Abstract
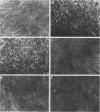
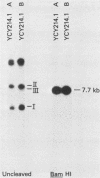
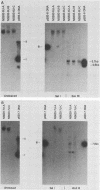
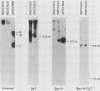
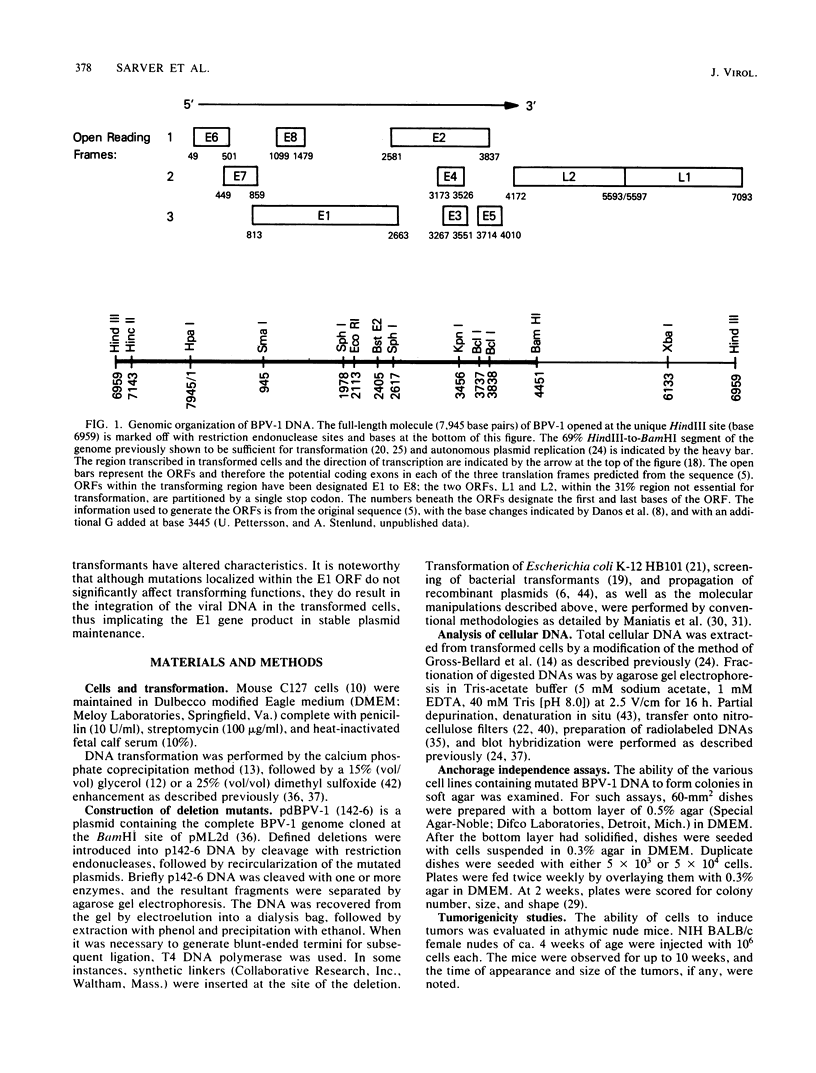
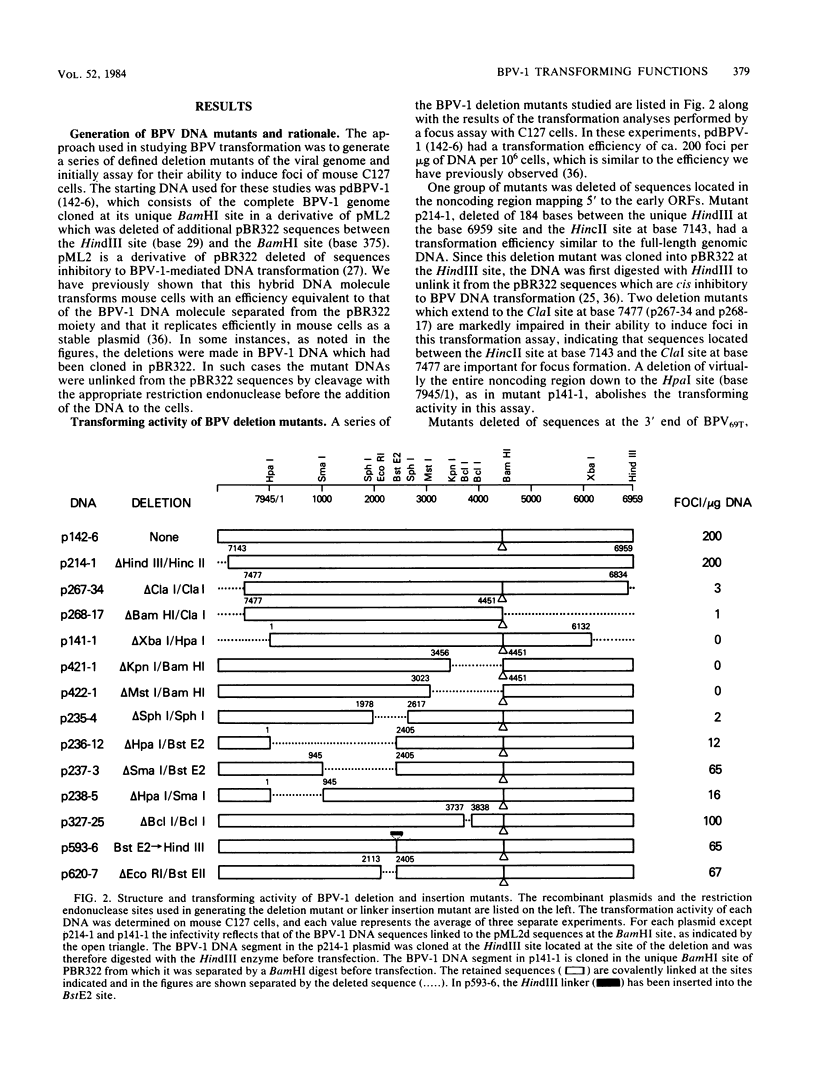
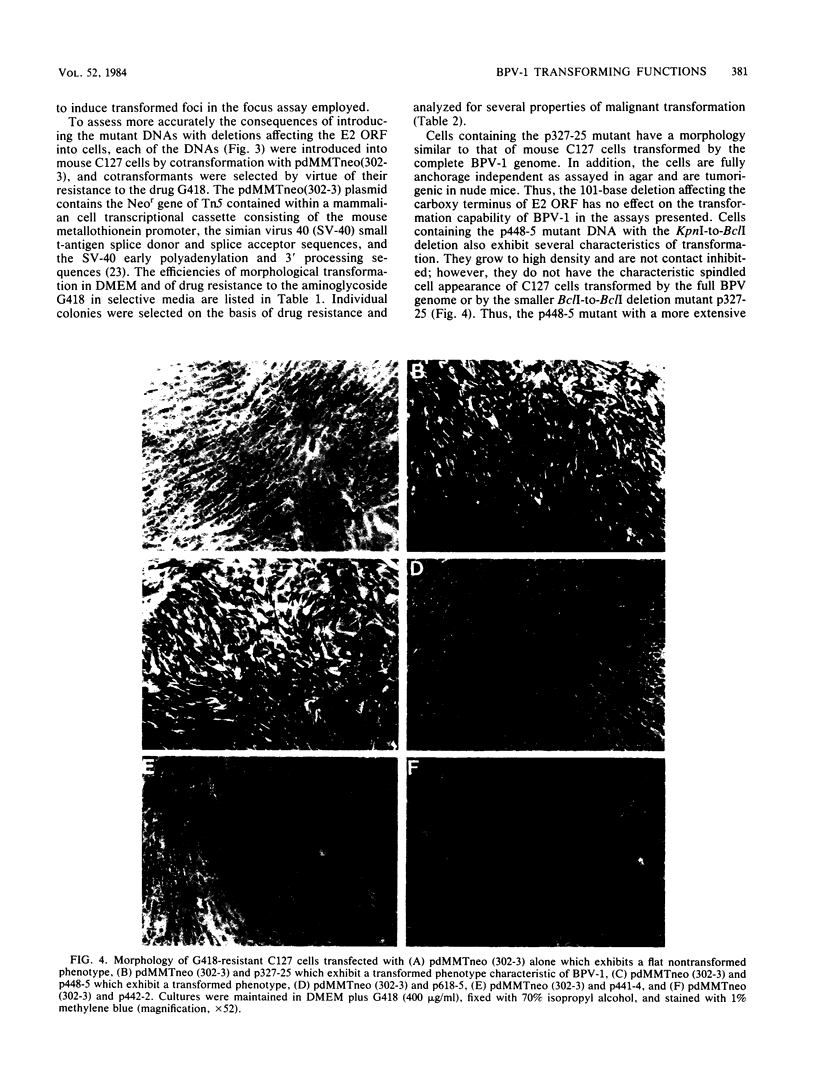
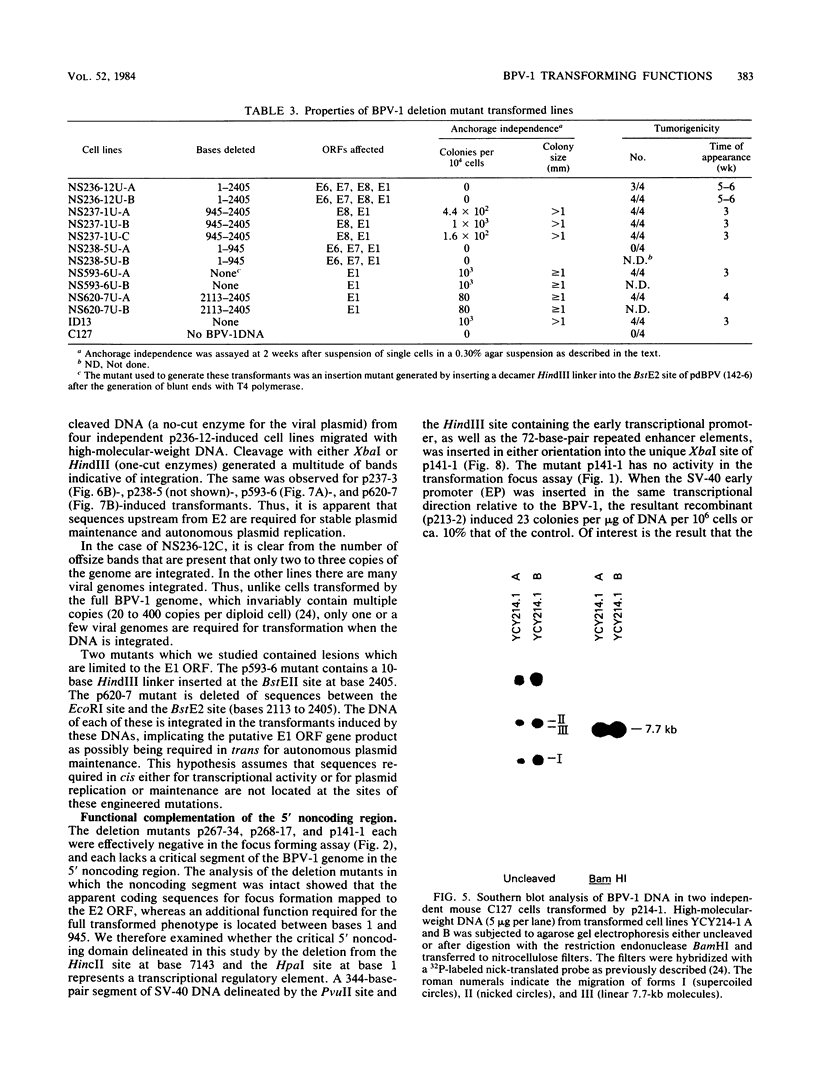
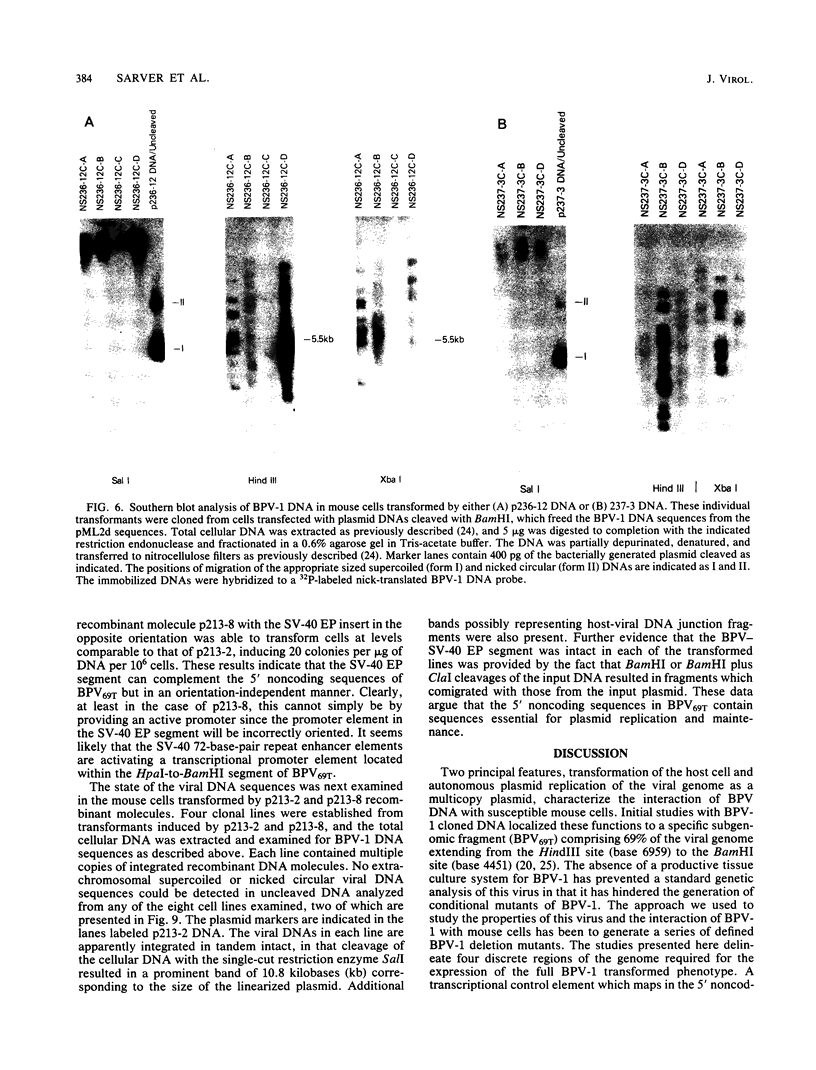
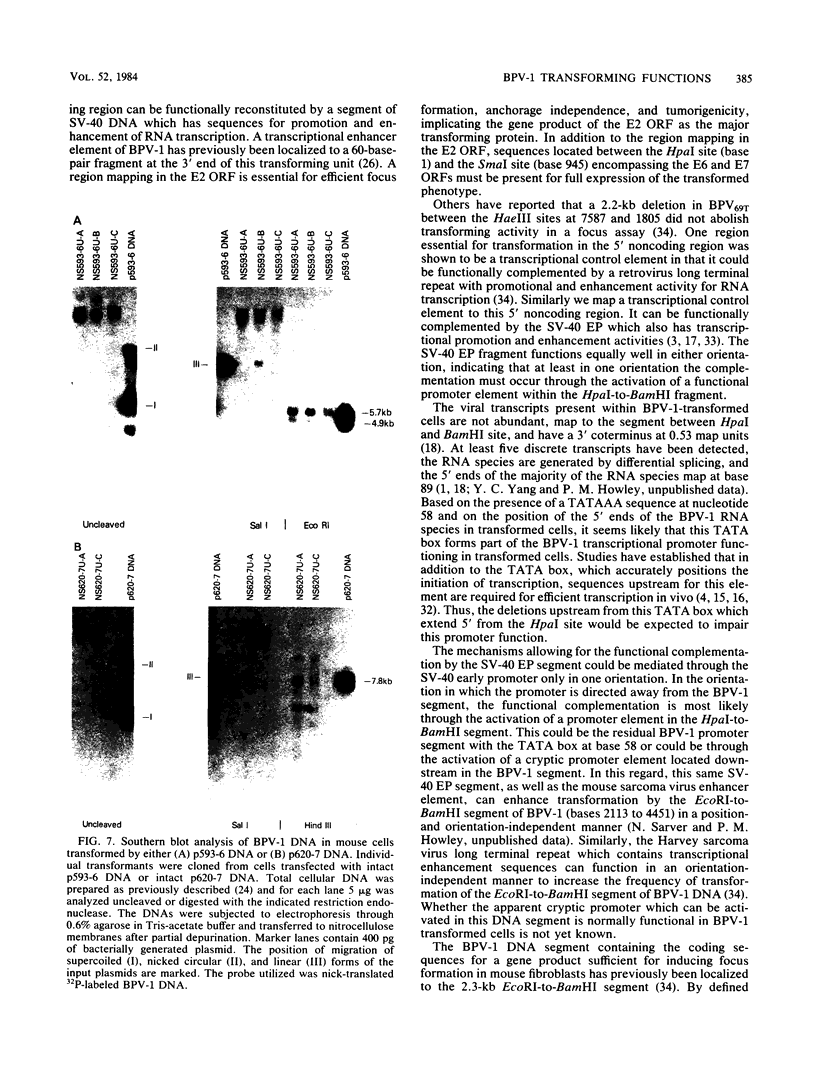
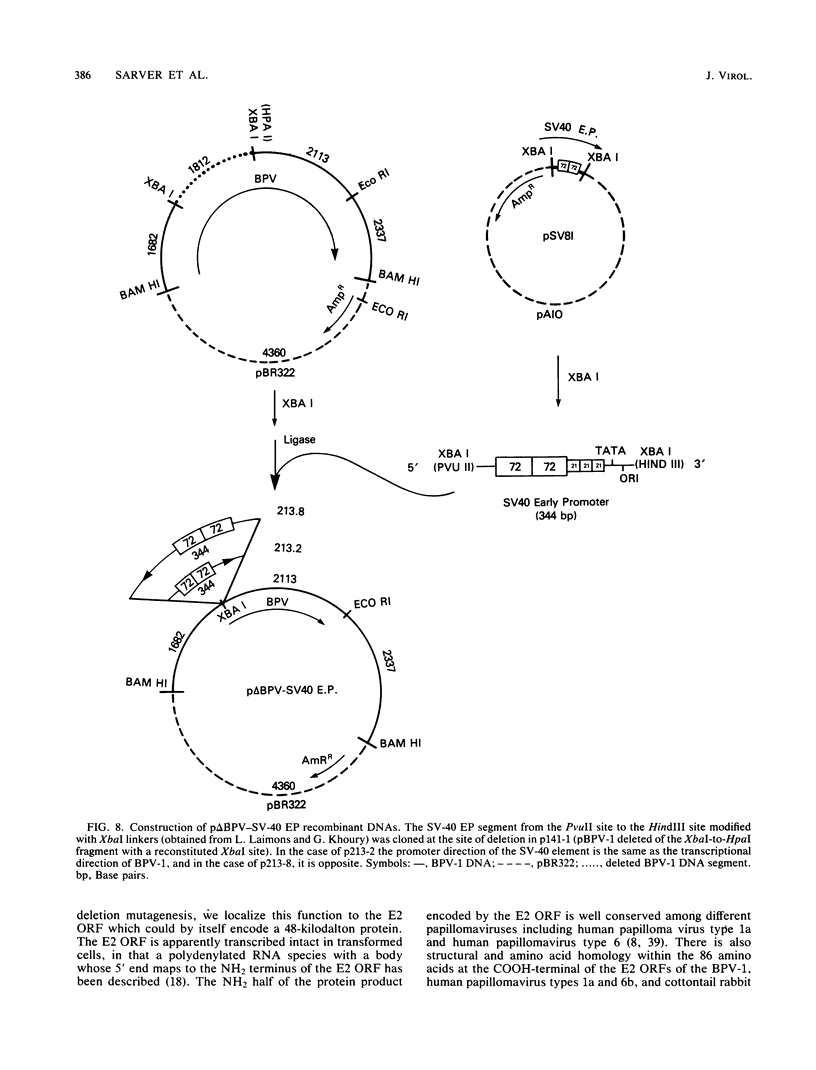
Bovine papillomavirus type 1 (BPV-1) or cloned BPV-1 DNA can transform susceptible rodent cells, and the viral DNA remains as a stable extrachromosomal plasmid in the transformed cells. The transforming region of the BPV-1 genome has previously been localized to a specific fragment comprising 69% of the genome, which also contains the elements sufficient for extrachromosomal plasmid maintenance. To define more precisely the viral DNA sequences which are involved in cellular transformation, we have tested the ability of defined deletion mutants of BPV-1 DNA to morphologically transform mouse C127 cells. Cells containing the mutated DNAs have been examined for anchorage independence and tumorigenicity in nude mice. Several distinct regions of the BPV-1 genome were found to influence expression of the viral transformation functions. A transcriptional regulatory region located in the noncoding region 5' to the early open reading frames is essential for transcriptional activity and transformation. A