Abstract
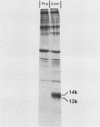
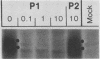
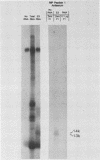
The DNA sequence of the early E3 transcription unit of adenovirus 2 (Ad2) (J. Hérissé et al., Nucleic Acids Res. 8:2173-2192, 1980), indicates that an open reading frame exists between nucleotides 1860 and 2163 that could encode a protein of Mr 11,600 (11.6K). We have determined the DNA sequence of the corresponding region in Ad5 (closely related to Ad2) and have established that this putative gene is conserved in Ad5 (a 10.5K protein). To determine whether this protein is expressed, we prepared an antiserum in rabbits against a synthetic peptide corresponding to amino acids 66 to 74 in the 11.6K protein of Ad2. The peptide antiserum immunoprecipitated a ca. 13K-14K protein doublet, as estimated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, from [35S]methionine-labeled Ad2- or Ad5-early-infected KB cells. The antiserum also immunoprecipitated a 13K-14K protein doublet translated in vitro from Ad2 or Ad5 early E3-specific mRNA purified by hybridization to Ad2 EcoRI-D (nucleotides -236 to 2437). The synthetic peptide successfully competed with the 13K-14K protein doublet in immunoprecipitation experiments, thereby confirming the specificity of the antiserum. As deduced from the DNA sequence, the 11.6K protein (and the corresponding 10.5K Ad5 protein) has a conserved 22-amino-acid hydrophobic domain, suggesting that the protein may be associated with membranes. We conclude that a gene located at nucleotides 1860 to 2143 in the Ad2 E3 transcription unit (nucleotides 1924 to 2203) in the Ad5 E3 transcription unit) encodes an 11.6K protein (10.5K in Ad5).
Full text
PDF

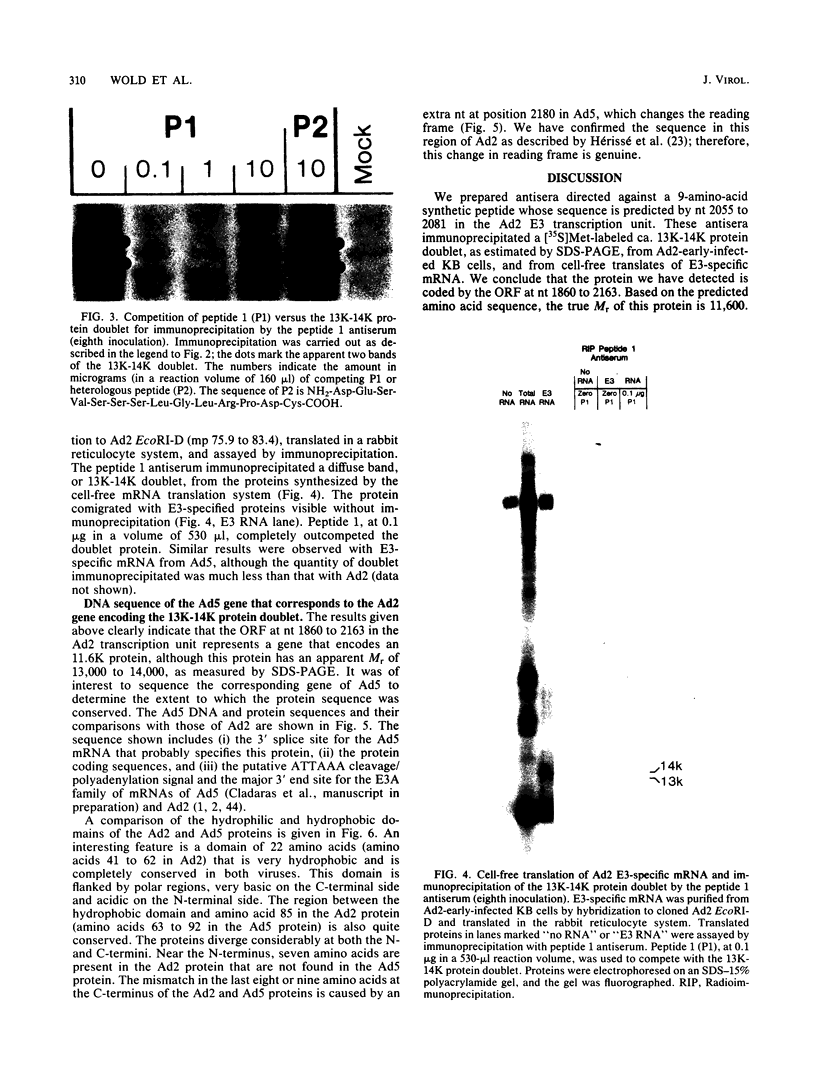

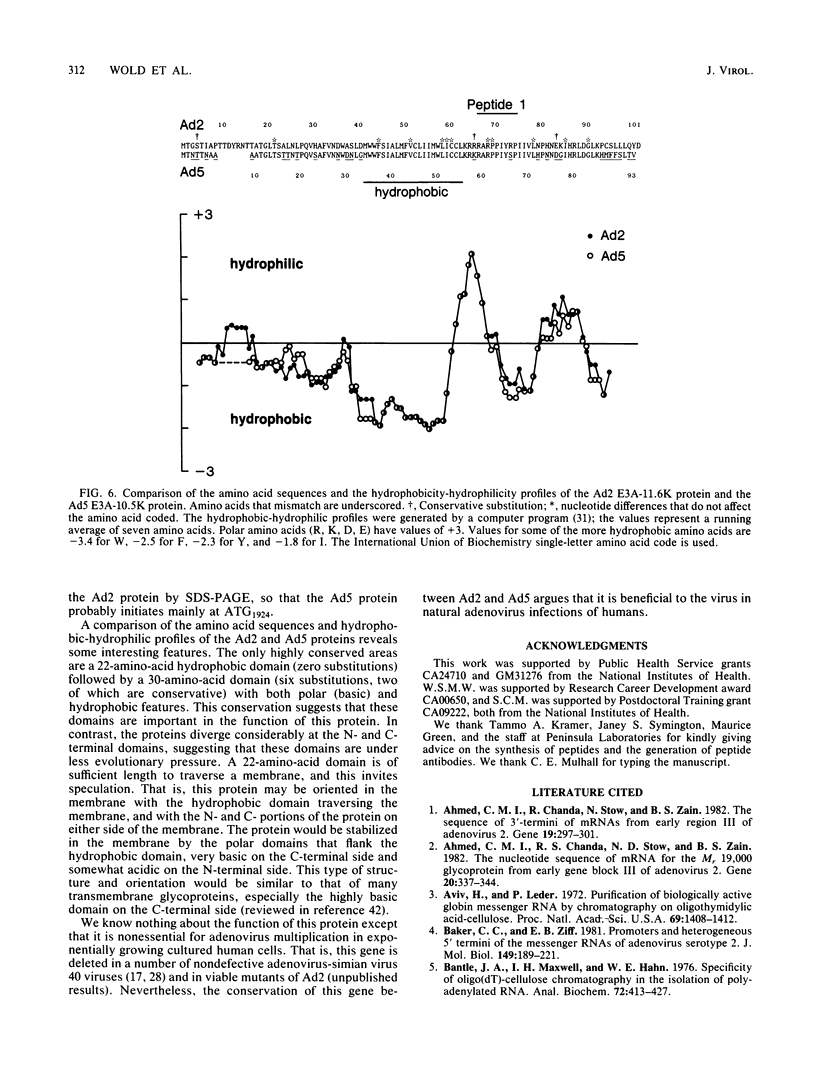

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed C. M., Chanda R., Stow N., Zain B. S. The sequence of 3'-termini of mRNAs from early region III of adenovirus 2. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):297–301. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. C., Ziff E. B. Promoters and heterogeneous 5' termini of the messenger RNAs of adenovirus serotype 2. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 25;149(2):189–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bantle J. A., Maxwell I. H., Hahn W. E. Specificity of oligo (dT)-cellulose chromatography in the isolation of polyadenylated RNA. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:413–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90549-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Structure of the adenovirus 2 early mRNAs. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):695–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90252-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Ultraviolet mapping of the adenovirus 2 early promoters. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):45–55. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90184-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brackmann K. H., Green M., Wold W. S., Cartas M., Matsuo T., Hashimoto S. Identification and peptide mapping of human adenovirus type 2-induced early polypeptides isolated by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and immunoprecipitation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6772–6779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Broker T. R., Lewis J. B. Complex splicing patterns of RNAs from the early regions of adenovirus-2. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 25;134(2):265–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr Variety in the level of gene control in eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):365–371. doi: 10.1038/297365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Fraser N., Ziff E., Weber J., Wilson M., Darnell J. E. The initiation sites for RNA transcription in Ad2 DNA. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):733–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint S. J., Berget S. M., Sharp P. A. Adenovirus transcription. III. Mapping of viral RNA sequences in cells productively infected by adenovirus type 5. Virology. 1976 Jul 15;72(2):443–455. