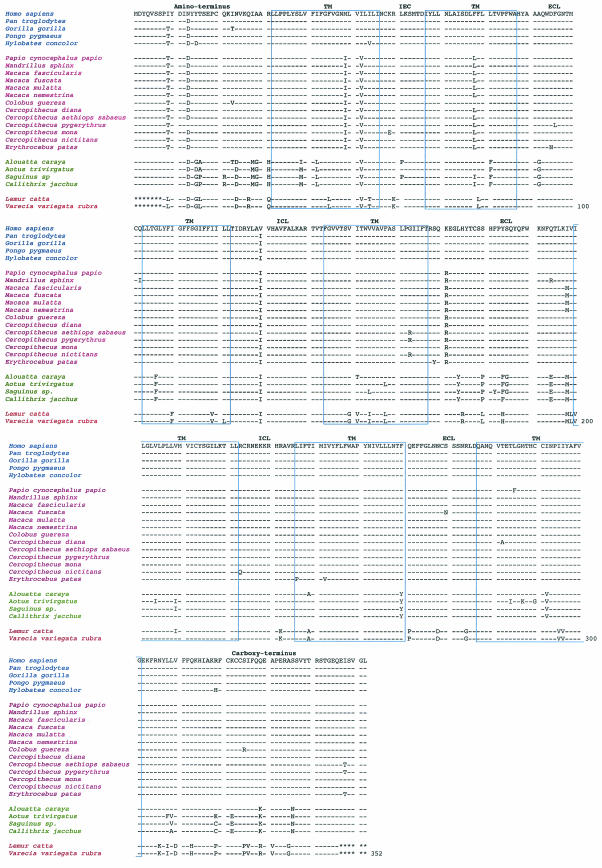
Figure 2 shows the alignments of the deduced amino acid sequences of the CCR5 homologues from the nonhuman and human primate species. We observed length conservation of the predicted CCR5 protein sequences for all primates of the suborder Anthropoidea, each of which was 353 amino acids long. Because we able to amplify the CCR5 DNA of members of the family Lorisidae by using PCR with oligonucleotide primer pairs for the CCR5 coding region, the peptide sequences of the CCR5 homologues of L. catta and V. variegata rubra were 339 amino acids long. Nevertheless, among all the primate species and subspecies of the taxonomic suborders Prosimii and Anthropoidea, the 12 cysteine residues in CCR5 were highly conserved.
FIG. 2.
Alignment of deduced human and nonhuman primate CCR5 homologue amino acid sequences. Directly below the human CCR5 consensus sequence are the nonhuman primate CCR5 homologue sequences for apes (P. troglodytes, G. gorilla, P. pygmaeus, and H. concolor), Old World monkeys (P. cynocephalus papio, M. sphinx, M. fascicularis, M. fuscata, M. mulatta, M. nemestrina, C. guereza, C. diana, C. aethiops sabaeus, C. pygerythrus, C. mona, C. nictitans, and E. patas), New World monkeys (A. caraya, A. trivirgatus, Saguinus sp., and C. jacchus), and prosimians (L. catta and V. variegata rubra). Each nonhuman primate CCR5 homologue sequence is the consensus sequence of six clones obtained from each animal to ensure a 97% probability that both alleles were represented. Amino acids in the alignment that share similarity with the human CCR5 consensus sequence shown at the top are indicated by a dash. The truncated 5′ and 3′ ends of the prosimian CCR5 homologues are indicated by asterisks. The amino acid alignment is annotated for the amino terminus, extracellular loops (ECL), intracellular loops (ICL), transmembrane regions (TM), and carboxy terminus. Apes are highlighted in blue, Old World monkeys are highlighted in magenta, New World monkeys are highlighted in green, and prosimians are highlighted in red.
