Abstract
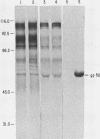
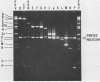
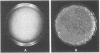
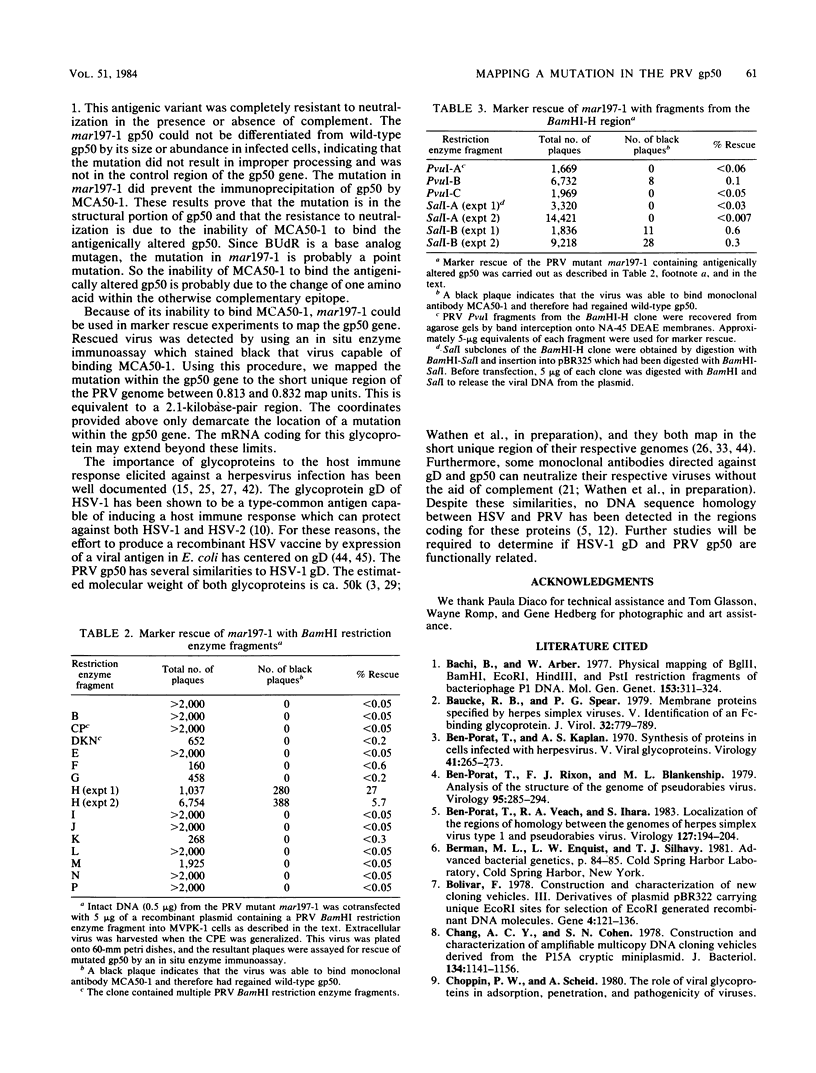
A pseudorabies virus variant ( mar197 -1) containing a mutation in a viral glycoprotein with a molecular weight of 50,000 ( gp50 ) was isolated by selecting for resistance to a neurtralizing monoclonal antibody ( MCA50 -1) directed against gp50 . This mutant was completely resistant to neutralization with MCA50 -1 in the presence or absence of complement, and was therefore defined as a mar (monoclonal-antibody-resistant) mutant. The mutation did not affect neutralization with polyvalent immune serum. The mar197 -1 mutant synthesized and processed gp50 normally, but the mutation prevented the binding and immunoprecipitation of gp50 by MCA50 -1. Thus, the mutation was within the structural portion of the gp50 gene affecting the epitope of the monoclonal antibody. The mutation was mapped by marker rescue with cloned pseudorabies restriction enzyme fragments to the short region of the pseudorabies genome between 0.813 and 0.832 map units. This is equivalent to a 2.1-kilobase-pair region.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baucke R. B., Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. V. Identification of an Fc-binding glycoprotein. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):779–789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.779-789.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Porat T., Kaplan A. S. Synthesis of proteins in cells infected with herpesvirus. V. Viral glycoproteins. Virology. 1970 Jun;41(2):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Porat T., Rixon F. J., Blankenship M. L. Analysis of the structure of the genome of pseudorabies virus. Virology. 1979 Jun;95(2):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90484-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Porat T., Veach R. A., Ihara S. Localization of the regions of homology between the genomes of herpes simplex virus, type 1, and pseudorabies virus. Virology. 1983 May;127(1):194–204. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90383-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. III. Derivatives of plasmid pBR322 carrying unique Eco RI sites for selection of Eco RI generated recombinant DNA molecules. Gene. 1978 Oct;4(2):121–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bächi B., Arber W. Physical mapping of BglII, BamHI, EcoRI, HindIII and PstI restriction fragments of bacteriophage P1 DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jun 24;153(3):311–324. doi: 10.1007/BF00431596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Katze M., Hydrean-Stern C., Eisenberg R. J. Type-common CP-1 antigen of herpes simplex virus is associated with a 59,000-molecular-weight envelope glycoprotein. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):172–181. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.172-181.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Boyer H. W., Helling R. B. Construction of biologically functional bacterial plasmids in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3240–3244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Wilkie N. M. Location and orientation of homologous sequences in the genomes of five herpesviruses. J Gen Virol. 1983 Sep;64(Pt 9):1927–1942. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-9-1927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dretzen G., Bellard M., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. A reliable method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose and acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90296-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman L., Rixon F. J., Jean J. H., Ben-Porat T., Kaplan A. S. Transcription of the genome of pseudorabies virus (A herpesvirus) is strictly controlled. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):316–327. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90343-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glorioso J. C., Levine M., Holland T. C., Szczesiul M. S. Mutant analysis of herpes simplex virus-induced cell surface antigens: resistance to complement-mediated immune cytolysis. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):672–681. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.672-681.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glorioso J. C., Smith J. W. Immune interactions with cells infected with herpes simplex virus: antibodies to radioiodinated surface antigens. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):114–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., LeBlanc D. J., Falkow S. General method for the isolation of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):1064–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.1064-1066.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Honess R. W., Cassai E., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XII. The virion polypeptides of type 1 strains. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):640–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.640-651.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland T. C., Marlin S. D., Levine M., Glorioso J. Antigenic variants of herpes simplex virus selected with glycoprotein-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):672–682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.672-682.