Abstract
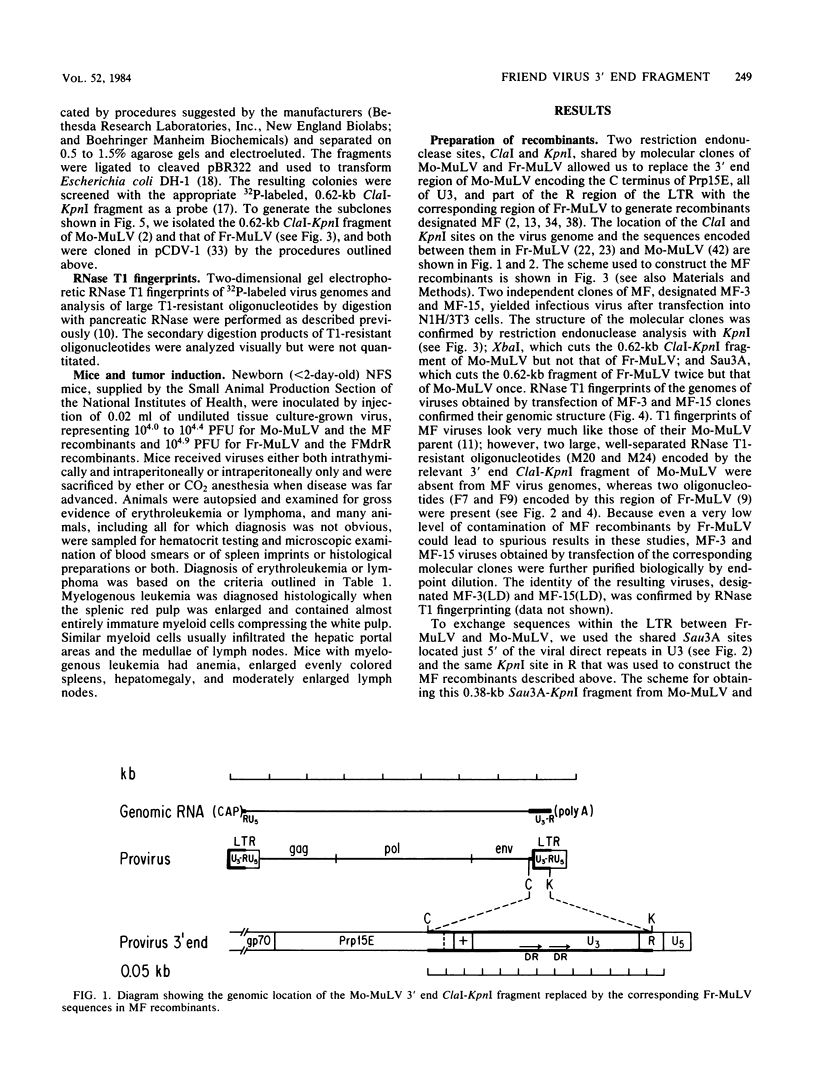
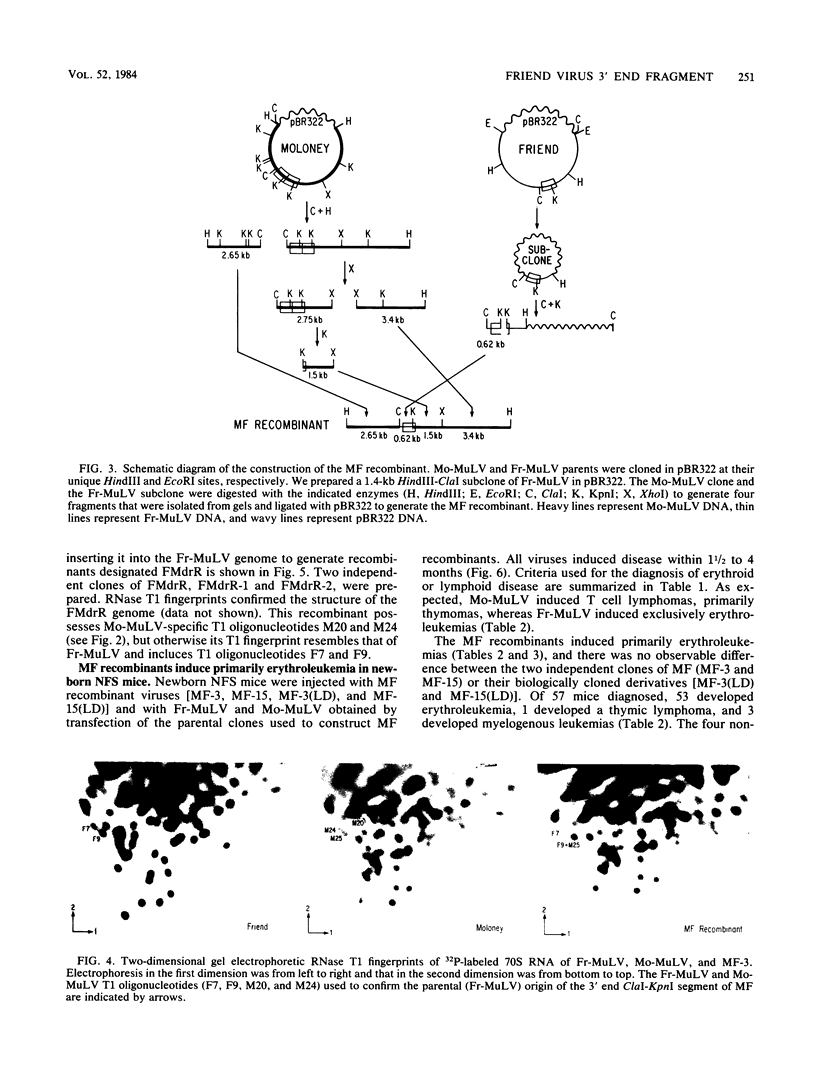
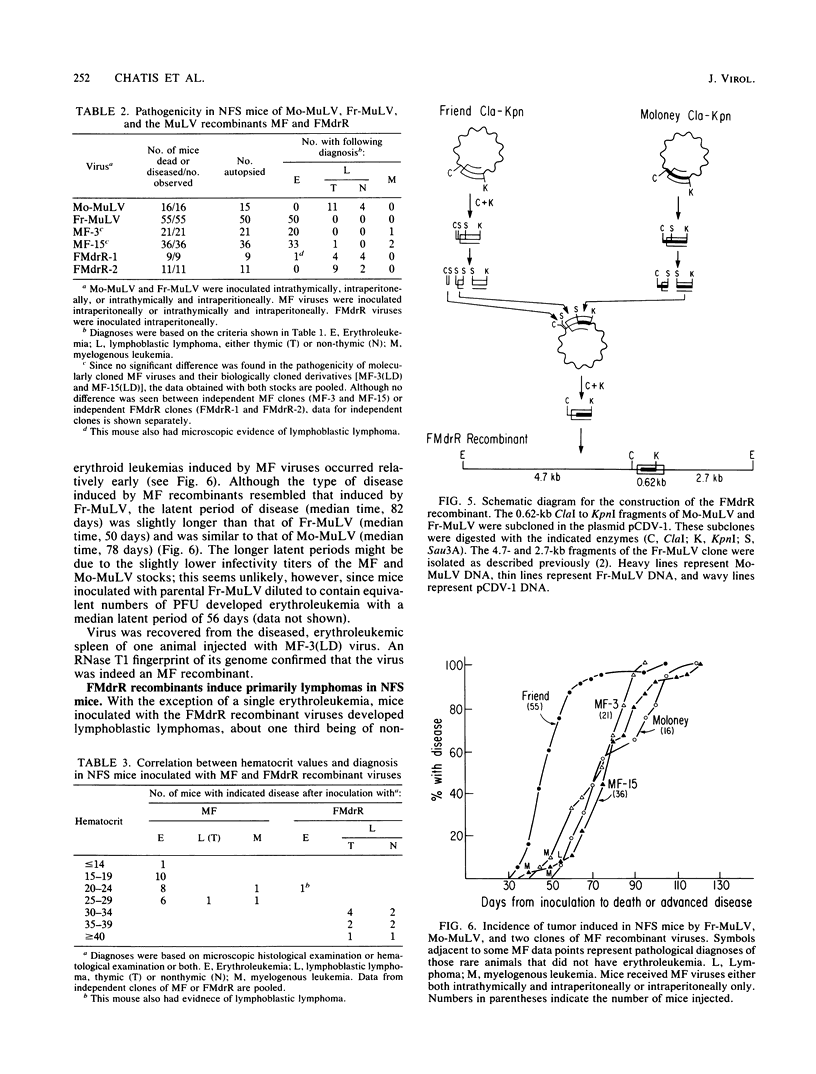
Nondefective Friend helper murine leukemia virus (Fr-MuLV) induces primarily erythroleukemias in NFS mice, whereas Moloney murine leukemia virus (Mo-MuLV) induces T cell lymphomas. Using molecular clones of these two viruses, we constructed a recombinant in which a 0.62-kilobase fragment encompassing the U3 region at the 3' end of the Fr-MuLV genome replaced the corresponding region of Mo-MuLV. The recombinant virus obtained by transfection of this clone, whose genome is derived primarily from Mo-MuLV, induces almost exclusively erythroleukemias in NFS mice. This and the previous result of Chatis et al. (Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80:4408-4411), showing that the reciprocal recombinant whose genome is primarily derived from Fr-MuLV induces almost exclusively lymphomas, argue that a strong determinant of the distinct disease specificities of Fr-MuLV and Mo-MuLV lies in this 3' end 0.62-kilobase fragment which contains the putative virus enhancers. To more precisely define this determinant, we have begun to construct recombinants in which smaller 3' end fragments of the Fr-MuLV and Mo-MuLV genomes are exchanged. Analysis of the first such recombinant showed that Fr-MuLV can be converted to a lymphoma-inducing virus in NFS mice by substitution of a 0.38-kilobase fragment encompassing the virus enhancers in U3 with the corresponding region of the Mo-MuLV genome.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in virions of RNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1209–1211. doi: 10.1038/2261209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Holland C. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. Role for the 3' end of the genome in determining disease specificity of Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4408–4411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen I. S., McLaughlin J., Golde D. W. Long terminal repeats of human T-cell leukaemia virus II genome determine target cell specificity. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):276–279. doi: 10.1038/309276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran L. M., Adams J. M., Dunn A. R., Cory S. Murine T lymphomas in which the cellular myc oncogene has been activated by retroviral insertion. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90306-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuypers H. T., Selten G., Quint W., Zijlstra M., Maandag E. R., Boelens W., van Wezenbeek P., Melief C., Berns A. Murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphomagenesis: integration of proviruses in a distinct chromosomal region. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Rassart E., Jolicoeur P. Thymotropism of murine leukemia virus is conferred by its long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4203–4207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Villemur R., Jolicoeur P. The high leukemogenic potential of Gross passage A murine leukemia virus maps in the region of the genome corresponding to the long terminal repeat and to the 3' end of env. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):24–32. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.24-32.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Gautsch J. W., Jensen F. C., Lerner R. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Biochemical evidence that MCF murine leukemia viruses are envelope (env) gene recombinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4676–4680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L., Nunn M., Duesberg P. H., Troxler D., Scolnick E. RNAs of defective and nondefective components of Friend anemia and polycythemia virus strains identified and compared. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):823–835. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faller D. V., Hopkins N. RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides of B-tropic murine leukemia virus from BALB/c and five of its NB-tropic derivatives. J Virol. 1977 Jul;23(1):188–195. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.1.188-195.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faller D. V., Hopkins N. T1 oligonucleotide maps of Moloney and HIX murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1978 Oct 15;90(2):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90310-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. K., Lewis W. G., Crittenden L. B., Kung H. J. Activation of the cellular oncogene c-erbB by LTR insertion: molecular basis for induction of erythroblastosis by avian leukosis virus. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):357–368. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90417-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilboa E., Goff S., Shields A., Yoshimura F., Mitra S., Baltimore D. In vitro synthesis of a 9 kbp terminally redundant DNA carrying the infectivity of Moloney murine leukemia virus. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):863–874. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90101-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Clonal cells lines from a feral mouse embryo which lack host-range restrictions for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):128–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Neel B. G., Astrin S. M. Activation of a cellular onc gene by promoter insertion in ALV-induced lymphoid leukosis. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):475–480. doi: 10.1038/290475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jainchill J. L., Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J. Murine sarcoma and leukemia viruses: assay using clonal lines of contact-inhibited mouse cells. J Virol. 1969 Nov;4(5):549–553. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.5.549-553.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W., Hunsmann G., Friedrich R. Nucleotide sequence of the envelope gene of Friend murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.1-9.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W., Zimmermann W., Oliff A., Friedrich R. Molecular analysis of the envelope gene and long terminal repeat of Friend mink cell focus-inducing virus: implications for the functions of these sequences. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):828–840. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.828-840.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Gruss P., Pozzatti R., Khoury G. Characterization of enhancer elements in the long terminal repeat of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):183–189. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.183-189.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Khoury G., Gorman C., Howard B., Gruss P. Host-specific activation of transcription by tandem repeats from simian virus 40 and Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6453–6457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemay G., Jolicoeur P. Rearrangement of a DNA sequence homologous to a cell-virus junction fragment in several Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced rat thymomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):38–42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz J., Celander D., Crowther R. L., Patarca R., Perkins D. W., Haseltine W. A. Determination of the leukaemogenicity of a murine retrovirus by sequences within the long terminal repeat. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):467–470. doi: 10.1038/308467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson B., Khoury G., Vande Woude G., Gruss P. Activation of SV40 genome by 72-base pair tandem repeats of Moloney sarcoma virus. Nature. 1982 Feb 18;295(5850):568–572. doi: 10.1038/295568a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linemeyer D. L., Ruscetti S. K., Scolnick E. M., Evans L. H., Duesberg P. H. Biological activity of the spleen focus-forming virus is encoded by a molecularly cloned subgenomic fragment of spleen focus-forming virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1401–1405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lung M. L., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. H. Large RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides encoding p15E and the U3 region of the long terminal repeat distinguish two biological classes of mink cell focus-forming type C viruses of inbred mice. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):275–290. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.275-290.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lung M. L., Hering C., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. Analysis of the genomes of mink cell focus-inducing murine type-C viruses: a progress report. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):1269–1274. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath M. S., Weissman I. L. AKR leukemogenesis: identification and biological significance of thymic lymphoma receptors for AKR retroviruses. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):65–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90295-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliff A. I., Hager G. L., Chang E. H., Scolnick E. M., Chan H. W., Lowy D. R. Transfection of molecularly cloned Friend murine leukemia virus DNA yields a highly leukemogenic helper-independent type C virus. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):475–486. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.475-486.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliff A., Collins L., Mirenda C. Molecular cloning of Friend mink cell focus-inducing virus: identification of mink cell focus-inducing virus-like messages in normal and transformed cells. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):542–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.542-546.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliff A., Linemeyer D., Ruscetti S., Lowe R., Lowy D. R., Scolnick E. Subgenomic fragment of molecular cloned Friend murine leukemia virus DNA contains the gene(s) responsible for Friend murine leukemia virus-induced disease. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):924–936. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.924-936.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliff A., Ruscetti S. A 2.4-kilobase-pair fragment of the Friend murine leukemia virus genome contains the sequences responsible for friend murine leukemia virus-induced erythroleukemia. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):718–725. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.718-725.