Abstract
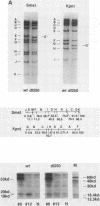
The early region E1b of adenovirus type 2 (Ad2) codes for two major tumor antigens of 53 and 19 kilodaltons (kd). The adenovirus lp+ locus maps within the 19-kd tumor antigen-coding region (G. Chinnadurai, Cell 33:759-766, 1983). We have now constructed a large-plaque deletion mutant (dl250) of Ad2 that has a specific lesion in the 19-kd tumor antigen-coding region. In contrast to most other Ad2 lp mutants (G. Chinnadurai, Cell 33:759-766, 1983), mutant dl250 is cytocidal (cyt) on infected KB cells, causing extensive cellular destruction. Cells infected with Ad2 wt or most of these other Ad2 lp mutants are rounded and aggregated without cell lysis (cyt+). The cyt phenotype of dl250 resembles the cyt mutants of highly oncogenic Ad12, isolated by Takemori et al. (Virology 36:575-586, 1968). By intertypic complementation analysis, we showed that the Ad12 cyt mutants indeed map within the 19-kd tumor antigen-coding region. The transforming potential of dl250 was assayed on an established rat embryo fibroblast cell line, CREF, and on primary rat embryo fibroblasts and baby rat kidney cells. On all these cells, dl250 induced transformation at greatly reduced frequency compared with wt. The cells transformed by this mutant are defective in anchorage-independent growth on soft agar. Our results suggest that the 19-kd tumor antigen (in conjunction with E1a tumor antigens) may play an important role in the maintenance of cell transformation. Since we have mapped the low-oncogenic or nononcogenic Ad12 cyt mutants within the 19-kd tumor antigen-coding region, our results further indicate that the 19-kd tumor antigen also directly or indirectly plays an important role in tumorigenesis of Ad12. Our results show that the cyt+ locus is an allele of the lp+ locus and that the cyt phenotype may be the result of mutations in specific domains of the 19-kd tumor antigen.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. W., Lewis J. B. Amino-terminal sequence of adenovirus type 2 proteins: hexon, fiber, component IX, and early protein 1B-15K. Virology. 1980 Jul 15;104(1):27–41. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90363-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. W., Schmitt R. C., Smart J. E., Lewis J. B. Early region 1B of adenovirus 2 encodes two coterminal proteins of 495 and 155 amino acid residues. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):387–396. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.387-396.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernards R., Schrier P. I., Houweling A., Bos J. L., van der Eb A. J., Zijlstra M., Melief C. J. Tumorigenicity of cells transformed by adenovirus type 12 by evasion of T-cell immunity. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):776–779. doi: 10.1038/305776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brusca J. S., Chinnadurai G. Transforming genes among three different oncogenic subgroups of human adenoviruses have similar replicative functions. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):300–305. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.300-305.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinnadurai G. Adenovirus 2 Ip+ locus codes for a 19 kd tumor antigen that plays an essential role in cell transformation. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):759–766. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinnadurai G., Chinnadurai S., Brusca J. Physical mapping of a large-plaque mutation of adenovirus type 2. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):623–628. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.623-628.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. B., Babiss L. E., Weinstein I. B., Ginsberg H. S. Analysis of type 5 adenovirus transformation with a cloned rat embryo cell line (CREF). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3527–3531. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Saito I., Shiroki K., Shimojo H. Isolation of transformation-defective, replication-nondefective early region 1B mutants of adenovirus 12. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):154–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.154-161.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor R. B., Tsukamoto A., Montell C., Berk A. J. Enhanced expression of adenovirus transforming proteins. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):276–285. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.276-285.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingeras T. R., Sciaky D., Gelinas R. E., Bing-Dong J., Yen C. E., Kelly M. M., Bullock P. A., Parsons B. L., O'Neill K. E., Roberts R. J. Nucleotide sequences from the adenovirus-2 genome. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13475–13491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M., Brackmann K. H., Cartas M. A., Matsuo T. Identification and purification of a protein encoded by the human adenovirus type 2 transforming region. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):30–41. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.30-41.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M., Brackmann K. H., Lucher L. A., Symington J. S., Kramer T. A. Human adenovirus 2 E1B-19K and E1B-53K tumor antigens: antipeptide antibodies targeted to the NH2 and COOH termini. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):604–615. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.604-615.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M., Wold W. S., Brackmann K. H., Cartas M. A. Identification of families of overlapping polypeptides coded by early "transforming" gene region 1 of human adenovirus type 2. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):275–286. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90339-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y. Polyoma virus-specific 55K protein isolated from plasma membrane of productively infected cells is virus-coded and important for cell transformation. Virology. 1979 Oct 15;98(1):261–266. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90545-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Fatt R. B., Mak S. Mapping of an adenovirus function involved in the inhibition of DNA degradation. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):969–977. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.969-977.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Courtneidge S. A., Bishop J. M. Structural and functional domains of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein (pp60src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1624–1628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak I., Mak S. Transformation of rat cells by cyt mutants of adenovirus type 12 and mutants of adenovirus type 5. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1107–1117. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1107-1117.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. T., Graham F. L. Complementation of adenovirus type 5 host range mutants by adenovirus type 12 in coinfected HeLa and BHK-21 cells. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):191–197. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.191-197.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier P. I., Bernards R., Vaessen R. T., Houweling A., van der Eb A. J. Expression of class I major histocompatibility antigens switched off by highly oncogenic adenovirus 12 in transformed rat cells. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):771–775. doi: 10.1038/305771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemori N., Riggs J. L., Aldrich C. D. Genetic studies with tumorigenic adenoviruses. II. Heterogeneity of cyt mutants of adenovirus type 12. Virology. 1969 May;38(1):8–15. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90122-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemori N., Riggs J. L., Aldrich C. Genetic studies with tumorigenic adenoviruses. I. Isolation of cytocidal (cyt) mutants of adenovirus type 12. Virology. 1968 Dec;36(4):575–586. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90189-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen A., Pettersson U. The molecular structure of the 9S mRNA from early region 1A of adenovirus serotype 2. J Mol Biol. 1983 Apr 15;165(3):496–499. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80215-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J., Ho Y. S., Galos R. Evidence for functional relatedness of products encoded by the transforming sequences of human adenovirus types 5 and 12. Virology. 1981 Apr 15;110(1):208–212. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Jay G., Pastan I. Localization of the ASV src gene product to the plasma membrane of transformed cells by electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90361-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Shih T. Y., Scolnick E. M. Localization of the src gene product of the Harvey strain of MSV to plasma membrane of transformed cells by electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):1005–1014. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold W. S., Green M. Adenovirus type 2 early polypeptides immunoprecipitated by antisera to five lines of adenovirus-transformed rat cells. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):297–310. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.297-310.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]