Abstract
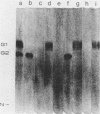
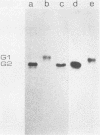
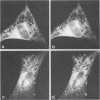
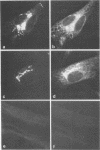
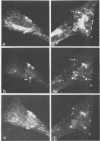
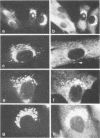
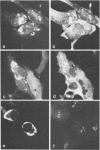
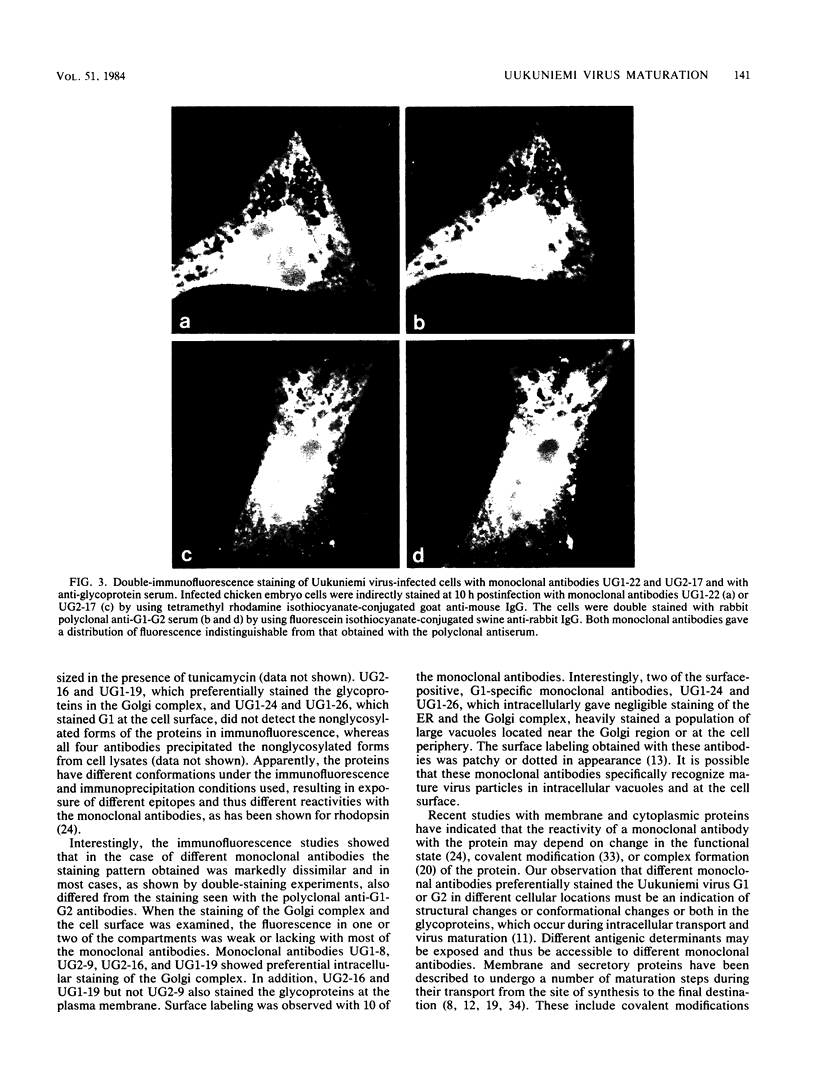
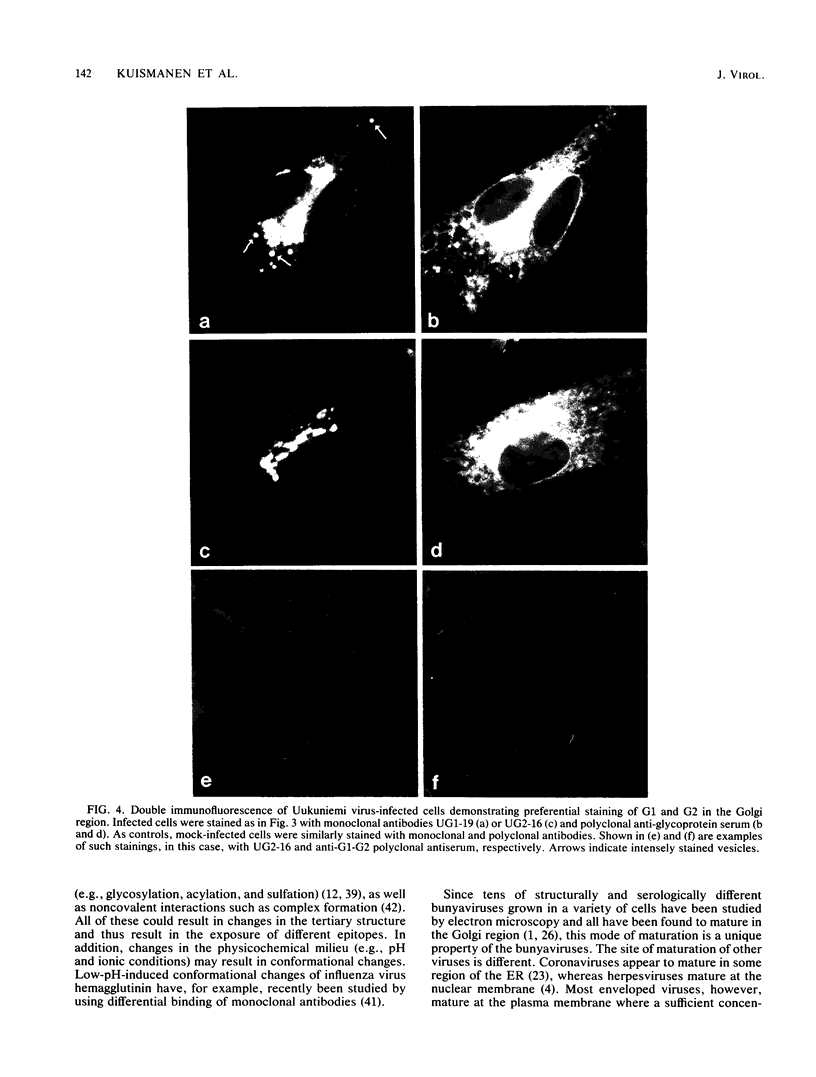
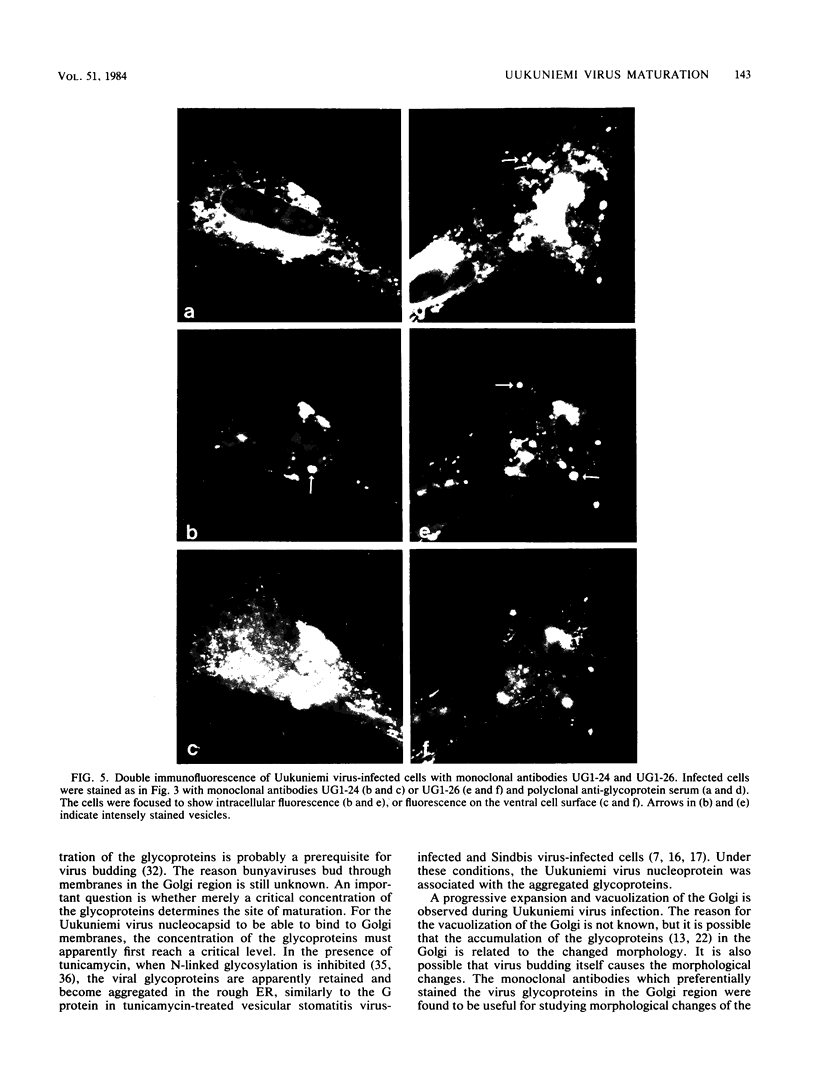
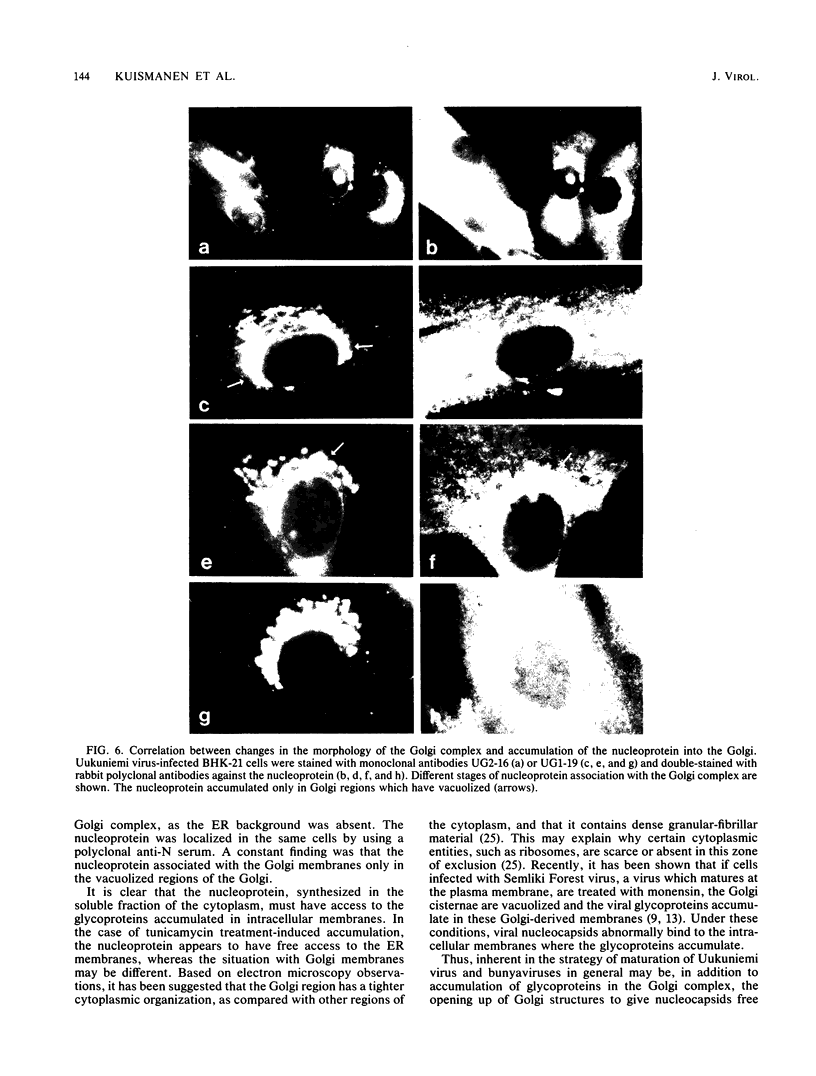
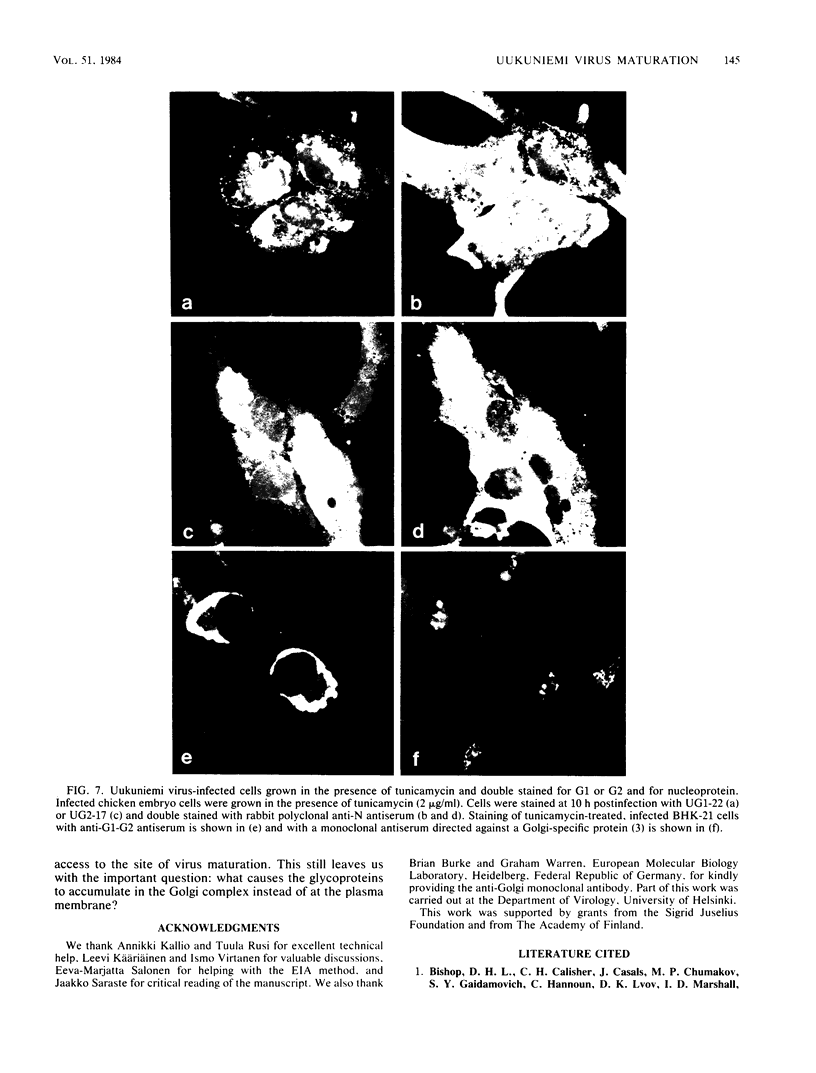
Monoclonal antibodies directed against Uukuniemi virus glycoproteins G1 and G2 in combination