Abstract
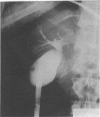
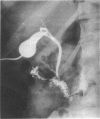
A percutaneous method was used to remove stones from otherwise normal gall bladders, as assessed by cholecystography and ultrasonography. The procedure was performed in a single stage under general anaesthesia, adopting the method and instruments used for one stage percutaneous nephrolithotomy. A Foley catheter was left in the gall bladder and the system checked with contrast at 10 days to ensure free drainage and exclude residual calculi. Seven out of eight patients had a successful percutaneous cholecystolithotomy. An adequate track could not be secured in one man; he had an uneventful cholecystectomy under the same anaesthetic. Follow up at three months of the seven patients showed no calculi and no complications.
Percutaneous cholecystolithotomy may prove complementary to extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy in patients in whom there is difficulty focusing the shock waves on the gall bladder or who have had incomplete disintegration of stones.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Charig C. R., Webb D. R., Payne S. R., Wickham J. E. Comparison of treatment of renal calculi by open surgery, percutaneous nephrolithotomy, and extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Mar 29;292(6524):879–882. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6524.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das G., Dick J., Bailey M. J., Fletcher M. S., Webb D. R., Kellett M. J., Whitfield H. N., Wickham J. E. Extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy: first 1000 cases at the London Stone Clinic. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Oct 10;295(6603):891–893. doi: 10.1136/bmj.295.6603.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerlan R. K., Jr, LaBerge J. M., Ring E. J. Percutaneous cholecystolithotomy: preliminary experience. Radiology. 1985 Dec;157(3):653–656. doi: 10.1148/radiology.157.3.4059554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. F., Tweedle D. E. Endoscopic management of common duct stones without cholecystectomy. Br J Surg. 1987 Mar;74(3):209–211. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800740320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neoptolemos J. P., Carr-Locke D. L., Fraser I., Fossard D. P. The management of common bile duct calculi by endoscopic sphincterotomy in patients with gallbladders in situ. Br J Surg. 1984 Jan;71(1):69–71. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800710123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse D. M., Hawkins I. F., Jr, Shaver R., Vogel S. Percutaneous cholecystostomy in acute cholecystitis and common duct obstruction. Radiology. 1984 Aug;152(2):365–367. doi: 10.1148/radiology.152.2.6739800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauerbruch T., Delius M., Paumgartner G., Holl J., Wess O., Weber W., Hepp W., Brendel W. Fragmentation of gallstones by extracorporeal shock waves. N Engl J Med. 1986 Mar 27;314(13):818–822. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198603273141304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teplick S. K., Haskin P. H. Monooctanoin perfusion for in vivo dissolution of biliary stones. A series of 11 patients. Radiology. 1984 Nov;153(2):379–383. doi: 10.1148/radiology.153.2.6484170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]