Among the diverse species and subspecies, greater amino acid differences were found for primates of the suborder Prosimii, family Lorisidae, than for primates of the suborder Anthropoidea, families Callitrichidae, Cebidae, Cercopithecidae, Hylobatidae, and Pongidae (Fig. 2). We found that amino acid substitutions in specific positions were highly conserved among the different primate species and subspecies of the taxonomic suborders Prosimii and Anthropoidea compared with the hominid CCR5 consensus sequence. While amino acid substitutions in positions 13 (N to D) and 129 (V to I) were conserved among all nonhuman primate species and subspecies, greater differences were found among the evolutionarily more divergent species. In particular, greater amino acid differences were found for CCR5 homologues from primates of the suborder Prosimii, families Lorisidae, Tarsiidae, and Lemuridae, than for those from primates of the suborder Anthropoidea, families Callitrichidae, Cebidae, Cercopithecidae, Hylobatidae, and Pongidae. Because of the distant relationship between prosimians and New World and Old World monkeys, we anticipated this result.
Among the species of the superfamily Hominoidea, we found an additional amino acid substitution at position 9 (I to T) for H. leucogenys, G. gorilla, and P. pygmaeus but not for P. trogodytes. Among the species of the superfamily Cercopithecoidea, we commonly found amino acid substitutions in the amino terminus (position 9 [I to T]), the first intracellular loop (positions 58 [M to I] and 61 [I to V]), the second transmembrane domain (position 78 [F to L]), and the second extracellular loop (position 171 [K to R]). We found an additional conserved substitution in the second extracellular loop (position 198 [I to M]) for M. facicularis, M. fuscata, M. mulatta, M. tonkeana, and M. nemestrina. Among the species of the superfamily Ceboidea, we found amino acid substitutions in the amino terminus (positions 15 [Y to G], 16 [T to A and T to P], 24 [N to D], 27 [I to M], 28 [A to G], and 30 [R to H]), the first transmembrane domain (positions 38 [L to M and L to I] and 40 [I to L]), the first intracellular loop (position 61 [I to V]), and the second transmembrane domain (position 81 [L to F]). Additional amino acid substitutions were found in the first extracellular loop (position 92 [A to G]), the third transmembrane domain (position103 [L to F]), the second extracellular loop (positions 174 [L to Y], 180 [S to P], 184 [Y to F], 194 [Q to E], and 198 [I to M]), the sixth transmembrane domain (position 260 [F to Y]), the seventh transmembrane domain (position 292 [I to V]), and the carboxy terminus (positions 329 [E to K] and 335 [S to N]). Last, among the species of the suborder Prosimii, from which we were able to obtain representative clones of the CCR5 homologue with species-specific amino and carboxy termini, we found additional amino acid substitutions in positions throughout the molecule. The limited number of species of the suborder Prosimii precludes a formal analysis of deduced amino acid sequence conservation. Nevertheless, analysis of the number of synonymous mutations per site and the number of nonsynonymous mutations per site (24) suggests that the nonhuman CCR5 homologues underwent purifying selection, as witnessed by the high ratio of nonsynonymous to synonymous substitutions per site (average over all species, 6.62), especially in the carboxy-terminal third of the protein, the region beyond codon 200.
Diverse primate CCR5 homologues support membrane fusion by virus strains.