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90173-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint S. J., Gallimore P. H., Sharp P. A. Comparison of viral RNA sequences in adenovirus 2-transformed and lytically infected cells. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jul 25;96(1):47–68. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90181-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint S. J., Wewerka-Lutz Y., Levine A. S., Sambrook J., Sharp P. A. Adenovirus transcription. II. RNA sequences complementary to simian virus 40 and adenovirus 2DNA in AD2+ND1- and AD2+ND3-infected cells. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):662–673. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.662-673.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser N. W., Baker C. C., Moore M. A., Ziff E. B. Poly(A) sites of adenovirus serotype 2 transcription units. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 5;155(3):207–233. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M., Brackmann K. H., Lucher L. A., Symington J. S., Kramer T. A. Human adenovirus 2 E1B-19K and E1B-53K tumor antigens: antipeptide antibodies targeted to the NH2 and COOH termini. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):604–615. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.604-615.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M., Wold W. S., Büttner W. Integration and transcription of group C human adenovirus sequences in the DNA of five lines of transformed rat cells. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):337–366. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Alexander H., Olson A., Alexander S., Shinnick T. M., Sutcliffe J. G., Lerner R. A. Immunogenic structure of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harter M. L., Lewis J. B. Adenovirus type 2 early proteins synthesized in vitro and in vivo: identification in infected cells of the 38,000- to 50,000- molecular-weight protein encoded by the left end of the adenovirus type 2 genome. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):736–749. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.736-749.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hérissé J., Courtois G., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequence of the EcoRI D fragment of adenovirus 2 genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2173–2192. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hérissé J., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequence of the EcoRI E fragment of adenovirus 2 genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1229–1240. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.5.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeng Y. H., Wold W. S., Green M. Evidence for an adenovirus type 2-coded early glycoprotein. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):314–323. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.314-323.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson K., Persson H., Lewis A. M., Pettersson U., Tibbetts C., Philipson L. Viral DNA sequences and gene products in hamster cells transformed by adenovirus type 2. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):628–639. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.628-639.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor Q. S., Wold W. S., Chinnadurai G. A nonessential glycoprotein is coded by early region E3 of adenovirus type 7. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):780–784. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly T. J., Jr, Lewis A. M., Jr Use of nondefective adenovirus-simian virus 40 hybrids for mapping the simian virus 40 genome. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):643–652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.643-652.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchingman G. R., Westphal H. The structure of adenovirus 2 early nuclear and cytoplasmic RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1980 Feb 15;137(1):23–48. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90155-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Wold W. S. Structures of the oligosaccharides of the glycoprotein coded by early region E3 of adenovirus 2. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):440–449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.440-449.