Abstract
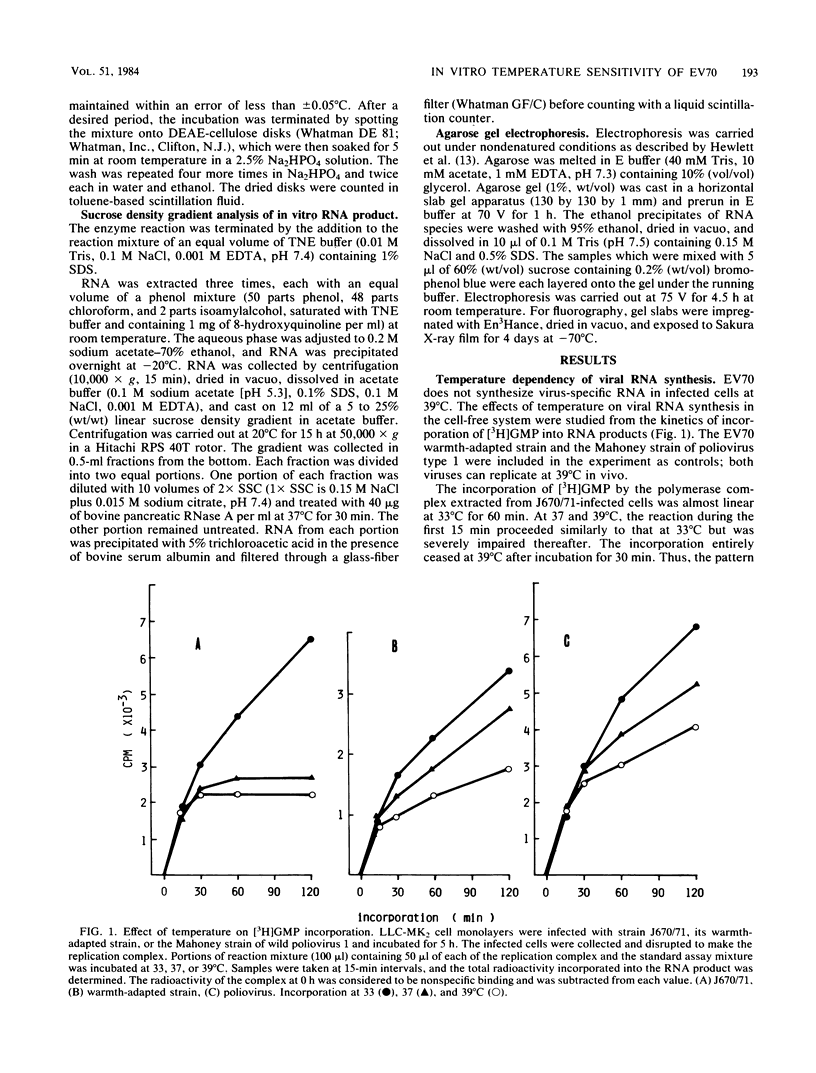
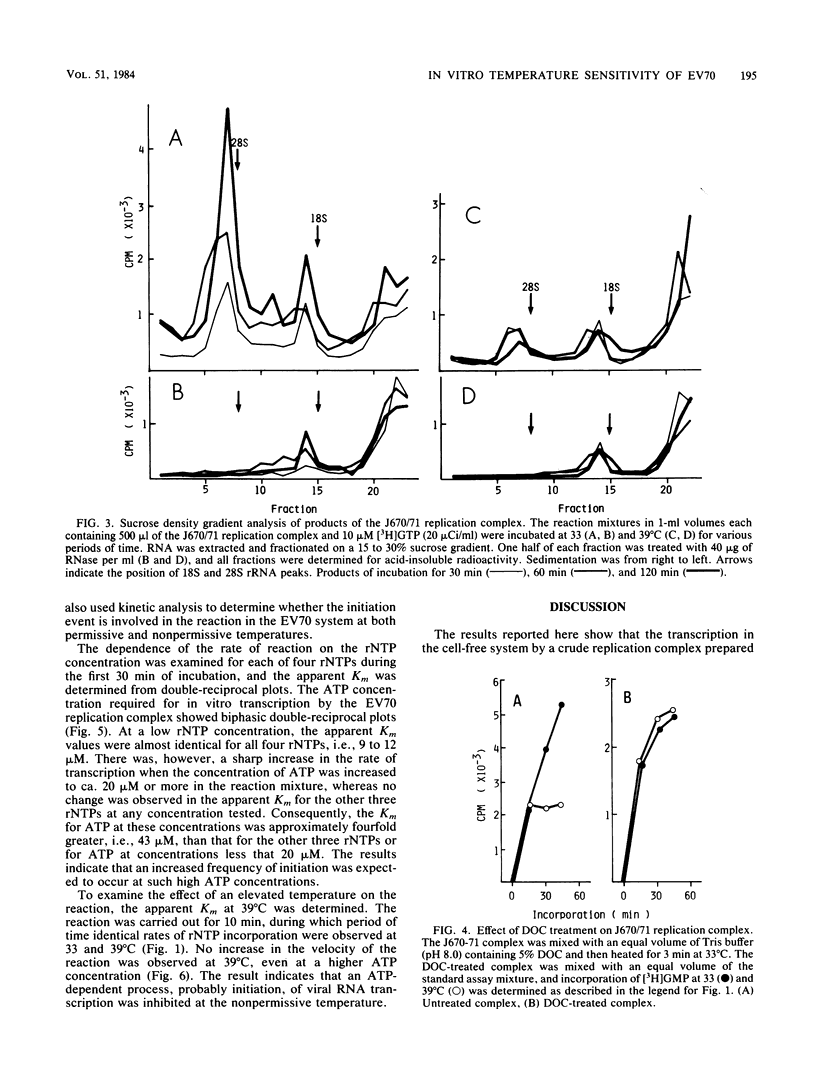
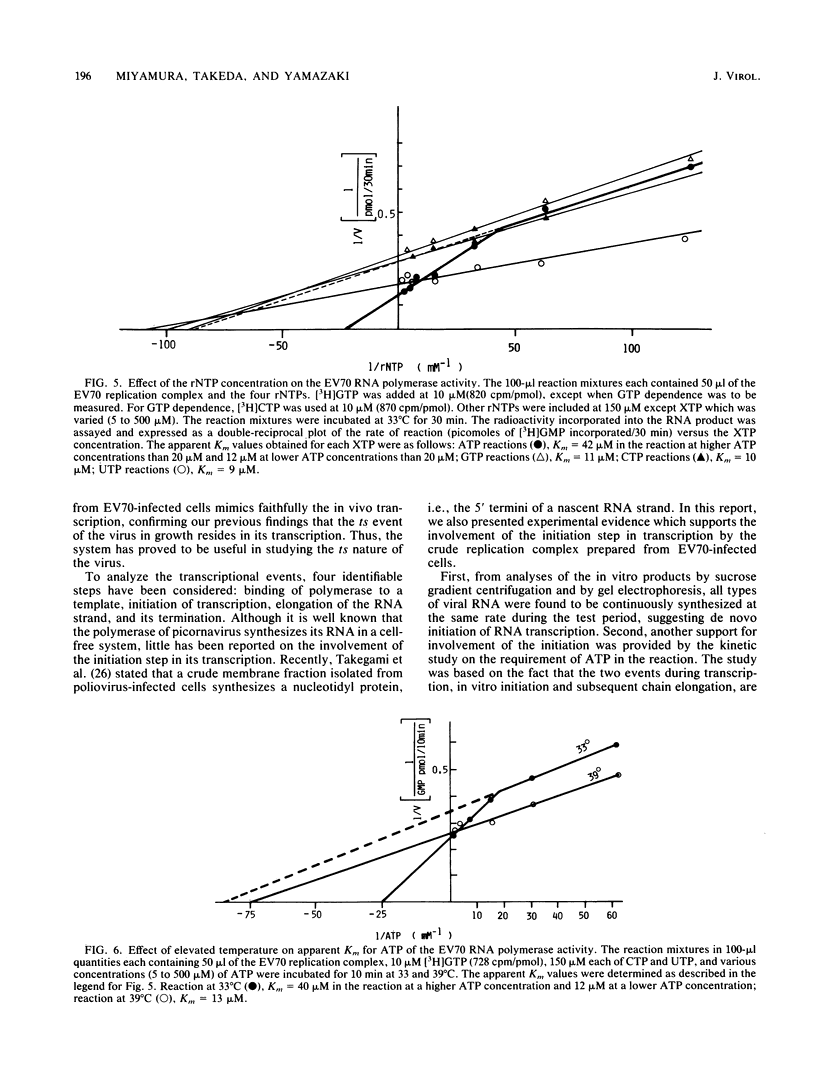
A crude replication complex prepared from enterovirus 70-infected cells was used to study the temperature-sensitive characteristic of the virus. The complex showed a temperature sensitivity in the in vitro incorporation of radiolabeled ribonucleoside triphosphate. The endonuclease itself did not account for the restricted RNA synthesis at the nonpermissive temperature. Analyses of the in vitro products by both gel electrophoresis and sucrose density gradient centrifugation showed that the complex synthesized three types of viral RNA only when incubated for a short period of time at the nonpermissive temperature. When the replication complex was treated with a detergent (deoxycholic acid), incorporation of ribonucleoside triphosphate into RNA at the permissive temperature was reduced to the level of that at the nonpermissive temperature. In addition, the in vitro RNA synthesis by the enterovirus 70 replication complex at the permissive temperature required a higher concentration of ATP than of other ribonucleoside triphosphates, whereas such a preference for ATP was not found in the reaction at the nonpermissive temperature. The results indicate that the initiation step of RNA synthesis by the complex is blocked at the nonpermissive temperature. The possible implications of these findings are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthony D. D., Goldthwait D. A., Wu C. W. Studies with the ribonucleic acid polymerase. II. Kinetic aspects of initiation and polymerization. Biochemistry. 1969 Jan;8(1):246–256. doi: 10.1021/bi00829a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Baltimore D. In vitro copying of viral positive strand RNA by poliovirus replicase. Characterization of the reaction and its products. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12359–12366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Purification and properties of a host cell protein required for poliovirus replication in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12351–12358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P. D., Stancek K., Summers D. F. Synthesis of double-stranded RNA by poliovirus temperature-sensitive mutants. Virology. 1970 Apr;40(4):971–977. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90143-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A. Antibody to host factor precipitates poliovirus RNA polymerase from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):252–259. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90336-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A., Zabel P., Baltimore D. Dependence of the activity of the poliovirus replicase on the host cell protein. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):423–429. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90516-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dmitrieva T. M., Agol V. I. Selective inhibition of the synthesis of single-stranded RNA of encephalomyocarditis virus by 2-(alpha-hydroxybenzyl)-benzimidazole in cell-free systems. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1974;45(1-2):17–26. doi: 10.1007/BF01240538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dmitrieva T. M., Shcheglova M. V., Agol V. I. Inhibition of activity of encephalomyocarditis virus-induced RNA polymerase by antibodies against cellular components. Virology. 1979 Jan 30;92(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E., Maizel J. V., Summers D. F. Soluble RNA polymerase complex from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1970 Apr;40(4):840–846. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90129-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Ehrenfeld E. Comparison of replication complexes synthesizing poliovirus RNA. Virology. 1981 May;111(1):33–46. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90651-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard M. In vitro synthesis of poliovirus ribonucleic acid: role of the replicative intermediate. J Virol. 1969 Apr;3(4):376–384. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.4.376-384.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett M. J., Rozenblatt S., Ambros V., Baltimore D. Separation and quantitation of intracellular forms of poliovirus RNA by agarose gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 14;16(12):2763–2767. doi: 10.1021/bi00631a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono R., Sasagawa A., Ishii K., Sugiura S., Ochi M. Pandemic of new type of conjunctivitis. Lancet. 1972 Jun 3;1(7762):1191–1194. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90921-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. F., Nomoto A., Detjen B. M., Wimmer E. A protein covalently linked to poliovirus genome RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):59–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell J. P., Levintow L. Kinetics of appearance of the products of poliovirus-induced RNA polymerase. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):999–1006. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90348-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J., Lundquist R. E., Maizel J. V., Jr Structural studies of the RNA component of the poliovirus replication complex. II. Characterization by electron microscopy and autoradiography. Virology. 1978 Apr;85(2):445–455. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90451-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovic R. R., Kono R., Yin-Murphy M., Sohier R., Schmidt N. J., Melnick J. L. Enterovirus type 70: the etiologic agent of pandemic acute haemorrhagic conjunctivitis. Bull World Health Organ. 1973;49(4):341–346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovic R. R., Schmidt N. J., Yin-Murphy M., Melnick J. L. Enterovirus etiology of the 1970 Singapore epidemic of acute conjunctivitis. Intervirology. 