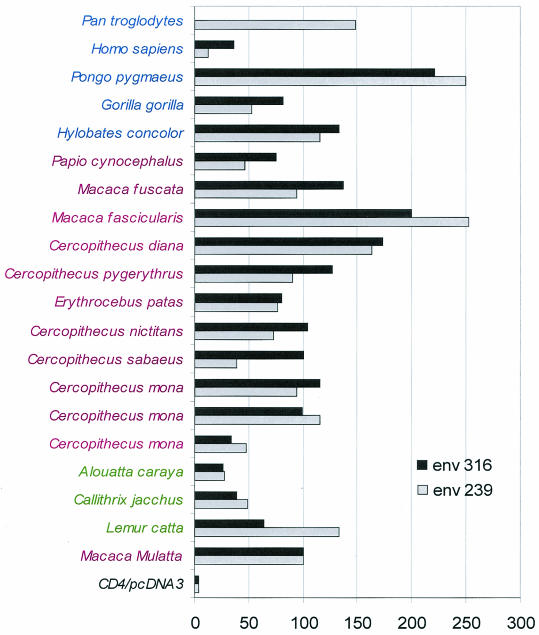
To determine whether the diverse primate CCR5 homologues function as coreceptors for SIV, we tested the recombinant proteins in a cell-cell fusion assay by using SIVmac Env 239.2 and SIVmac Env 316. No fusion was observed when Env-negative cells were used. Figure 3 shows that expression of the diverse nonhuman primate CCR5 homologues in QT6 cells along with human CD4 allowed fusion with QT6 effector cells expressing either of the two different envelope proteins.
FIG. 3.
Human and nonhuman primate CCR5 homologue proteins support membrane fusion. QT6 cells expressing the SIVmac Env 239.2 and SIVmac Env 316 proteins and T7 polymerase were mixed with QT6 cells expressing CD4, luciferase under the control of the T7 promoter, and the different primate CCR5 homologues. Cell-cell fusion was measured 8 to 10 h later by quantification of luciferase activity in relative light units. All results are the averages of at least three experiments with the different CCR5 homologues. Values are normalized to the luciferase activity for the M. fascicularis CCR5 homologue. Apes are highlighted in blue, Old World monkeys are highlighted in magenta, and New World monkeys are highlighted in green.
Primate CCR5 homologues support pseudovirus entry.
Envelope-mediated cell-cell fusion assays generally reflect the ability of a virus to enter cells; however, differences between cell-cell fusion and virus infection assays are sometimes observed. We therefore tested the ability of CCR5 homologue-transfected HOS.CD4 cells to support infection by luciferase reporter viruses. The HIV-1NL4-3 and SIVmac239 luciferase reporter viruses have a nonfunctional env gene and a luciferase gene inserted into nef. These features permit the single-round quantification of virus infection after complementation with the desired envelope protein. We created HOS.CD4 cell lines expressing each of the primate CCR5 homologues, except for those of the family Lorisoidea, since the full-length construct required the use of oligonucleotide primer pairs for the CCR5 coding region per se. These cell lines were infected with HIV-1NL4-3 or SIVmac239 luciferase reporter viruses pseudotyped with Env proteins that can use CCR5 (SIVmac1A11, HIV-1 JR-FL, and ADA) or an Env protein that uses only CXCR4 (HXB2). Reporter viruses bearing an amphotropic murine leukemia virus Env were used as a control. All but one of the representative primate CCR5 homologue constructs supported HIV-1 and SIV entry into their respective transfected cell lines (16, 28). The single exception was CCR5 of C. pygerythrus, which contained a polymorphism in the amino terminus, as reported previously (17) (data not shown).
DISCUSSION
In this study, we analyzed the structure and function of CCR5 derived from representative primate species and subspecies of the Prosimii superfamily Lemuroidea and the Anthropoidea superfamilies Ceboidea, Cercopithecoidea, and Hominoidea. We identified amino acid changes in the CCR5 homologues specific to each of the primate species and subspecies. Further, many amino acid changes were conserved among primates species and subspecies and shared between primates of the same family. Each nonhuman primate CCR5 homologue was used as an entry cofactor by HIV-1 regardless of the viral phenotype. The genetically divergent SIV strains tested here, SIVmac239, SIVmac1A11, SIVsmSL92b, and SIVsmFNJ, also used each of the nonhuman primate CCR5 homologues as an entry cofactor. Thus, despite the significant difference between SIV and HIV-2 strains and HIV-1 strains in the range of primate CD4+ cells that they productively infect and the efficiencies with which they do so, all of the primate immunodeficency viruses tested used the genetically diverse receptors for virus entry.