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson R., Messing J. Apple II computer software for DNA and protein sequence data. DNA. 1983;2(1):31–35. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1983.2.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. C., Roeder R. G., Wold W. S. DNA sequences affecting specific initiation of transcription in vitro from the EIII promoter of adenovirus 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):41–45. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Zinnecker M., Hamaoka T., Katz D. H. New procedures for preparation and isolation of conjugates of proteins and a synthetic copolymer of D-amino acids and immunochemical characterization of such conjugates. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):690–693. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Jansson M., Philipson L. Synthesis and genomic site for an adenovirus type 2 early glycoprotein. J Mol Biol. 1980 Feb 5;136(4):375–394. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90396-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Jörnvall H., Zabielski J. Multiple mRNA species for the precursor to an adenovirus-encoded glycoprotein: identification and structure of the signal sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6349–6353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Oberg B., Philipson L. Purification and characterization of an early protein (E14K) from adenovirus type 2-infected cells. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):119–139. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.119-139.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Signäs C., Philipson L. Purification and characterization of an early glycoprotein from adenovirus type 2-infected cells. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):938–948. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.938-948.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Jones R. L., Cepko C. L., Sharp P. A., Roberts B. E. Expression of early adenovirus genes requires a viral encoded acidic polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6121–6125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross S. R., Flint S. J., Levine A. J. Identification of the adenovirus early proteins and their genomic map positions. Virology. 1980 Jan 30;100(2):419–432. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90533-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross S., Levine A. J. The genomic map position of the adenovirus type 2 glycoprotein. Virology. 1979 Dec;99(2):427–430. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini D. D., Kreibich G., Morimoto T., Adesnik M. Mechanisms for the incorporation of proteins in membranes and organelles. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):1–22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarin V. K., Kent S. B., Tam J. P., Merrifield R. B. Quantitative monitoring of solid-phase peptide synthesis by the ninhydrin reaction. Anal Biochem. 1981 Oct;117(1):147–157. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90704-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storch T. G., Maizel J. V., Jr The early proteins of the nondefective Ad2-SV40 hybrid viruses: the 19K glycoprotein is coded by Ad2 early region 3. Virology. 1980 May;103(1):54–67. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90125-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stålhandske P., Persson H., Perricaudet M., Philipson L., Pettersson U. Structure of three spliced mRNAs from region E3 of adenovirus type 2. Gene. 1983 May-Jun;22(2-3):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90099-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold W. S., Green M. Adenovirus type 2 early polypeptides immunoprecipitated by antisera to five lines of adenovirus-transformed rat cells. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):297–310. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.297-310.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold W. S., Green M., Brackmann K. H., Cartas M. A., Devine C. Genome expression and mRNA maturation at late stages of productive adenovirus type 2 infection. J Virol. 1976 Nov;20(2):465–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.2.465-477.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]