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland T. C., Sandri-Goldin R. M., Holland L. E., Marlin S. D., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Physical mapping of the mutation in an antigenic variant of herpes simplex virus type 1 by use of an immunoreactive plaque assay. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):649–652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.649-652.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killington R. A., Yeo J., Honess R., Watson D. H., Duncan B. E., Halliburton I. W., Mumford J. Comparative analyses of the proteins and antigens of five herpesviruses. J Gen Virol. 1977 Nov;37(2):297–310. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-37-2-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawman M. J., Courtney R. J., Eberle R., Schaffer P. A., O'Hara M. K., Rouse B. T. Cell-mediated immunity to herpes simplex virus: specificity of cytotoxic T cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):451–461. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.451-461.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G. T., Para M. F., Spear P. G. Location of the structural genes for glycoproteins gD and gE and for other polypeptides in the S component of herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):41–49. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.41-49.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrild B., Shore S. L., Nahmias A. J. Herpes simplex virus glycoproteins: participation of individual herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein antigens in immunocytolysis and their correlation with previously identified glycopolypeptides. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):741–748. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.741-748.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul P. S., Mengeling W. L., Pirtle E. C. Differentiation of pseudorabies (Aujeszky's disease) virus strains by restriction endonuclease analysis. Arch Virol. 1982;73(2):193–198. doi: 10.1007/BF01314727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizer L. I., Cohen G. H., Eisenberg R. J. Effect of tunicamycin on herpes simplex virus glycoproteins and infectious virus production. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):142–153. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.142-153.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein A. S., Kaplan A. S. Electron microscopic studies of the DNA of defective and standard pseudorabies virions. Virology. 1975 Aug;66(2):385–392. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90211-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruyechan W. T., Morse L. S., Knipe D. M., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. II. Mapping of the major viral glycoproteins and of the genetic loci specifying the social behavior of infected cells. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):677–697. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.677-697.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen Y. M., Hirschhorn R. R., Mercer W. E., Surmacz E., Tsutsui Y., Soprano K. J., Baserga R. Gene transfer: DNA microinjection compared with DNA transfection with a very high efficiency. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1145–1154. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. I. Identification of four glycoprotein precursors and their products in type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):991–1008. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.991-1008.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F. Sequence of protein synthesis in cells infected by human cytomegalovirus: early and late virus-induced polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):686–701. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.686-701.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Wilkie N. M. Physical mapping of herpes simplex virus type 1 mutations by marker rescue. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):182–192. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.182-192.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus S. E., Aulakh H. S., Ruyechan W. T., Hay J., Casey T. A., Vande Woude G. F., Owens J., Smith H. A. Structure of varicella-zoster virus DNA. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):516–525. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.516-525.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaney L. M. Susceptibility of a new fetal pig kidney cell line (MVPK-1) to foot-and-mouth disease virus. Am J Vet Res. 1976 Nov;37(11):1319–1322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vestergaard B. F. Herpes simplex virus antigens and antibodies: a survey of studies based on quantitative immunoelectrophoresis. Rev Infect Dis. 1980 Nov-Dec;2(6):899–913. doi: 10.1093/clinids/2.6.899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walboomers J. M., Schegget J. T. A new method for the isolation of herpes simplex virus type 2 DNA. Virology. 1976 Oct 1;74(1):256–258. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90151-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Weis J. H., Salstrom J. S., Enquist L. W. Herpes simplex virus type-1 glycoprotein D gene: nucleotide sequence and expression in Escherichia coli. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):381–384. doi: 10.1126/science.6289440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis J. H., Enquist L. W., Salstrom J. S., Watson R. J. An immunologically active chimaeric protein containing herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):72–74. doi: 10.1038/302072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]