Alignment with and comparison to the human CCR5 amino acid sequence of the deduced nonhuman primate CCR5 homologue amino acid sequences showed species-specific changes among the diverse species, with greater amino acid differences for prosimians than for Old World monkeys, New World monkeys, and apes. Specifically, we found conserved amino acid substitutions at positions 33 (N to D) and 129 (V to I) among all nonhuman primate CCR5 homologue sequences relative to the human CCR5 consensus sequence. Additionally, we found highly conserved amino acid substitutions at position 9 (I to T) for apes and at positions 9 (I to T), 58 (M to I), 61 (I to V), 78 (F to L), and 171 (K to R) for Old World monkeys and an additional conserved substitution at position 198 (I to M) for macaques. Similar amino acid changes were observed in limited data sets of nonhuman primate CCR5 homologue sequences derived from representative species of the superfamilies Ceboidea and Cercopithecoidea (33). We observed larger numbers of relatively conserved amino acid substitutions among New World monkeys and prosimians.
CCR5 polymorphisms were also found within a given species, suggesting that, like humans (3, 38), nonhuman primates have polymorphisms (5, 28). Most of these chemokine receptors functioned as coreceptors for SIV and HIV-1 entry. Other than the stop codon found in two alleles, we identified only one mutation, an N13D change for the vervet CCR5 homologue, that adversely affected virus entry (17). Although we did not find any deletions within the nonhuman primate CCR5 homologue coding regions sequenced here, a 32-bp deletion allele exists in the human population (31, 38) and a 24-bp deletion allele exists in the C. torquatus torquatus population (36). Such polymorphisms may play a role in the limited pathogenicity of SIV in naturally and experimentally infected C. atys hosts.
Each of the nonhuman primate CCR5 homologues tested here permitted the entry of genetically diverse SIV and HIV-1 Env constructs, including SIVmac1A11 and HIV-1 laboratory strains JR-FL, ADA, and HXB2. Thus, whereas simian-human immunodeficiency virus constructs allow HIV-1 envelope fusion and entry in primate cells expressing CD4, the SIV accessory genes overcome the restrictions to replication at the postentry level. These findings indicate that the nonhuman primate CCR5 homologue is not a species-specific restriction for primate immunodeficiency virus entry and support the hypothesis that HIV-1 originated as a cross-species transmission event (4, 20).
The topology of the phylogenetic tree based on the nonhuman primate CCR5 homologues sequenced here agrees with that constructed by others using limited numbers of nonhuman primate CCR5 sequences from phylogenetically distinct species of Anthropoidea and Hominoidea (33, 43, 46). We generally found excellent agreement between the phylogenetic reconstructions of nonhuman primate CCR5 homologue sequences and available COii and CD4 gene sequences (12, 21, 52) created by using the maximum-likelihood method (data not shown). The branching patterns of the nonhuman primate CCR5 homologue sequence sets estimated by the maximum-likelihood and neighbor-joining methods revealed distinct genetic lineages, with quantitatively greater branch lengths for prosimians than for Old World monkeys, New World monkeys, and apes. The branching order was also consistent with the presumed historical diversification of the nonhuman primates (21, 46, 52). Specifically, closer linkages were observed among species representing Ceboidea, Cercopithecoidea, and Hominoidea. The only difference between the phylogenetic reconstructions created by using the maximum-likelihood and neighbor-joining methods was the location of Colobus, which clustered in an ancestral location relative to the C. aethiops cluster in the maximum-likelihood tree but in an ancestral location relative to all cercopithecines in the neighbor-joining tree (data not shown). This discrepancy, noted by others (52), suggests that the nonhuman primate CCR5 homologue may not be a suitable marker for low-level phylogenetic analysis. Analysis of the number of synonymous mutations per site and the number of nonsynonymous mutations per site (24, 34) suggests that the nonhuman primate CCR5 homologues underwent purifying selection. Furthermore, a difference in the number of synonymous mutations per site and the number of nonsynonymous mutations per site for cercopithecines and Colobus implies a difference in selective pressures for these two lineages (52).