with polyclonal antibodies against the nucleoprotein (N) were used to study the maturation of the virus in Golgi complexes of infected chicken embryo fibroblasts and BHK cells. Of 25 monoclonal antibodies obtained, 10 were shown to be G1 specific and 15 were shown to be G2 specific by immunoblotting and immunoprecipitation. In double-staining experiments, some of the monoclonal antibodies gave similar distributions of fluorescence as compared with the staining obtained from polyclonal rabbit anti-G1-G2 antibodies. Others, however, preferentially stained either the glycoproteins in the Golgi complex or those at the cell surface. This may indicate that the glycoproteins underwent conformational changes during their transport. Uukuniemi virus infection resulted in the vacuolization of the membranes of Golgi complexes where the maturation of the virus was taking place. Double-staining experiments with monoclonal antibodies which preferentially stained the Golgi-associated viral glycoproteins and with anti-N polyclonal rabbit antiserum showed a correlation between the progressive vacuolization of the Golgi complex and the accumulation of viral nucleoprotein in the Golgi region, suggesting that a morphological alteration of the Golgi complex may be a prerequisite for intracellular maturation of the virus. Treatment of Uukuniemi virus-infected cells with tunicamycin, a drug which inhibits N-linked glycosylation, resulted in the accumulation of both glycoproteins at an intracellular location, apparently representing the endoplasmic reticulum. Double-staining experiments showed a parallel accumulation of nucleoprotein at these sites, indicating that local accumulation of glycoproteins is required for nucleoprotein binding to intracellular membranes.