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliff A., Ruscetti S., Douglass E. C., Scolnick E. Isolation of transplantable erythroleukemia cells from mice infected with helper-independent Friend murine leukemia virus. Blood. 1981 Aug;58(2):244–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne G. S., Courtneidge S. A., Crittenden L. B., Fadly A. M., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Analysis of avian leukosis virus DNA and RNA in bursal tumours: viral gene expression is not required for maintenance of the tumor state. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):311–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90127-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. L., Blais B. M., Tsichlis P. N., Coffin J. M. At least two regions of the viral genome determine the oncogenic potential of avian leukosis viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1225–1229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver J. E., Fredrickson T. N. Susceptibility to Friend helper virus leukemias in CXB recombinant inbred mice. J Exp Med. 1983 Nov 1;158(5):1693–1702. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.5.1693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver J. Role of mink cell focus-inducing virus in leukemias induced by Friend ecotropic virus. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):872–877. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.872-877.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tambourin P. E., Wendling F., Jasmin C., Smadja-Joffe F. The physiopathology of Friend leukemia. Leuk Res. 1979;3(3):117–129. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(79)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. Y., Coffin J. M. Genetic alterations of RNA leukemia viruses associated with the development of spontaneous thymic leukemia in AKR/J mice. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):416–426. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.416-426.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troxler D. H., Ruscetti S. K., Linemeyer D. L., Scolnick E. M. Helper-independent and replication-defective erythroblastosis-inducing viruses contained within anemia-inducing Friend virus complex (FV-A). Virology. 1980 Apr 15;102(1):28–45. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90067-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troxler D. H., Yuan E., Linemeyer D., Ruscetti S., Scolnick E. M. Helper-independent mink cell focus-inducing strains of Friend murine type-C virus: potential relationship to the origin of replication-defective spleen focus-forming virus. J Exp Med. 1978 Sep 1;148(3):639–653. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.3.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Coffin J. M. Recombinants between endogenous and exogenous avian tumor viruses: role of the C region and other portions of the genome in the control of replication and transformation. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):238–249. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.238-249.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Strauss P. G., Hu L. F. A common region for proviral DNA integration in MoMuLV-induced rat thymic lymphomas. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):445–449. doi: 10.1038/302445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood T. G., McGeady M. L., Blair D. G., Vande Woude G. F. Long terminal repeat enhancement of v-mos transforming activity: identification of essential regions. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):726–736. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.726-736.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