In summary, nonhuman primate CCR5 homologue sequences are highly homologous, with amino acid sequence variations in the amino-terminal and second extracellular domains showing evolutionary conservation among the different species. Except for an N13D change for the C. aethiops CCR5 homologue (17), all other nonhuman primate CCR5 homologues supported SIV and HIV-1 entry. The topologies of the nonhuman primate CCR5 homologue phylogenetic trees recapitulated the presumed evolutionary relationship among the nonhuman primates, suggesting that this phylogenetic information is useful for resolving the relationships among the taxonomic suborders.
Acknowledgments
We thank John Moore for critical review of the manuscript.
Support for this work was provided by grants from the Public Health Service (HD37356, AI41420, and AI40880), the Elizabeth Glaser Pediatric AIDS Foundation, and the Burroughs Wellcome Fund and by a gift from an anonymous foundation.
REFERENCES
- 1.Alkhatib, G., C. Combadiere, C. C. Broder, Y. Feng, P. E. Kennedy, P. M. Murphy, and E. A. Berger. 1996. CC CKR5: a RANTES, MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta receptor as a fusion cofactor for macrophage-tropic HIV-1. Science 272:1955-1958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bjorndal, A., H. Deng, M. Jansson, J. R. Fiore, C. Colognesi, A. Karlsson, J. Albert, G. Scarlatti, D. R. Littman, and E. M. Fenyo. 1997. Coreceptor usage of primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates varies according to biological phenotype. J. Virol. 71:7478-7487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Carrington M., T. Kissner, B. Gerrard, S. Ivanov, S. J. O'Brien, and M. Dean. 1997. Novel alleles of the chemokine-receptor gene CCR5. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 61:1261-1267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chen, Z., P. Zhou, D. D. Ho, N. R. Landau, and P. A. Marx. 1997. Genetically divergent strains of simian immunodeficiency virus use CCR5 as a coreceptor for entry. J. Virol. 71:2705-2714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chen, Z., D. Kwon, Z. Jin, S. Monard, P. Telfer, M. S. Jones, C. Y. Lu, R. F. Aguilar, D. D. Ho, and P. A. Marx. 1998. Natural infection of a homozygous delta24 CCR5 red-capped mangabey with an R2b-tropic simian immunodeficiency virus. J. Exp. Med. 188:2057-2065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Choe, H., M. Farzan, Y. Sun, N. Sullivan, B. Rollins, P. D. Ponath, L. Wu, C. R. Mackay, G. LaRosa, W. Newman, N. Gerard, C. Gerard, and J. Sodroski. 1996. The beta-chemokine receptors CCR3 and CCR5 facilitate infection by primary HIV-1 isolates. Cell 85:1135-1148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cocchi, F., A. L. DeVico, A. Garzino-Demo, S. K. Arya, R. C. Gallo, and P. Lusso. 1995. Identification of RANTES, MIP-1 alpha, and MIP-1 beta as the major HIV-suppressive factors produced by CD8+ T cells. Science 270:1811-1815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Connor, R. I., W. A. Paxton, K. E. Sheridan, and R. A. Koup. 1996. Macrophages and CD4+ T lymphocytes from two multiply exposed, uninfected individuals resist infection with primary non-syncytium-inducing isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 70:8758-8764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Connor, R. I., K. E. Sheridan, D. Ceradini, S. Choe, and N. R. Landau. 1997. Change in coreceptor use correlates with disease progression in HIV-1-infected individuals. J. Exp. Med. 185:621-628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dalgleish, A. G., P. C. Beverley, P. R. Clapham, D. H. Crawford, M. F. Greaves, and R. A. Weiss. 1984. The CD4 (T4) antigen is an essential component of the receptor for the AIDS retrovirus. Nature 312:763-767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Deng, H., R. Liu, W. Ellmeier, S. Choe, D. Unutmaz, M. Burkhart, P. Di Marzio, S. Marmon, R. E. Sutton, C. M. Hill, C. B. Davis, S. C. Peiper, T. J. Schall, D. R. Littman, and N. R. Landau. 