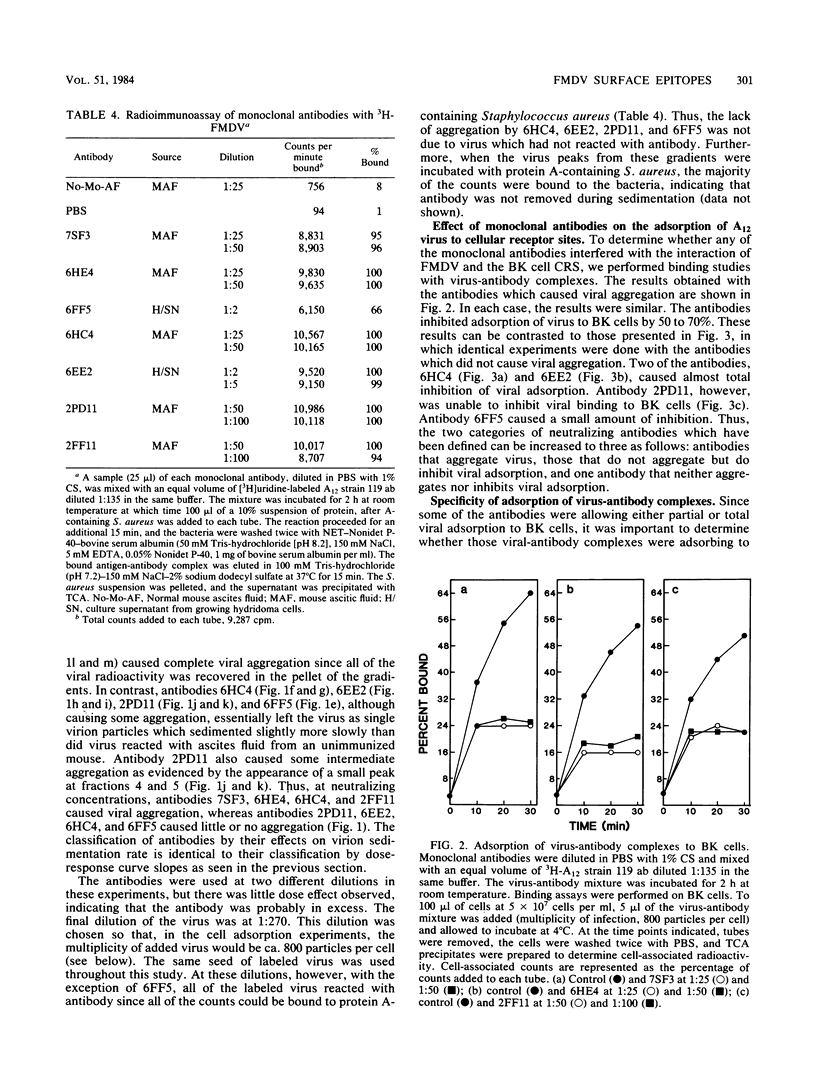
Abstract
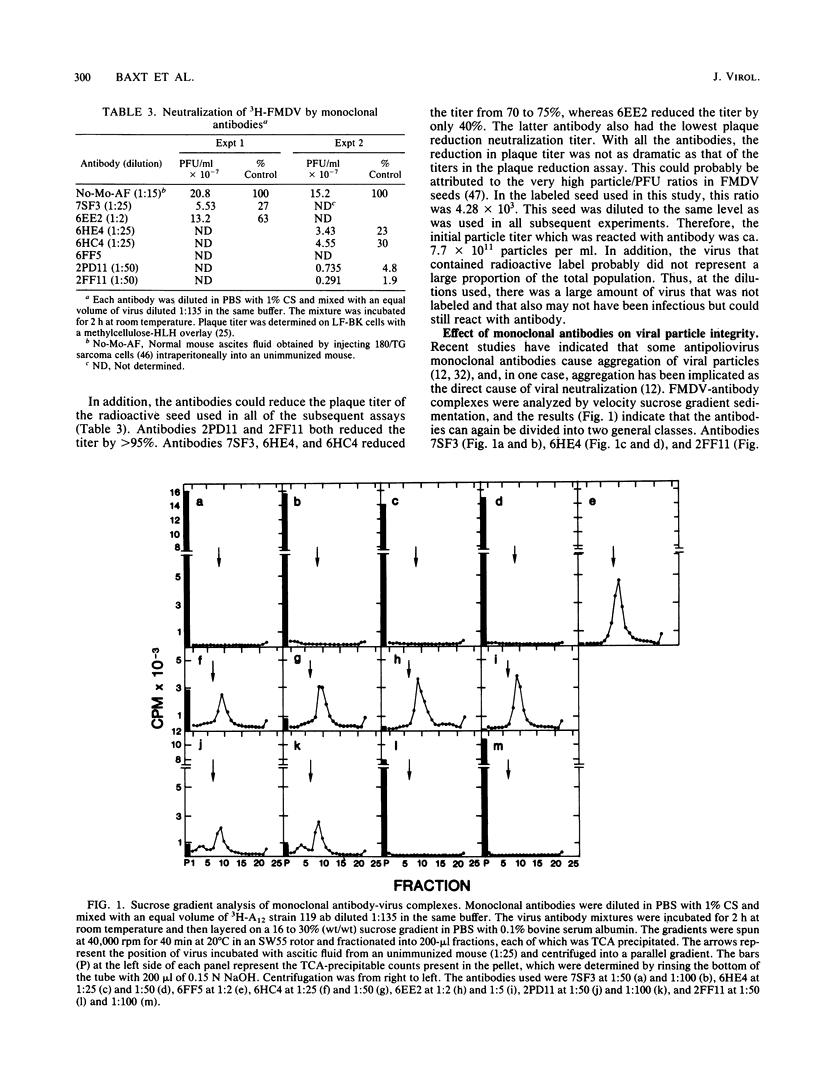
Foot-and-mouth disease virus structural protein VP1 elicits neutralizing and protective antibody and is probably the viral attachment protein which interacts with cellular receptor sites on cultured cells. To study the relationships between epitopes on the molecule related to neutralization and cell attachment, we tested monoclonal antibodies prepared against type A12 virus, isolated A12 VP1, and a CNBr-generated A12 VP1 fragment for neutralization and effect on viral absorption. The antibodies selected for analysis neutralized viral infectivity with varying efficiencies. One group of antibodies caused a high degree of viral aggregation and inhibited the adsorption of virus to cells by 50 to 70%. A second group of antibodies caused little or no viral aggregation but inhibited the adsorption of virus to cells by 80 to 90%. One antibody, which is specific for the intact virion, caused little viral aggregation and had no effect on the binding of virus to specific cellular receptor sites. Thus, at least three antigenic areas on the surface of foot-and-mouth disease virus which were involved in neutralization were demonstrated. One of the antigenic sites appears to have been responsible for interaction with the cellular receptor sites on the surface of susceptible cells.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BACHRACH H. L., TRAUTMAN R., BREESE S. S., Jr CHEMICAL PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF VIRTUALLY PURE FOOT-AND-MOUTH DISEASE VIRUS. Am J Vet Res. 1964 Mar;25:333–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachrach H. L., Moore D. M., McKercher P. D., Polatnick J. Immune and antibody responses to an isolated capsid protein of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1636–1641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachrach H. L., Morgan D. O., McKercher P. D., Moore D. M., Robertson B. H. Foot-and-mouth disease virus: immunogenicity and structure of fragments derived from capsid protein VP and of virus containing cleaved VP. Vet Microbiol. 1982 May;7(2):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(82)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachrach H. L., Morgan D. O., Moore D. M. Foot-and-mouth disease virus immunogenic capsid protein VPT: N-terminal sequences and immunogenic peptides obtained by CNBr and tryptic cleavages. Intervirology. 1979;12(2):65–72. doi: 10.1159/000149070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahnemann H. G. Binary ethylenimine as an inactivant for foot-and-mouth disease virus and its application for vaccine production. Arch Virol. 1975;47(1):47–56. doi: 10.1007/BF01315592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barteling S. J., Meloen R. H., Wagenaar F., Gielkens A. L. Isolation and characterization of trypsin-resistant O1 variants of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1979 May;43(2):383–393. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-2-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barteling S. J., Wagenaar F., Gielkens A. L. The positively charged structural virus protein (VP1) of foot-and-mouth disease virus (type O1) contains a highly basic part which may be involved in early virus-cell interaction. J Gen Virol. 1982 Oct;62(Pt 2):357–361. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-62-2-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxt B., Bachrach H. L. Early interactions of foot-and-mouth disease virus with cultured cells. Virology. 1980 Jul 15;104(1):42–55. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90364-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxt B., Bachrach H. L. The adsorption and degradation of foot-and-mouth disease virus by isolated BHK-21 cell plasma membranes. Virology. 1982 Jan 30;116(2):391–405. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90134-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blondel B., Akacem O., Crainic R., Couillin P., Horodniceanu F. Detection by monoclonal antibodies of an antigenic determinant critical for poliovirus neutralization present on VP1 and on heat-inactivated virions. Virology. 1983 Apr 30;126(2):707–710. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(83)80027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brioen P., Dekegel D., Boeyé A. Neutralization of poliovirus by antibody-mediated polymerization. Virology. 1983 Jun;127(2):463–468. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90159-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brioen P., Sijens R. J., Vrijsen R., Rombaut B., Thomas A. A., Jackers A., Boeyé A. Hybridoma antibodies to poliovirus N and H antigen. Arch Virol. 1982;74(4):325–330. doi: 10.1007/BF01314165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh D., Sangar D. V., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. Immunogenic and cell attachment sites of FMDV: further evidence for their location in a single capsid polypeptide. J Gen Virol. 1977 Apr;35(1):149–158. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-35-1-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A., DeLamarter J., Weiss S., Küpper H. Comparison of the major antigenic determinants of different serotypes of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):451–459. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.451-459.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan K. M. Immunochemical studies of foot-and-mouth disease. V. Antigenic variants of virus demonstrated by immunodiffusion analyses with 19S but not 7S antibodies. J Exp Med. 1969 Feb 1;129(2):333–350. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.2.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crainic R., Couillin P., Blondel B., Cabau N., Boué A., Horodniceanu F. Natural variation of poliovirus neutralization epitopes. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1217–1225. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1217-1225.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Jameson B. A., Lewis A. J., Larsen G. R., Wimmer E. Poliovirus neutralization epitopes: analysis and localization with neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):997–1005. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.997-1005.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Kao S. Y., Lewis A. J., Crainic R., Wimmer E. Functional basis of poliovirus neutralization determined with monospecific neutralizing antibodies. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):466–474. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.466-474.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Ostapchuk P., Wimmer E. Bivalent attachment of antibody onto poliovirus leads to conformational alteration and neutralization. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):547–550. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.547-550.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. M., Minor P. D., Schild G. S., Almond J. W. Critical role of an eight-amino acid sequence of VP1 in neutralization of poliovirus type 3. Nature. 1983 Aug 4;304(5925):459–462. doi: 10.1038/304459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M., Schild G. C., Minor P. D., Yates P. J., Spitz M. A hybridoma cell line secreting antibody to poliovirus type 3 D-antigen: detection in virus harvest of two D-antigen populations. J Gen Virol. 