Abstract
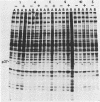
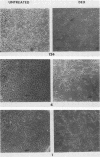
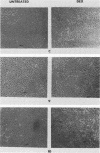
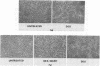
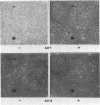
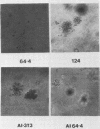
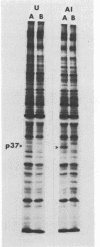
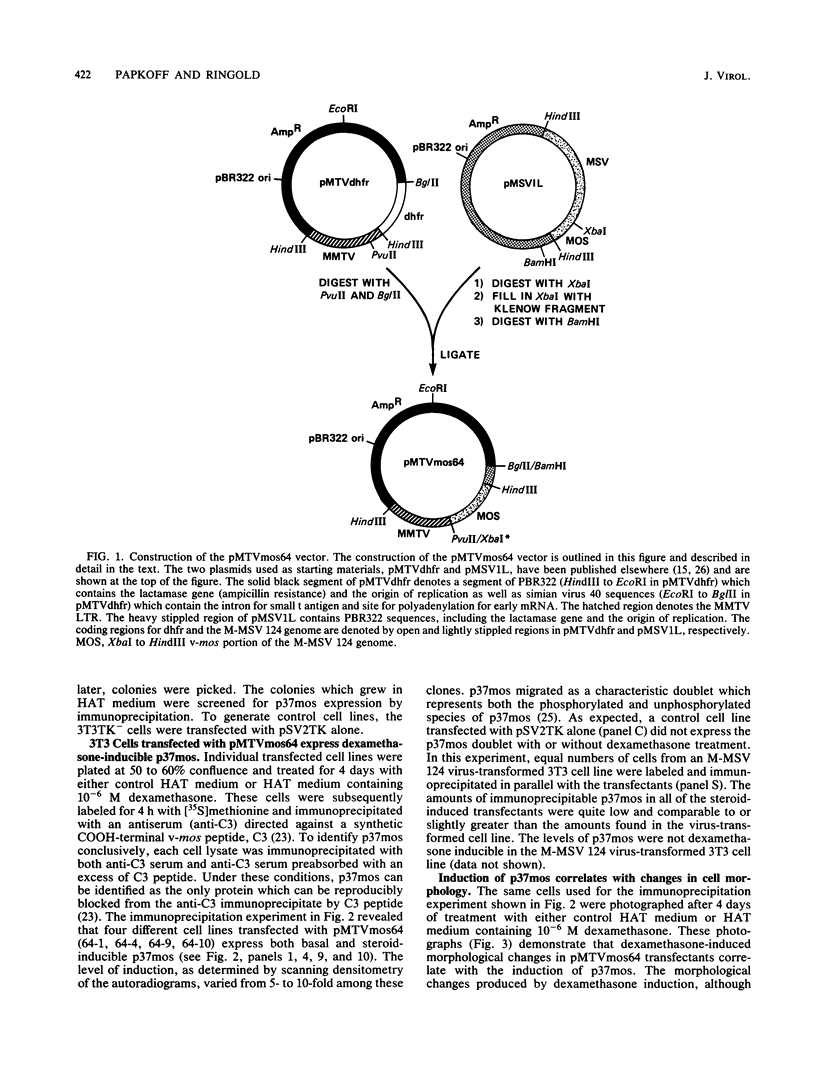
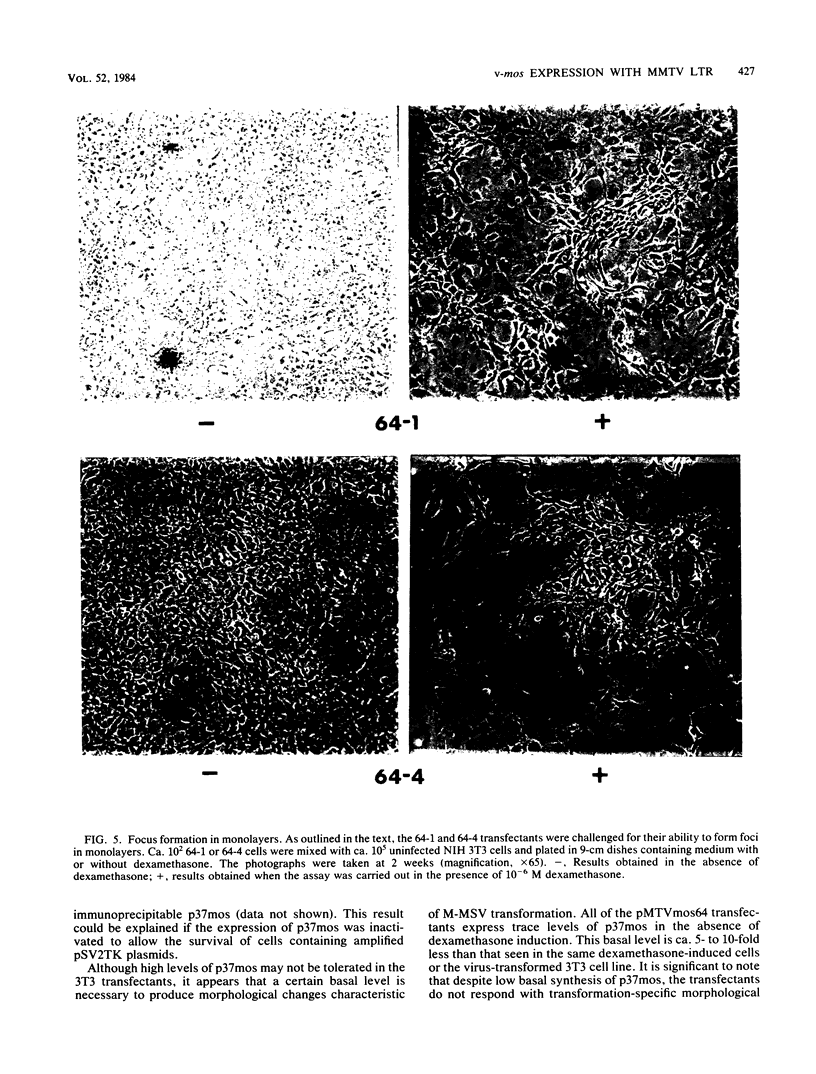
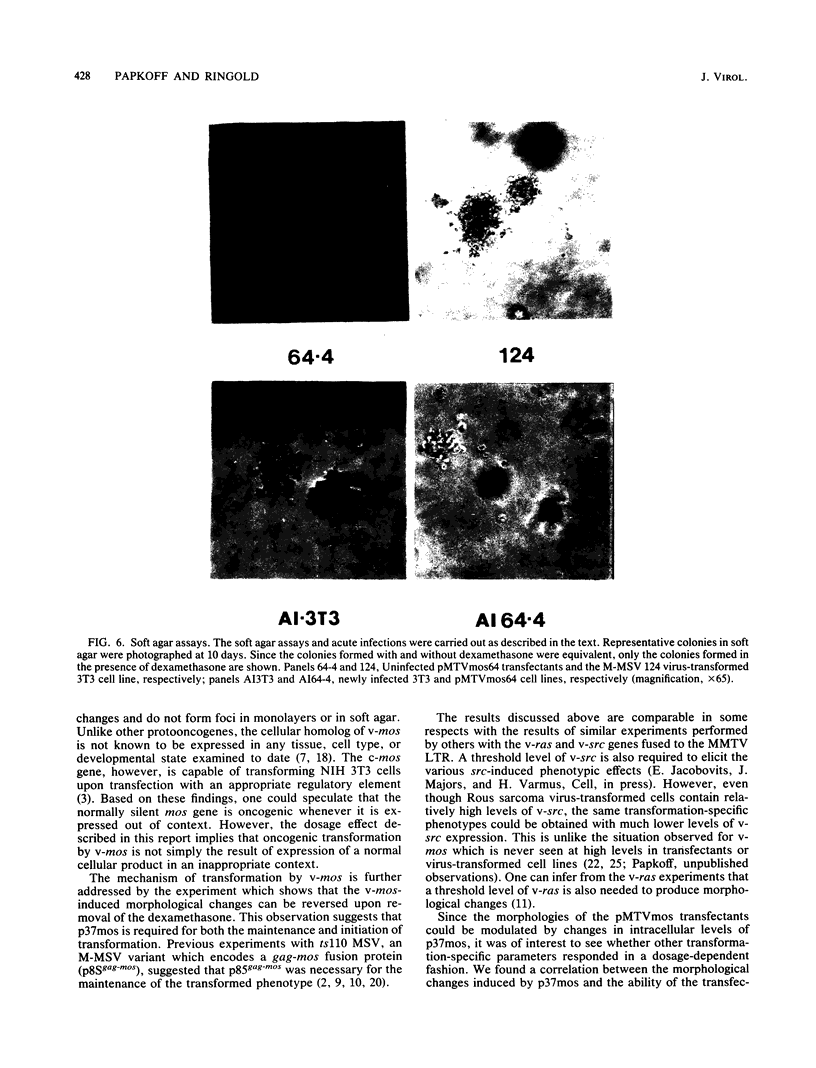
We used the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat to promote dexamethasone-regulated expression of the Moloney murine sarcoma virus (M-MSV) transforming gene, v-mos. A recombinant DNA vector containing the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat fused to the M-MSV 124 v-mos gene was cotransfected with a plasmid containing the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene (tk) into 3T3TK- cells. Individual clones of cells which grew in hypoxanthine-aminopterin-thymidine medium were tested for dexamethasone-regulated expression of p37mos as well as several transformation-specific phenotypic parameters. In the absence of dexamethasone, the v-mos transfectants appeared morphologically similar to the control cells despite low basal levels of p37mos expression. Upon hormone treatment, the levels of p37mos increased 5- to 10-fold, coincident with morphological changes typical of M-MSV transformation of 3T3 cells. The ability to form foci in monolayers also correlated with p37mos