transcriptional enhancer element, located 3' to the polyadenylation site for the viral RNAs expressed in transformed cells, has previously been shown to be essential for transformation (Lusky et al., Mol. Cell. Biol., 3:1108-1122, 1983). Deletion mutants affecting the E2 open reading frame, particularly the NH2 half, are significantly impaired in their ability to transform, suggesting that the E2 gene product is an important transforming protein of BPV-1. Mutants lacking the E6 and E7 open reading frames are still able to induce transformation but at a lowered efficiency, and the transformants have altered characteristics. Mutations localized within the E1 open reading frame do not significantly affect the transforming functions but result in the integration of the viral genome in the transformed cells, implicating the E1 gene product in stable plasmid replication and maintenance.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahola H., Stenlund A., Moreno-Lopez J., Pettersson U. Sequences of bovine papillomavirus type 1 DNA--functional and evolutionary implications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 11;11(9):2639–2650. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.9.2639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amtmann E., Sauer G. Bovine papilloma virus transcription: polyadenylated RNA species and assessment of the direction of transcription. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):59–66. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.59-66.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Expression of a beta-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Howley P. M., Levinson A. D., Seeburg P. H. The primary structure and genetic organization of the bovine papillomavirus type 1 genome. Nature. 1982 Oct 7;299(5883):529–534. doi: 10.1038/299529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B. Nature of Col E 1 plasmid replication in Escherichia coli in the presence of the chloramphenicol. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):667–676. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.667-676.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbère-Garapin F., Horodniceanu F., Kourilsky P., Garapin A. C. A new dominant hybrid selective marker for higher eukaryotic cells. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danos O., Engel L. W., Chen E. Y., Yaniv M., Howley P. M. Comparative analysis of the human type 1a and bovine type 1 papillomavirus genomes. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):557–566. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.557-566.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Treisman R., Maniatis T. Bovine papillomavirus vector that propagates as a plasmid in both mouse and bacterial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4030–4034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretzky I., Shober R., Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R. A quantitative in vitro focus assay for bovine papilloma virus. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):369–375. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90195-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel L. W., Heilman C. A., Howley P. M. Transcriptional organization of bovine papillomavirus type 1. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):516–528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.516-528.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost E., Williams J. Mapping temperature-sensitive and host-range mutations of adenovirus type 5 by marker rescue. Virology. 1978 Nov;91(1):39–50. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90353-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Spacer DNA sequences upstream of the T-A-T-A-A-A-T-A sequence are essential for promotion of H2A histone gene transcription in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7102–7106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld G. C., de Boer E., Shewmaker C. K., Flavell R. A. DNA sequences necessary for transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in vivo. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):120–126. doi: 10.1038/295120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Dhar R., Khoury G. Simian virus 40 tandem repeated sequences as an element of the early promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):943–947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilman C. A., Engel L., Lowy D. R., Howley P. M. Virus-specific transcription in bovine papillomavirus-transformed mouse cells. Virology. 1982 May;119(1):22–34. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison K. W., Halvorson H. O. Cloning of randomly sheared DNA fragments from a phi 105 lysogen of Bacillus subtilis identification of prophage-containing clones. Gene. 1980 Feb;8(3):267–278. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketner G., Kelly T. J., Jr Integrated simian virus 40 sequences in transformed cell DNA: analysis using restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1102–1106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law M. F., Byrne J. C., Howley P. M. A stable bovine papillomavirus hybrid plasmid that expresses a dominant selective trait. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):2110–2115. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law M. F., Lowy D. R., Dvoretzky I., Howley P. M. Mouse cells transformed by bovine papillomavirus contain only extrachromosomal viral DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2727–2731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy D. R., Dvoretzky I., Shober R., Law M. F., Engel L., Howley P. M. In vitro tumorigenic transformation by a defined sub-genomic fragment of bovine papilloma virus DNA. Nature. 