1996. Identification of a major co-receptor for primary isolates of HIV-1. Nature 381:661-666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Disotell, T. R., R. L. Honeycutt, and M. Ruvolo. 1992. Mitochondrial DNA phylogeny of the Old-World monkey tribe Papionini. Mol. Biol. Evol. 9:1-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Doranz, B. J., J. Rucker, Y. Yi, R. J. Smyth, M. Samson, S. C. Peiper, M. Parmentier, R. G. Collman, and R. W. Doms. 1996. A dual-tropic primary HIV-1 isolate that uses fusin and the beta-chemokine receptors CKR-5, CKR-3, and CKR-2b as fusion cofactors. Cell 85:1149-1158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dragic, T., V. Litwin, G. P. Allaway, S. R. Martin, Y. Huang, K. A. Nagashima, C. Cayanan, P. J. Maddon, R. A. Koup, J. P. Moore, and W. A. Paxton. 1996. HIV-1 entry into CD4+ cells is mediated by the chemokine receptor CC-CKR-5. Nature 381:667-673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Dragic, T., A. Trkola, S. W. Lin, K. A. Nagashima, F. Kajumo, L. Zhao, W. C. Olson, L. Wu, C. R. Mackay, G. P. Allaway, T. P. Sakmar, J. P. Moore, and P. J. Maddon. 1998. Amino-terminal substitutions in the CCR5 coreceptor impair gp120 binding and human immunodeficiency virus type 1 entry. J. Virol. 72:279-285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Edinger, A. L., A. Amedee, K. Miller, B. J. Doranz, M. Endres, M. Sharron, M. Samson, Z. H. Lu, J. E. Clements, M. Murphey-Corb, S. C. Peiper, M. Parmentier, C. C. Broder, and R. W. Doms. 1997. Differential utilization of CCR5 by macrophage and T cell tropic simian immunodeficiency virus strains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94:4005-4010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Edinger, A. L., C. Blaincpain, K. J. Kunstman, S. M. Wolinsky, M. Parmentier, and R. W. Doms. 1999. Functional dissection of CCR5 coreceptor function through the use of CD4-independent simian immunodeficiency virus strains. J. Virol. 73:4062-4073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Faulkner, D. V., and A. Jurka. 1988. Multiple aligned sequence editor (MASE). Trends Biochem. Sci. 13:321-326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Feng, Y., C. C. Broder, P. E. Kennedy, and E. A. Berger. 1997. HIV-1 entry cofactor: functional cDNA cloning of a seven-transmembrane, G protein-coupled receptor. Science 272:872-877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Fomsgaard, A., M. C. Muller-Trutwin, O. Diop, J. Hansen, C. Mathiot, S. Corbet, F. Barre-Sinoussi, and J. S. Allan. 1997. Relation between phylogeny of African green monkey CD4 genes and their respective simian immunodeficiency virus genes. J. Med. Primatol. 26:120-128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Goodman, M., C. A. Porter, J. Czelusniak, S. L. Page, H. Schneider, J. Shoshani, G. Gunnell, and C. P. Groves. 1998. Towards a phylogenetic classification of primates based on DNA evidence complemented by fossil evidence. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 9:585-598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Huelsenbeck, J. P., and B. Rannala. 1997. Phylogenetic methods come of age: testing hypotheses in an evolutionary context. Science 276:227-232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Huelsenbeck, J. P., and K. A. Crandall. 1997. Phylogeny estimation and hypothesis testing using maximum likelihood. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 28:437-466. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ina, T. 1995. New methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous substitutions. J. Mol. Evol. 40:190-226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Klatzmann, D., E. Champagne, S. Chamaret, J. Gruest, D. Guetard, T. Hercend, J. C. Gluckman, and L. Montagnier. 