Full text
PDF

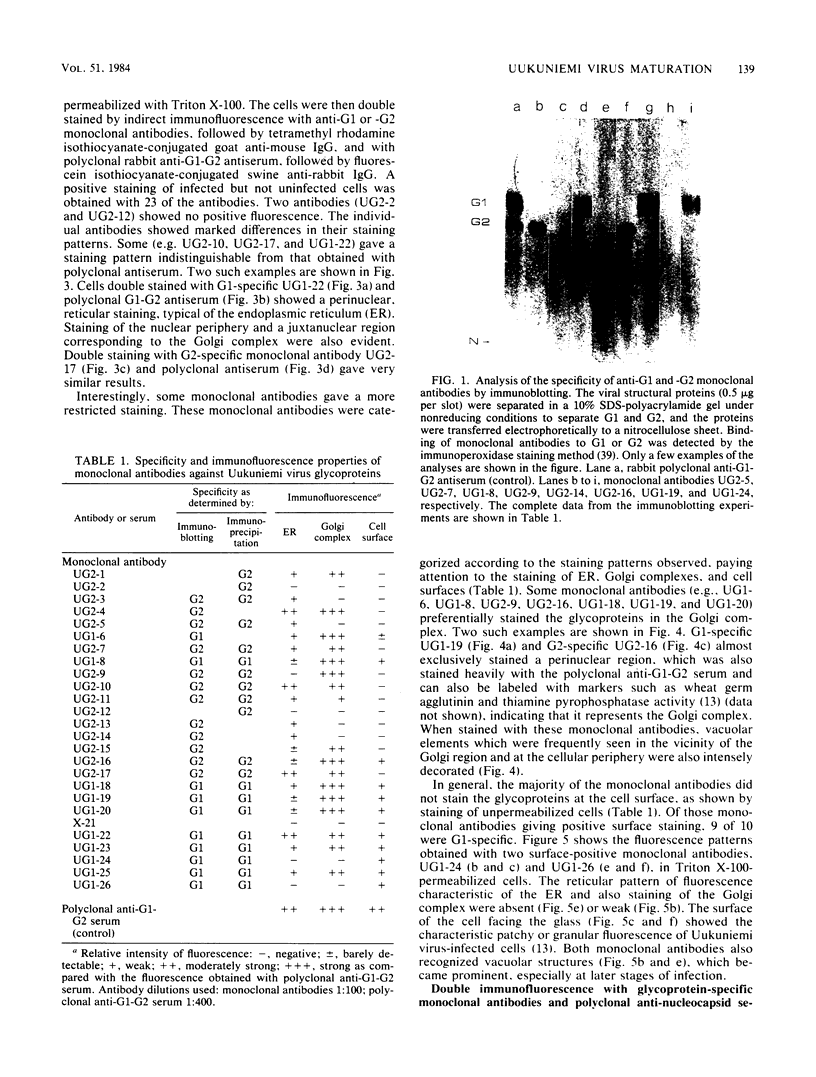


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop D. H., Calisher C. H., Casals J., Chumakov M. P., Gaidamovich S. Y., Hannoun C., Lvov D. K., Marshall I. D., Oker-Blom N., Pettersson R. F. Bunyaviridae. Intervirology. 1980;14(3-4):125–143. doi: 10.1159/000149174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke B., Griffiths G., Reggio H., Louvard D., Warren G. A monoclonal antibody against a 135-K Golgi membrane protein. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1621–1628. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01364.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlington R. W., Moss L. H., 3rd Herpesvirus envelopment. J Virol. 1968 Jan;2(1):48–55. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.1.48-55.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfre G., Howe S. C., Milstein C., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. Antibodies to major histocompatibility antigens produced by hybrid cell lines. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):550–552. doi: 10.1038/266550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson R., Schlesinger S., Kornfeld S. The nonglycosylated glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus is temperature-sensitive and undergoes intracellular aggregation at elevated temperatures. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3600–3607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J., Griffiths G., Louvard D., Quinn P., Warren G. Passage of viral membrane proteins through the Golgi complex. J Mol Biol. 1981 Nov 15;152(4):663–698. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90122-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Quinn P., Warren G. Dissection of the Golgi complex. I. Monensin inhibits the transport of viral membrane proteins from medial to trans Golgi cisternae in baby hamster kidney cells infected with Semliki Forest virus. J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):835–850. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., von Bonsdorff C. H. Semlike Forest virus membrane proteins. Preparation and characterization of spike complexes soluble in detergent-free medium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 15;436(4):895–899. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90421-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaluza G., Rott R., Schwarz R. T. Carbohydrate-induced conformational changes of Semliki forest virus glycoproteins determine antigenicity. Virology. 1980 Apr 30;102(2):286–299. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuismanen E., Hedman K., Saraste J., Pettersson R. F. Uukuniemi virus maturation: accumulation of virus particles and viral antigens in the Golgi complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;2(11):1444–1458. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.11.1444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurila P., Virtanen I., Wartiovaara J., Stenman S. Fluorescent antibodies and lectins stain intracellular structures in fixed cells treated with nonionic detergent. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Apr;26(4):251–257. doi: 10.1177/26.4.207770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavitt R., Schlesinger S., Kornfeld S. Impaired intracellular migration and altered solubility of nonglycosylated glycoproteins of vesicular stomatitis virus and Sindbis virus. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 25;252(24):9018–9023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavitt R., Schlesinger S., Kornfeld S. Tunicamycin inhibits glycosylation and multiplication of Sindbis and vesicular stomatitis viruses. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):375–385. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.375-385.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Braell W. A., Schwartz A. L., Strous G. J., Zilberstein A. Synthesis and assembly of membrane and organelle proteins. Int Rev Cytol Suppl. 1981;12:247–307. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-364373-5.50016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louvard D., Morris C., Warren G., Stanley K., Winkler F., Reggio H. A monoclonal antibody to the heavy chain of clathrin. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1655–1664. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01640.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons M. J., Heyduk J. Aspects of the developmental morphology of California encephalitis virus in cultured vertebrae and arthropod cells and in mouse brain. Virology. 1973 Jul;54(1):37–52. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90112-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madoff D. H., Lenard J. A membrane glycoprotein that accumulates intracellularly: cellular processing of the large glycoprotein of LaCrosse virus. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):821–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massalski A., Coulter-Mackie M., Dales S. Assembly of mouse hepatitis virus strain JHM. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1981;142:111–118. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0456-3_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molday R. S., MacKenzie D. Monoclonal antibodies to rhodopsin: characterization, cross-reactivity, and application as structural probes. Biochemistry. 1983 Feb 1;22(3):653–660. doi: 10.1021/bi00272a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollenhauer H. H., Morré D. J. Structural compartmentation of the cytosol: zones of exclusion, zones of adhesion, cytoskeletal and intercisternal elements. Subcell Biochem. 1978;5:327–359. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-7942-7_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy F. A., Harrison A. K., Whitfield S. G. Bunyaviridae: morphologic and morphogenetic similarities of Bunyamwera serologic supergroup viruses and several other arthropod-borne viruses. Intervirology. 1973;1(4):297–316. doi: 10.1159/000148858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesonen M., Kuismanen E., Pettersson R. F. Monosaccharide sequence of protein-bound glycans of Uukuniemi virus. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):390–400. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.390-400.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson R. F., Hewlett M. J., Baltimore D., Coffin J. M. The genome of Uukuniemi virus consists of three unique RNA segments. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):51–63. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90316-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson R., Käriäinen L. The ribonucleic acids of Uukuniemi virus, a noncubical tick-borne arbovirus. Virology. 1973 Dec;56(2):608–619. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson R., Käriäinen L., von Bonsdorff C. H., Oker-Blom N. Structural components of Uukuniemi virus, a noncubical tick-borne arbovirus. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):721–729. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen E. M., Vaheri A. Rapid solid-phase enzyme immunoassay for antibodies to viruses and other microbes: effects of polyethylene glycol. J Immunol Methods. 1981;41(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90277-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Garoff H. The budding mechanisms of enveloped animal viruses. J Gen Virol. 1980 Sep;50(1):1–21. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger L. A., Sternberger N. H. Monoclonal antibodies distinguish phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated forms of neurofilaments in situ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):6126–6130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.6126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strous G. J., Lodish H. F. Intracellular transport of secretory and membrane proteins in hepatoma cells infected by vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90547-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takatsuki A., Arima K., Tamura G. Tunicamycin, a new antibiotic. I. Isolation and characterization of tunicamycin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Apr;24(4):215–223. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tkacz J. S., Lampen O. Tunicamycin inhibition of polyisoprenyl N-acetylglucosaminyl pyrophosphate formation in calf-liver microsomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 8;65(1):248–257. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulmanen I., Seppälä P., Pettersson R. F. In vitro translation of Uukuniemi virus-specific RNAs: identification of a nonstructural protein and a precursor to the membrane glycoproteins. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):72–79. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.72-79.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uy R., Wold F. Posttranslational covalent modification of proteins. Science. 1977 Dec 2;198(4320):890–896. doi: 10.1126/science.337487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Bonsdorff C. H., Saikku P., Oker-Blom N. Electron microscope study on the development of Uukuniemi virus. Acta Virol. 1970 Mar;14(2):109–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Gerhard W., Bachi T. Monoclonal anti-hemagglutinin antibodies detect irreversible antigenic alterations that coincide with the acid activation of influenza virus A/PR/834-mediated hemolysis. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):239–248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.239-248.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziemiecki A., Garofff H. Subunit composition of the membrane glycoprotein complex of Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jul 5;122(3):259–269. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90189-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de StGroth S. F., Scheidegger D. Production of monoclonal antibodies: strategy and tactics. J Immunol Methods. 1980;35(1-2):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]