Abstract
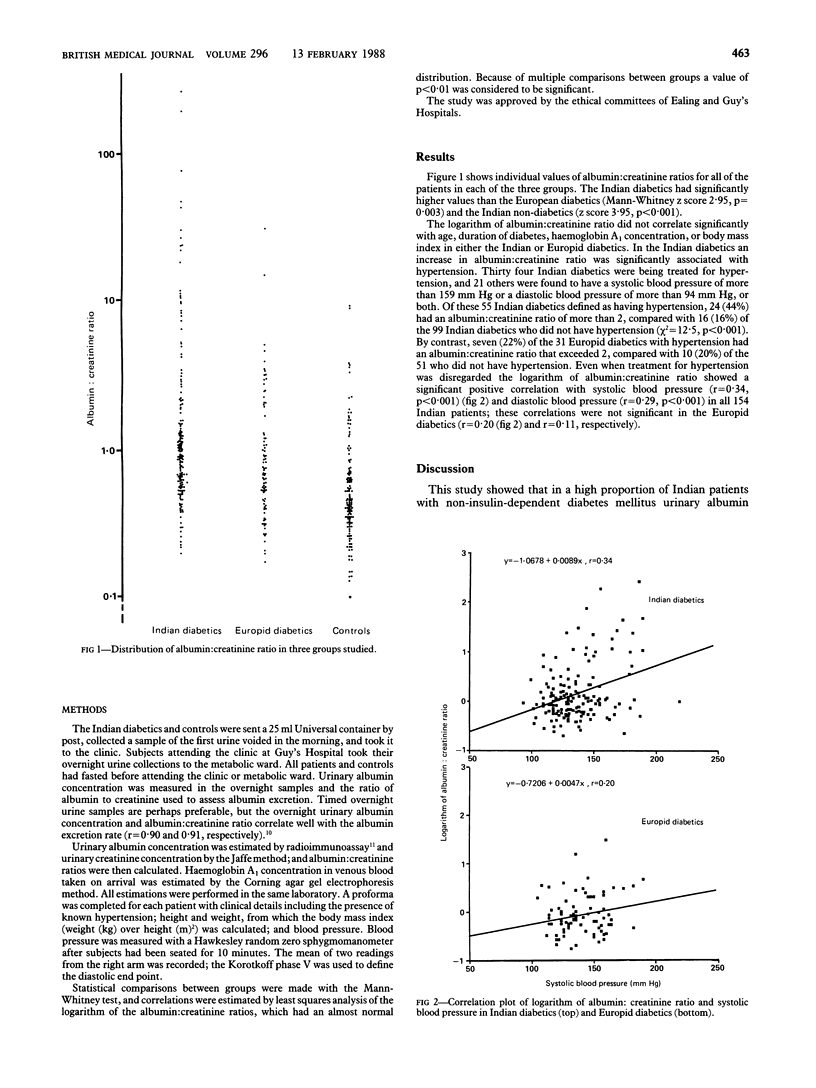
Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus is strikingly common in British Indians, but their susceptibility to diabetic complications is unknown. The ratio of albumin to creatinine concentrations was measured in samples of the first urine voided in the morning in 154 Indian and 82 Europid patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes and in a control group of 129 non-diabetic Indians. The ratio was significantly higher in the Indian patients than in the Europid patients and the Indian controls. There were no significant correlations between the logarithm of the albumin: creatinine ratio and age, known duration of diabetes, haemoglobin A1 concentration, or body mass index within either diabetic group. Hypertension and raised albumin:creatinine ratio were significantly associated, and significant correlations were seen between the logarithm of the albumin:creatinine ratio and systolic and diastolic blood pressures in the Indian but not the Europid diabetics.
Because of the high prevalence of diabetes at a relatively early age in Indians, nephropathy may emerge as an important clinical problem.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Damsgaard E. M., Mogensen C. E. Microalbuminuria in elderly hyperglycaemic patients and controls. Diabet Med. 1986 Sep-Oct;3(5):430–435. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1986.tb00785.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman B. J. For debate...Caucasian. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Mar 3;288(6418):696–698. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6418.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatling W., Knight C., Hill R. D. Screening for early diabetic nephropathy: which sample to detect microalbuminuria? Diabet Med. 1985 Nov;2(6):451–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1985.tb00681.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett R. J., Viberti G. C., Argyropoulos A., Hill R. D., Mahmud U., Murrells T. J. Microalbuminuria predicts mortality in non-insulin-dependent diabetics. Diabet Med. 1984 May;1(1):17–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1984.tb01915.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEEN H., CHLOUVERAKIS C. AN IMMUNOASSAY METHOD FOR URINARY ALBUMIN AT LOW CONCENTRATIONS. Lancet. 1963 Nov 2;2(7314):913–914. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)90620-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen H., Chlouverakis C., Fuller J., Jarrett R. J. The consomitants of raised blood sugar: studies in newly-detected hyperglycaemics. II. Urinary albumin excretion, blood pressure and their relation to blood sugar levels. Guys Hosp Rep. 1969;118(2):247–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather H. M., Keen H. The Southall Diabetes Survey: prevalence of known diabetes in Asians and Europeans. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Oct 19;291(6502):1081–1084. doi: 10.1136/bmj.291.6502.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E., Christensen C. K. Predicting diabetic nephropathy in insulin-dependent patients. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jul 12;311(2):89–93. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198407123110204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. Microalbuminuria predicts clinical proteinuria and early mortality in maturity-onset diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1984 Feb 9;310(6):356–360. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198402093100605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholl C. G., Levy J. C., Mohan V., Rao P. V., Mather H. M. Asian diabetes in Britain: a clinical profile. Diabet Med. 1986 May;3(3):257–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1986.tb00757.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parving H. H., Oxenbøll B., Svendsen P. A., Christiansen J. S., Andersen A. R. Early detection of patients at risk of developing diabetic nephropathy. A longitudinal study of urinary albumin excretion. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1982 Aug;100(4):550–555. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1000550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen E. B., Mogensen C. E. Effect of antihypertensive treatment on urinary albumin excretion, glomerular filtration rate, and renal plasma flow in patients with essential hypertension. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1976 May;36(3):231–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samanta A., Burden A. C., Feehally J., Walls J. Diabetic renal disease: differences between Asian and white patients. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Aug 9;293(6543):366–367. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6543.366-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viberti G. C., Hill R. D., Jarrett R. J., Argyropoulos A., Mahmud U., Keen H. Microalbuminuria as a predictor of clinical nephropathy in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1982 Jun 26;1(8287):1430–1432. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92450-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