1981 Jun;54(Pt 2):437–442. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-54-2-437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubman M. J., Baxt B., Bachrach H. L. Foot-and-mouth disease virion RNA: studies on the relation between the length of its 3'-poly(A) segment and infectivity. Virology. 1979 Aug;97(1):22–31. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90369-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubman M. J. In vitro morphogenesis of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):760–765. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.760-765.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy M. M., Moore D. M. Neutralization of foot-and-mouth disease virus. I. Sensitization of the 140S virion by antibody also reactive with the 12S protein subunit. J Gen Virol. 1981 Aug;55(Pt 2):415–427. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-55-2-415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy M. M., Moore D. M. Neutralization of foot-and-mouth disease virus. II. Further parameters related to the sensitization of the 140S virion by antibody. J Gen Virol. 1982 Oct;62(Pt 2):287–295. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-62-2-287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haresnape J. M., King A. M., McCahon D. Location of an immunizing determinant within polypeptide VP1 of type O aphthovirus. J Gen Virol. 1983 Nov;64(Pt 11):2357–2365. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-11-2357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haresnape J. M., McCahon D. Four independent antigenic determinants on the capsid polypeptides of aphthovirus. J Gen Virol. 1983 Nov;64(Pt 11):2345–2355. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-11-2345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey D. D., Kew O. M., Feorino P. M. Monoclonal antibodies of four different specificities for neutralization of type 1 polioviruses. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):841–843. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.841-843.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Icenogle J., Gilbert S. F., Grieves J., Anderegg J., Rueckert R. A neutralizing monoclonal antibody against poliovirus and its reaction with related antigens. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):211–215. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Icenogle J., Shiwen H., Duke G., Gilbert S., Rueckert R., Anderegg J. Neutralization of poliovirus by a monoclonal antibody: kinetics and stoichiometry. Virology. 1983 Jun;127(2):412–425. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90154-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaaden O. R., Adam K. H., Strohmeier K. Induction of neutralizing antibodies and immunity in vaccinated guinea pigs by cyanogen bromide-peptides of VP3 of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Feb;34(2):397–400. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-2-397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleid D. G., Yansura D., Small B., Dowbenko D., Moore D. M., Grubman M. J., McKercher P. D., Morgan D. O., Robertson B. H., Bachrach H. L. Cloned viral protein vaccine for foot-and-mouth disease: responses in cattle and swine. Science. 1981 Dec 4;214(4525):1125–1129. doi: 10.1126/science.6272395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel B. Neutralization of animal viruses. Adv Virus Res. 1978;23:205–268. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60101-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel B. Neutralization of poliovirus: a hypothesis to explain the mechanism and the one-hit character of the neutralization reaction. Virology. 