Abstract
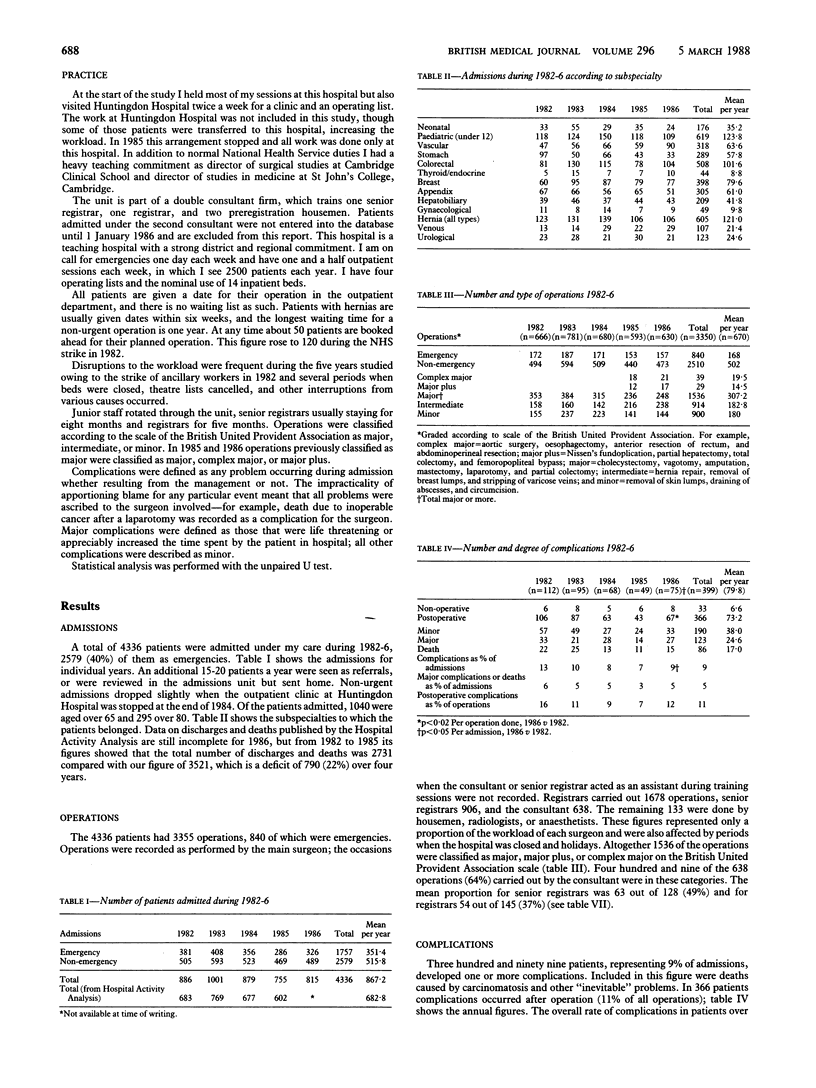
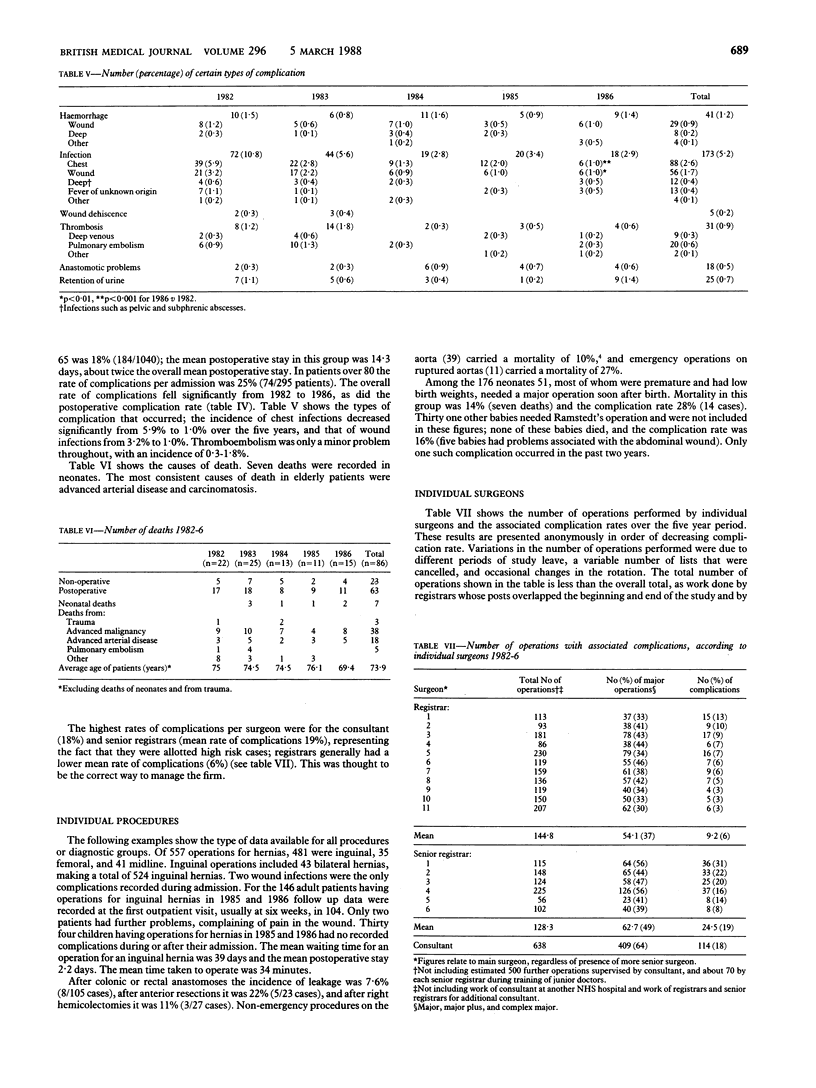
From 1982 to 1986 inclusive work of one surgical firm was audited with a microcomputer. Data were recorded on 4336 patients having 3355 operations, who were under the care of one consultant in a general surgical unit; fifty items of information were recorded on each patient, allowing a wide range of analyses to be performed—for example, the number of admissions and operations, grades of operation, diagnostic grouping, complications, and complication rates associated with individual surgeons. Data collected for the audit provided a valuable baseline for the unit, defining aspects of practice that could be reviewed and improved. During the audit the overall rate of complications as a percentage of admissions fell significantly from 13% to 9% and the rate of postoperative complications decreased significantly from 16% in 1982 to 11% in 1986. The incidence of chest and wound infections also decreased significantly. The system was improved by using the data to produce discharge summaries as well as audit; the microcomputer thus became an integral part of the office work of the unit.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Broughton N. S., Bunker T. D., Ackroyd C. E. The use of a microcomputer for inpatient audit in an orthopaedic department. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1985 Jul;67(4):259–262. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn D. C., Dale R. F. Combined computer generated discharge documents and surgical audit. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Mar 22;292(6523):816–818. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6523.816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore O. J., Griffiths N. J., Connolly J. C., Dunlop A. W., Hart S., Thomson J. P., Todd I. P. Surgical audit: Comparison of the work load and results of two hospitals in the same district. Br Med J. 1980 Oct 18;281(6247):1050–1052. doi: 10.1136/bmj.281.6247.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass R. E., Thomas P. A. Surgical audit in a district general hospital: a stimulus for improving patient care. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1987 May;69(3):135–139. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough M. H., Kettlewell M. G., Marks C. G., Holmes S. J., Holderness J. Audit: an annual assessment of the work and performance of a surgical firm in a regional teaching hospital. Br Med J. 1980 Oct 4;281(6245):913–918. doi: 10.1136/bmj.281.6245.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving M., Temple J. Surgical audit: one year's experience in a teaching hospital. Br Med J. 1976 Sep 25;2(6038):746–747. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6038.746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prout W. G., Blood P. A. The establishment of a microcomputer-based diagnosis and operations index in the Department of Surgery of a district general hospital. Br J Surg. 1985 Jan;72(1):48–51. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800720119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


