Abstract
Diabetic nephropathy is the main cause of the increased morbidity and mortality in patients with insulin dependent diabetes. The prevalence of microalbuminuria was determined in adults with insulin dependent diabetes of five or more years' duration that had started before the age of 41. All eligible patients (n=982) attending a diabetes clinic were asked to collect a 24 hour urine sample for analysis of albumin excretion by radio-immunoassay; 957 patients complied. Normoalbuminuria was defined as urinary albumin excretion of ≤30 mg/24 h (n=562), microalbuminuria as 31-299 mg/24 h (n=215), and macroalbuminuria as ≥300 mg/24 h (n=180). The prevalence of microalbuminuria and macroalbuminuria was significantly higher in patients whose diabetes had developed before rather than after the age of 20. The prevalence of arterial hypertension increased with increased albuminuria, being 19%, 30%, and 65% in patients with normoalbuminuria, microalbuminuria, and macroalbuminuria respectively. The prevalence of proliferative retinopathy and blindness rose with increasing albuminuria, being 12% and 1·4%, respectively, in patients with normoalbuminuria, 28% and 5·6% in those with microalbuminuria and 58% and 10·6% in those with macroalbuminuria. An abnormal vibratory perception threshold was more common in patients with microalbuminuria (31%) and macroalbuminuria (50%) than in those with normoalbuminuria (21%).
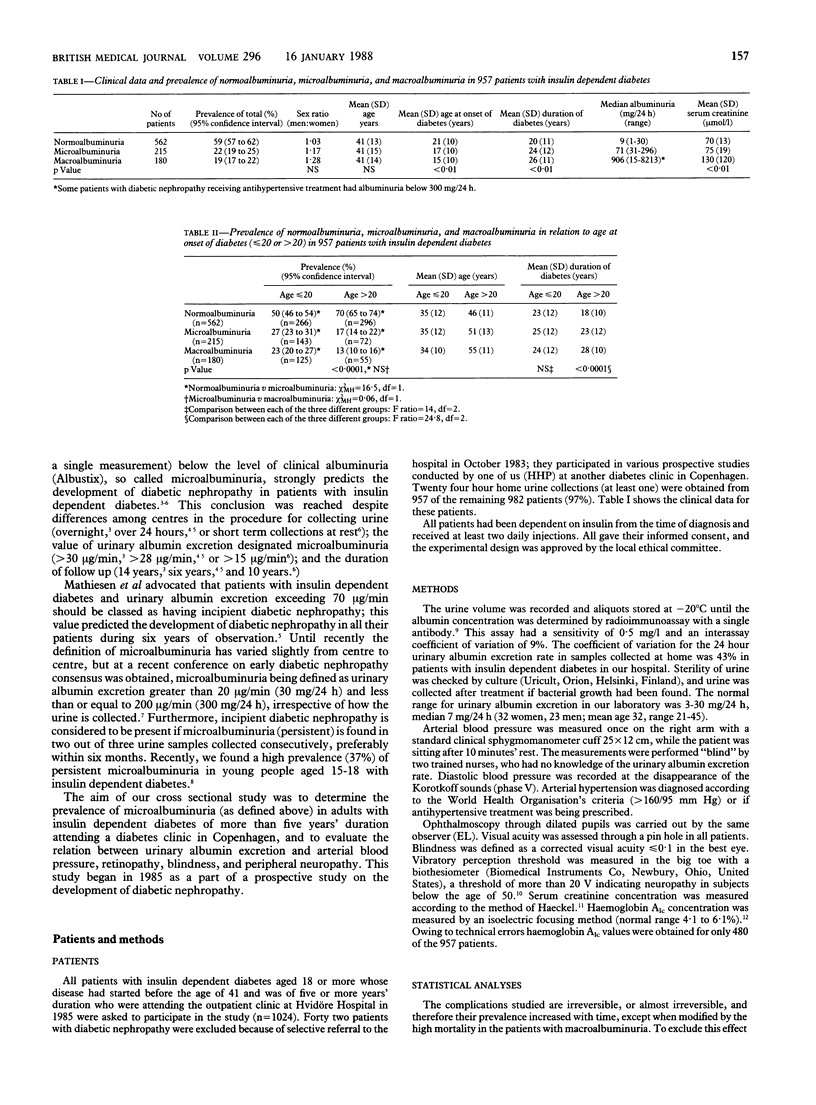
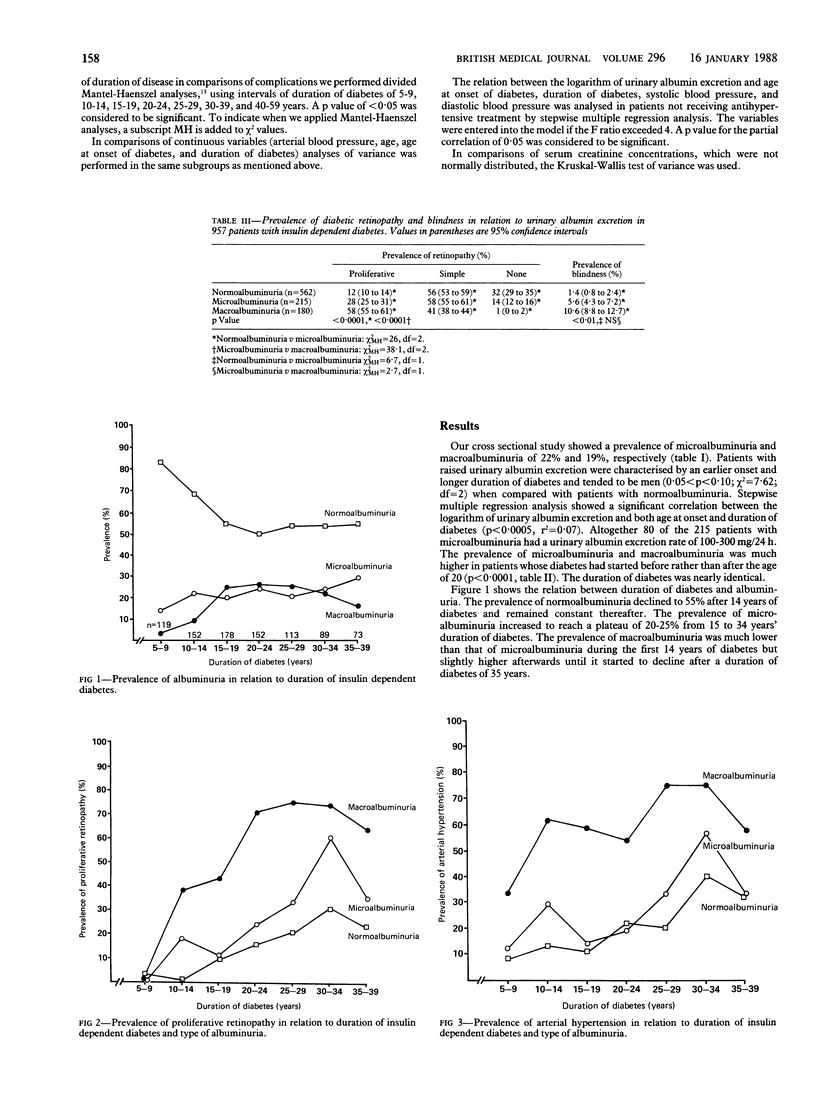
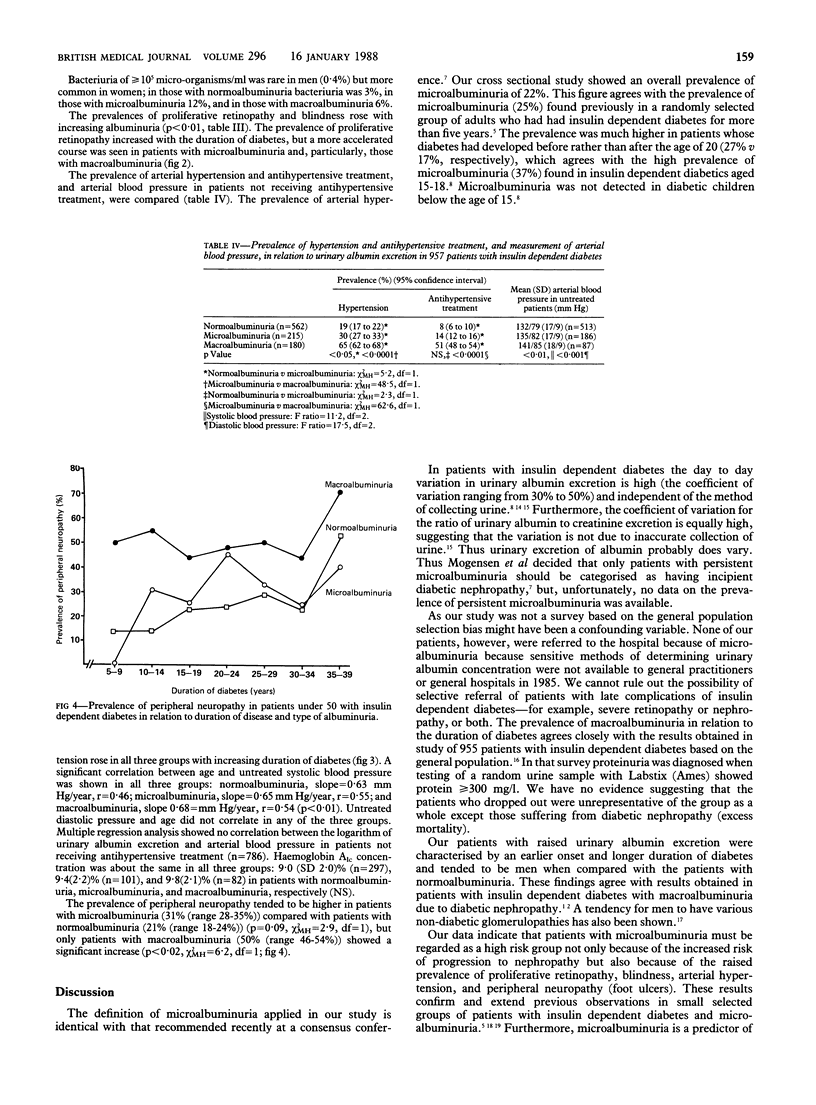
This study found a high prevalence (22%) of microalbuminuria, which is predictive of the later development of diabetic nephropathy. Microalbuminuria is also characterised by an increased prevalence of arterial hypertension, proliferative retinopathy, blindness, and peripheral neuropathy. Thus, urinary excretion of albumin should be monitored routinely in patients with insulin dependent diabetes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnett A. H., Dallinger K., Jennings P., Fletcher J., Odugbesan O. Microalbuminuria and diabetic retinopathy. Lancet. 1985 Jan 5;1(8419):53–54. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bending J. J., Viberti G. C., Bilous R. W., Keen H. Eight-month correction of hyperglycemia in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus is associated with a significant and sustained reduction of urinary albumin excretion rates in patients with microalbuminuria. Diabetes. 1985 Aug;34 (Suppl 3):69–73. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.3.s69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkman J., Rifkin H. Unilateral nodular diabetic glomerulosclerosis (Kimmelstiel-Wilson): report of a case. Metabolism. 