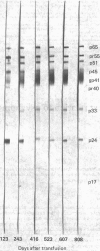
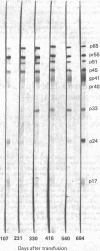
Abstract
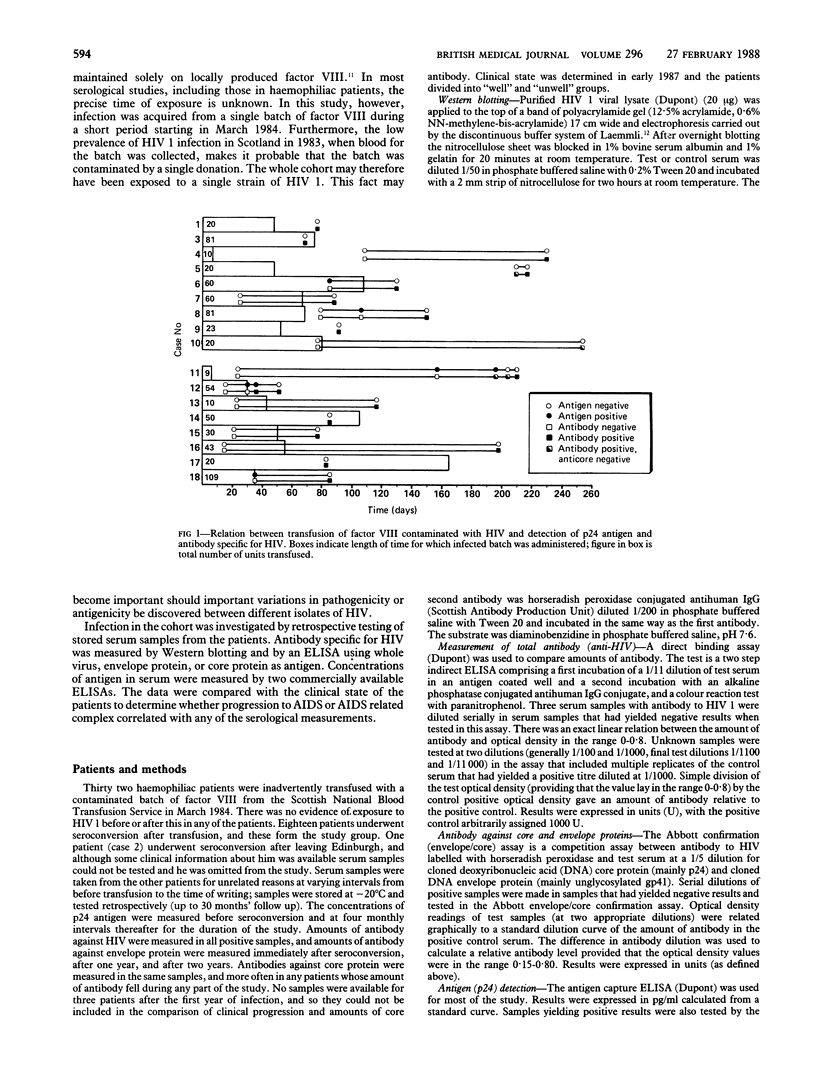
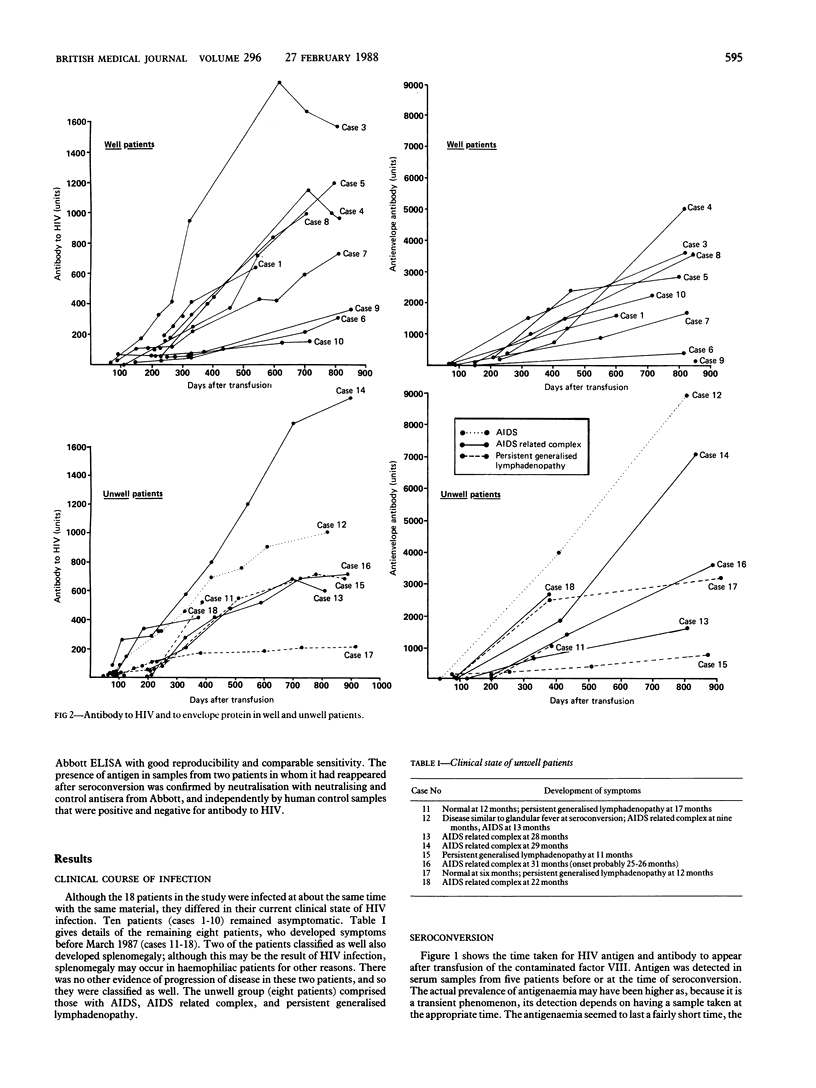
Sequential serum samples from 18 haemophiliac patients exposed simultaneously to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV 1) in early 1984 were tested retrospectively for serological markers of infection. Assay for total antibodies to HIV established that the time to seroconversion might be as long as 110 days after exposure to contaminated factor VIII; serum samples were also tested by Western blotting, by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for specific antibodies to envelope and core proteins, and for p24 antigen by two assay systems during the two years after infection. The studies showed that five of the 12 patients for whom serum samples obtained between exposure and seroconversion were available had transient p24 antigenaemia. Although amounts of total antibody to HIV and of antibodies to envelope proteins rose continuously during the two years of the study, amounts of antibody to the core protein were variable and tended to decline in patients who became symptomatic. Two patients had persistent p24 antigenaemia that began four months after seroconversion; these patients remained asymptomatic. One patient who developed the acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) had transient antigenaemia at the time of seroconversion but failed to show any antigen for the rest of the study; progression to AIDS was accompanied by an increase in antibodies to envelope proteins.
Much of the variability in the course of infection with HIV must represent the differences in the susceptibility of the patients to infection.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allain J. P., Laurian Y., Paul D. A., Senn D. Serological markers in early stages of human immunodeficiency virus infection in haemophiliacs. Lancet. 1986 Nov 29;2(8518):1233–1236. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92673-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arya S. K., Gallo R. C. Three novel genes of human T-lymphotropic virus type III: immune reactivity of their products with sera from acquired immune deficiency syndrome patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2209–2213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange J. M., Coutinho R. A., Krone W. J., Verdonck L. F., Danner S. A., van der Noordaa J., Goudsmit J. Distinct IgG recognition patterns during progression of subclinical and clinical infection with lymphadenopathy associated virus/human T lymphotropic virus. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Jan 25;292(6515):228–230. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6515.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange J. M., Paul D. A., Huisman H. G., de Wolf F., van den Berg H., Coutinho R. A., Danner S. A., van der Noordaa J., Goudsmit J. Persistent HIV antigenaemia and decline of HIV core antibodies associated with transition to AIDS. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Dec 6;293(6560):1459–1462. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6560.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlam C. A., Tucker J., Steel C. M., Tedder R. S., Cheingsong-Popov R., Weiss R. A., McClelland D. B., Philp I., Prescott R. J. Human T-lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III) infection in seronegative haemophiliacs after transfusion of factor VIII. Lancet. 1985 Aug 3;2(8449):233–236. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90288-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow W. J., Wharton M., Stricker R. B., Levy J. A. Circulating immune complexes in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome contain the AIDS-associated retrovirus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Sep;40(3):515–524. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(86)90196-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reesink H. W., Lelie P. N., Huisman J. G., Schaasberg W., Gonsalves M., Aaij C., Winkel I. N., van der Does J. A., Hekker A. C., Desmyter J. Evaluation of six enzyme immunoassays for antibody against human immunodeficiency virus. Lancet. 1986 Aug 30;2(8505):483–486. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90358-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safai B., Sarngadharan M. G., Groopman J. E., Arnett K., Popovic M., Sliski A., Schüpbach J., Gallo R. C. Seroepidemiological studies of human T-lymphotropic retrovirus type III in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Lancet. 1984 Jun 30;1(8392):1438–1440. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91933-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. N., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Parker D., Roberts C., Duncan J., Weller I., Carne C., Tedder R. S., Pinching A. J. Human immunodeficiency virus infection in two cohorts of homosexual men: neutralising sera and association of anti-gag antibody with prognosis. Lancet. 1987 Jan 17;1(8525):119–122. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91964-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]