1980 Sep 4;287(5777):72–74. doi: 10.1038/287072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Berg L., Weiher H., Botchan M. Bovine papilloma virus contains an activator of gene expression at the distal end of the early transcription unit. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1108–1122. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. R. Characterization of the bovine papilloma virus plasmid maintenance sequences. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):391–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I., MONTAGNIER L. AGAR SUSPENSION CULTURE FOR THE SELECTIVE ASSAY OF CELLS TRANSFORMED BY POLYOMA VIRUS. Virology. 1964 Jun;23:291–294. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90301-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Gavis E. R., Kingsbury R., Axel R. Analysis of transcriptional regulatory signals of the HSV thymidine kinase gene: identification of an upstream control region. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):385–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau P., Hen R., Wasylyk B., Everett R., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 base repair repeat has a striking effect on gene expression both in SV40 and other chimeric recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6047–6068. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabayashi Y., Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R. The transforming function of bovine papillomavirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5832–5836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarver N., Byrne J. C., Howley P. M. Transformation and replication in mouse cells of a bovine papillomavirus--pML2 plasmid vector that can be rescued in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7147–7151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarver N., Gruss P., Law M. F., Khoury G., Howley P. M. Bovine papilloma virus deoxyribonucleic acid: a novel eucaryotic cloning vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;1(6):486–496. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.6.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz E., Dürst M., Demankowski C., Lattermann O., Zech R., Wolfsperger E., Suhai S., zur Hausen H. DNA sequence and genome organization of genital human papillomavirus type 6b. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2341–2348. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01744.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Wilkie N. M. An improved technique for obtaining enhanced infectivity with herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. J Gen Virol. 1976 Dec;33(3):447–458. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-3-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wensink P. C., Finnegan D. J., Donelson J. E., Hogness D. S. A system for mapping DNA sequences in the chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1974 Dec;3(4):315–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]