1984. T-lymphocyte T4 molecule behaves as the receptor for human retrovirus LAV. Nature 312:767-768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Korber, B., M. Muldoon, J. Theiler, F. Gao, A. Lapedes, R. Gupta, S. Wolinsky, B. Hahn, and T. Bhattacharya. 2000. Timing the ancestor of the HIV-1 pandemic strains. Science 288:1789-1796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Korber, B. T., K. J. Kunstman, B. K. Patterson, M. Furtado, M. M. McEvilly, R. Levy, and S. M. Wolinsky. 1994. Genetic differences between blood- and brain-derived viral sequences from human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected patients: evidence of conserved elements in the V3 region of the envelope protein of brain-derived sequences. J. Virol. 68:7467-7481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kuhmann, S. E., E. J. Platt, S. L. Kozak, and D. Kabat. 1997. Polymorphisms in the CCR5 genes of African green monkeys and mice implicate specific amino acids in infections by simian and human immunodeficiency viruses. J. Virol. 71:8642-8656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kuiken, C., B. Foley, E. Freed, B. Hahn, P. Marx, J. Mellors, S. Wolinsky, and B. Korber. 2002. HIV sequence compendium. Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, N.Mex.
- 30.Learn, G. H., B. T. Korber, B. Foley, B. H. Hahn, S. M. Wolinsky, and J. I. Mullins. 1996. Maintaining the integrity of human immunodeficiency virus sequence databases. J. Virol. 70:5720-5730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Liu, R., W. A. Paxton, S. Choe, D. Ceradini, S. R. Martin, R. Horuk, M. E. MacDonald, H. Stuhlmann, R. A. Koup, and N. R. Landau. 1996. Homozygous defect in HIV-1 coreceptor accounts for resistance of some multiply-exposed individuals to HIV-1 infection. Cell 86:367-377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Marcon, L., H. Choe, K. A. Martin, M. Farzan, P. D. Ponath, L. Wu, W. Newman, N. Gerard, C. Gerard, and J. Sodrowski. 1997. Utilization of CC-chemokine receptor 5 by the envelope glycoproteins of pathogenic SIVmac239. J. Virol. 71:2522-2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Mummidi, S., M. Bamshad, S. S. Ahuja, E. Gonzalez, P. M. Feuillet, K. Begum, M. C. Galvis, V. Kostecki, A. J. Valente, K. K. Murthy, L. Haro, M. J. Dolan, J. S. Allan, and S. K. Ahuja. 2000. Evolution of human and non-human primate CC chemokine receptor 5 gene and mRNA. J. Biol. Chem. 275:18946-18961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Nei, M., and T. Gojobori. 1986. Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol. Biol. Evol. 3:418-426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Olsen, G. J., H. Matsuda, R. Hagstrom, and R. Overbeek. 1994. fastDNAmL: a tool for construction of phylogenetic trees of DNA sequences using maximum likelihood. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 10:41-48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Palacios, E., L. Digilio, H. M. McClure, Z. Chen, P. A. Marx, M. A. Goldsmith, and R. M. Grant. 1998. Parallel evolution of CCR5-null phenotypes in humans and in a natural host of simian immunodeficiency virus. Curr. Biol. 1998. 8:943-946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Posada, D., and K. A. Crandall. 1998. MODELTEST: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14:817-818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Quillent, C., E. Oberlin, J. Braun, D. Rousset, G. Gonzalez-Canali, P. Metais, L. Montagnier, J. L. Virelizier, F. Arenzana-Seisdedos, and A. Beretta. 1998. HIV-1-resistance phenotype conferred by combination of two separate inherited mutations of CCR5 gene. Lancet 351:14-18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Rana, S., G. Besson, D. G. Cook, J. Rucker, R. J. Smyth, Y. Yi, J. D. Turner, H. H. Guo, J. G. Du, S. C. Peiper, E. Lavi, M. Samson, F. Libert, C. Liesnard, G. Vassart, R. W. Doms, M. Parmentier, and R. G. Collman. 