1974;4(2):119–127. doi: 10.1159/000149850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamura K., Sasagawa A., Tajiri E., Kono R. Growth characteristics of acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis (AHC) virus in monkey kidney cells. II. Temperature sensitivity of the isolates obtained at various epidemic areas. Intervirology. 1976;7(4-5):192–200. doi: 10.1159/000149952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamura K., Yamazaki S., Tajiri E., Kono R. Growth characteristics of acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis (AHC) virus in monkey kidney cells. I. Effect of temperature on viral growth. Intervirology. 1974;4(5):279–286. doi: 10.1159/000149860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamura K., Yamazaki S., Tajiri E., Kono R. Growth characteristics of acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis virus in monkey kidney cells. III. Viral RNA synthesis at permissive and nonpermissive temperatures. Intervirology. 1978;9(4):206–213. doi: 10.1159/000148938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Detjen B., Pozzatti R., Wimmer E. The location of the polio genome protein in viral RNAs and its implication for RNA synthesis. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):208–213. doi: 10.1038/268208a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer E., Arias M. L. In vitro transcription catalyzed by heat-treated human rotavirus. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):1–10. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.1-10.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda N., Miyamura K., Kono R., Yamazaki S. Characterization of a temperature-sensitive defect of enterovirus type 70. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):98–106. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.98-106.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takegami T., Kuhn R. J., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Membrane-dependent uridylylation of the genome-linked protein VPg of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7447–7451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takegami T., Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Membrane fractions active in poliovirus RNA replication contain VPg precursor polypeptides. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):33–47. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90316-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tershak D. R. Inhibition of poliovirus polymerase by guanidine in vitro. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):313–318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.313-318.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Testa D., Banerjee A. K. Initiation of RNA synthesis in vitro by vesicular stomatitis virus. Role of ATP. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):2053–2058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin F. H., Knight E., Jr In vivo and in vitro synthesis of human rhinovirus type 2 ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Jul;10(1):93–98. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.1.93-98.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]