1976 Feb;69(2):500–510. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90480-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel B. The interaction of neutralized poliovirus with HeLa cells. I. Adsorption. Virology. 1967 Feb;31(2):238–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90167-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCullough K. C., Butcher R. Monoclonal antibodies against foot-and-mouth disease virus 146S and 12S particles. Arch Virol. 1982;74(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF01320777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloen R. H., Briaire J., Woortmeyer R. J., van Zaane D. The main antigenic determinant detected by neutralizing monoclonal antibodies on the intact foot-and-mouth disease virus particle is absent from isolated VPI. J Gen Virol. 1983 May;64(Pt 5):1193–1198. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-5-1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Bootman J., Evans D. M., Ferguson M., Reeve P., Spitz M., Stanway G., Cann A. J., Hauptmann R. Location and primary structure of a major antigenic site for poliovirus neutralization. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):674–679. doi: 10.1038/301674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Ferguson M., Mackay A., Magrath D. I., John A., Yates J. P., Spitz M. Genetic and antigenic variation in type 3 polioviruses: characterization of strains by monoclonal antibodies and T1 oligonucleotide mapping. J Gen Virol. 1982 Aug;61(Pt 2):167–176. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-61-2-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson B. H., Moore D. M., Grubman M. J., Kleid D. G. Identification of an exposed region of the immunogenic capsid polypeptide VP1 on foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):311–316. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.311-316.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartorelli A. C., Fischer D. S., Downs W. G. Use of sarcoma 180/TG to prepare hyperimmune ascitic fluid in the mouse. J Immunol. 1966 Apr;96(4):676–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi K., Franke A. J., Baxt B. Competition for cellular receptor sites among selected aphthoviruses. Arch Virol. 1982;74(1):53–64. doi: 10.1007/BF01320782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strohmaier K., Franze R., Adam K. H. Location and characterization of the antigenic portion of the FMDV immunizing protein. J Gen Virol. 1982 Apr;59(Pt 2):295–306. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-59-2-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautman R., Harris W. F. Modeling and computer stimulation approach to the mechanism of foot-and-mouth disease virus neutralization assays. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(8):831–841. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb02158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner G. G., Card J. L., Cowan K. M. Immunochemical studies of foot-and-mouth disease. VII. Characterization of foot-and-mouth disease virus concentrated by polyethylene glycol precipitation. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1970;30(4):343–352. doi: 10.1007/BF01258364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Werf S., Wychowski C., Bruneau P., Blondel B., Crainic R., Horodniceanu F., Girard M. Localization of a poliovirus type 1 neutralization epitope in viral capsid polypeptide VP1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5080–5084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