1997. Role of CCR5 in infection of primary macrophages and lymphocytes by macrophage-tropic strains of human immunodeficiency virus: resistance to patient-derived and prototype isolates resulting from the Δccr5 mutation. J. Virol. 71:3219-3227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Raport, C. J., J. Gosling, V. L. Schweickart, P. W. Gray, and I. F. Charo. 1996. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a novel human CC chemokine receptor (CCR5) for RANTES, MIP-1beta, and MIP-1alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 271:17161-17166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Rucker, J., A. L. Edinger, M. Sharron, M. Samson, B. Lee, J. F. Berson, Y. Yi, B. Margulies, R. G. Collman, B. J. Doranz, M. Parmentier, and R. W. Doms. 1997. Utilization of chemokine receptors, orphan receptors, and herpesvirus-encoded receptors by diverse human and simian immunodeficiency viruses. J. Virol. 71:8999-9007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Rucker, J., B. J. Doranz, A. E. Edinger, D. Long, J. F. Berson, and R. W. Doms. 1997. Use of a cell-cell fusion assay to study the role of chemokine receptors in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) entry. Methods Enzymol. 288:118-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ruvolo, M., D. Pan, S. Zehr, T. Goldberg, T. R. Disotell, and M. von Dornum. 1994. Gene trees and hominoid phylogeny. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:8900-8904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sattentau, Q. J., J. P. Moore, F. Vignaux, F. Traincard, and P. Poignard. 1993. Conformational changes induced in the envelope glycoproteins of the human and simian immunodeficiency viruses by soluble receptor binding. J. Virol. 67:7383-7393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Scarlatti, G., E. Tresoldi, A. Bjorndal, R. Fredriksson, C. Colognesi, H. K. Deng, M. S. Malnati, A. Plebani, A. G. Siccardi, D. R. Littman, E. M. Fenyo, and P. Lusso. 1997. In vivo evolution of HIV-1 co-receptor usage and sensitivity to chemokine-mediated suppression. Nat. Med. 3:1259-1265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Shoshani, J., C. P. Groves, E. L. Simons, and G. F. Gunnell. 1996. Primate phylogeny: morphological vs. molecular results. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 5:102-154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Simmons, G., D. Wilkinson, J. D. Reeves, M. T. Dittmar, S. Beddows, J. Weber, G. Carnegie, U. Desselberger, P. W. Gray, R. A. Weiss, and P. R. Clapham. 1996. Primary, syncytium-inducing human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates are dual-tropic, and most can use either Lestr or CCR5 as coreceptors for virus entry. J. Virol. 70:8355-8360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Swofford, D. L. 2002. PAUP*4.0610: phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (and other methods). Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, Mass.
- 49.Willett, B. J., L. Picard, M. J. Hoxie, J. D. Turner, K. Adema, and P. R. Clapham. 1997. Shared usage of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 by the feline and human immunodeficiency viruses. J. Virol. 71:6407-6415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Zacharova, V., V. Zachar, and A. S. Goustin. 1997. Sequence of chemokine receptor gene CCR5 in chimpanzees, a natural HIV type 1 host. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 13:1159-1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Zhang, L., T. He, A. Talal, G. Wang, S. S. Frankel, and D. D. Ho. 1998. In vivo distribution of the human immunodeficiency virus-simian immunodeficiency virus coreceptors: CXCR4, CCR3, and CCR5. J. Virol. 72:5035-5045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Zhang, Y., and O. A. Ryder. 1998. Mitochondrial cytochrome b sequences of Old World monkeys: with special reference on evolution of Asian colobines. Primates 39:29-49. [Google Scholar]