1973 May;22(5):715–722. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90243-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björck S., Nyberg G., Mulec H., Granerus G., Herlitz H., Aurell M. Beneficial effects of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition on renal function in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Aug 23;293(6545):471–474. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6545.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borch-Johnsen K., Andersen P. K., Deckert T. The effect of proteinuria on relative mortality in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1985 Aug;28(8):590–596. doi: 10.1007/BF00281993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke E. A., Anderson T. W. Does screening by "Pap" smears help prevent cervical cancer? A case-control study. Lancet. 1979 Jul 7;2(8132):1–4. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90172-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldt-Rasmussen B., Mathiesen E. R., Deckert T. Effect of two years of strict metabolic control on progression of incipient nephropathy in insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1986 Dec 6;2(8519):1300–1304. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91433-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haeckel R. Simplified determinations of the "true" creatinine concentration in serum and urine. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1980 Jul;18(7):385–394. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1980.18.7.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hommel E., Mathiesen E., Edsberg B., Bahnsen M., Parving H. H. Acute reduction of arterial blood pressure reduces urinary albumin excretion in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients with incipient nephropathy. Diabetologia. 1986 Apr;29(4):211–215. doi: 10.1007/BF00454877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett R. J., Viberti G. C., Argyropoulos A., Hill R. D., Mahmud U., Murrells T. J. Microalbuminuria predicts mortality in non-insulin-dependent diabetics. Diabet Med. 1984 May;1(1):17–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1984.tb01915.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krolewski A. S., Warram J. H., Christlieb A. R., Busick E. J., Kahn C. R. The changing natural history of nephropathy in type I diabetes. Am J Med. 1985 May;78(5):785–794. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90284-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANTEL N., HAENSZEL W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1959 Apr;22(4):719–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marre M., Leblanc H., Suarez L., Guyenne T. T., Ménard J., Passa P. Converting enzyme inhibition and kidney function in normotensive diabetic patients with persistent microalbuminuria. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Jun 6;294(6585):1448–1452. doi: 10.1136/bmj.294.6585.1448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathiesen E. R., Oxenbøll B., Johansen K., Svendsen P. A., Deckert T. Incipient nephropathy in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes. Diabetologia. 1984 Jun;26(6):406–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00262210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathiesen E. R., Saurbrey N., Hommel E., Parving H. H. Prevalence of microalbuminuria in children with type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1986 Sep;29(9):640–643. doi: 10.1007/BF00869263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauer S. M., Steffes M. W., Azar S., Sandberg S. K., Brown D. M. The effects of Goldblatt hypertension on development of the glomerular lesions of diabetes mellitus in the rat. Diabetes. 1978 Jul;27(7):738–744. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.7.738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E., Chachati A., Christensen C. K., Close C. F., Deckert T., Hommel E., Kastrup J., Lefebvre P., Mathiesen E. R., Feldt-Rasmussen B. Microalbuminuria: an early marker of renal involvement in diabetes. Uremia Invest. 1985;9(2):85–95. doi: 10.3109/08860228509088195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E., Christensen C. K. Predicting diabetic nephropathy in insulin-dependent patients. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jul 12;311(2):89–93. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198407123110204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. Long-term antihypertensive treatment inhibiting progression of diabetic nephropathy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Sep 11;285(6343):685–688. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6343.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. Microalbuminuria predicts clinical proteinuria and early mortality in maturity-onset diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1984 Feb 9;310(6):356–360. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198402093100605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen H. B. Quantitative determination of hemoglobin A1c by thin-layer isoelectric focusing. J Chromatogr. 1980 Jun 13;182(3-4):325–333. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)81481-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parving H. H., Andersen A. R., Smidt U. M., Hommel E., Mathiesen E. R., Svendsen P. A. Effect of antihypertensive treatment on kidney function in diabetic nephropathy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Jun 6;294(6585):1443–1447. doi: 10.1136/bmj.294.6585.1443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parving H. H., Andersen A. R., Smidt U. M., Oxenbøll B., Edsberg B., Christiansen J. S. Diabetic nephropathy and arterial hypertension. Diabetologia. 1983 Jan;24(1):10–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00275939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parving H. H., Andersen A. R., Smidt U. M., Svendsen P. A. Early aggressive antihypertensive treatment reduces rate of decline in kidney function in diabetic nephropathy. Lancet. 1983 May 28;1(8335):1175–1179. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92462-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parving H. H., Oxenbøll B., Svendsen P. A., Christiansen J. S., Andersen A. R. Early detection of patients at risk of developing diabetic nephropathy. A longitudinal study of urinary albumin excretion. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1982 Aug;100(4):550–555. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1000550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINESS I. Diabetic neuropathy. Vibration sense and abnormal tendon reflexes in diabetics. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1963;394:1–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svejgaard A., Jakobsen B. K., Platz P., Ryder L. P., Nerup J., Christy M., Borch-Johnsen K., Parving H. H., Deckert T., Mølsted-Pedersen L. HLA associations in insulin-dependent diabetes: search for heterogeneity in different groups of patients from a homogeneous population. Tissue Antigens. 1986 Oct;28(4):237–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1986.tb00489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viberti G. C., Hill R. D., Jarrett R. J., Argyropoulos A., Mahmud U., Keen H. Microalbuminuria as a predictor of clinical nephropathy in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1982 Jun 26;1(8287):1430–1432. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92450-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman M., Viberti G., Mackintosh D., Jarrett R. J., Keen H. Glycaemia, arterial pressure and micro-albuminuria in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1984 Jun;26(6):401–405. doi: 10.1007/BF00262209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