induction. The extent of morphological changes varied in individual clones of cells with similar levels of induced p37mos. Although the induced levels of p37mos were comparable to those seen in stable M-MSV 124 virus-transformed NIH 3T3 cells, the transfectants were unable to grow in soft agar under conditions which support growth of the virus-transformed cells. Acute infection of the transfectants with M-MSV 124 virus, a situation which resulted in elevated levels of p37mos, allowed these cells to grow in soft agar. The results described in this paper suggest that different threshold levels of p37mos may be necessary for the expression of various parameters of the transformed phenotype and also that continued expression of p37mos is necessary for maintenance of the transformed state. However, it also appears that the sensitivity to given levels of p37mos varies among clonal cell lines.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker W. C., Dayhoff M. O. Viral src gene products are related to the catalytic chain of mammalian cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2836–2839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. G., Hull M. A., Finch E. A. The isolation and preliminary characterization of temperature-sensitive transformation mutants of Moloney sarcoma virus. Virology. 1979 Jun;95(2):303–316. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90486-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. G., Oskarsson M., Wood T. G., McClements W. L., Fischinger P. J., Vande Woude G. G. Activation of the transforming potential of a normal cell sequence: a molecular model for oncogenesis. Science. 1981 May 22;212(4497):941–943. doi: 10.1126/science.7233190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Miller A. D., Zokas L., Verma I. M. Viral and cellular fos proteins: a comparative analysis. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dina D., Nadal-Ginard B. Moloney murine sarcoma virions contain subgenome-length mRNA-like molecules that direct the synthesis of sarcoma-specific polypeptides in vitro. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):901–905. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gattoni S., Kirschmeier P., Weinstein I. B., Escobedo J., Dina D. Cellular Moloney murine sarcoma (c-mos) sequences are hypermethylated and transcriptionally silent in normal and transformed rodent cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;2(1):42–51. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampe A., Laprevotte I., Galibert F., Fedele L. A., Sherr C. J. Nucleotide sequences of feline retroviral oncogenes (v-fes) provide evidence for a family of tyrosine-specific protein kinase genes. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):775–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90282-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn J. P., Wood T. G., Blair D. G., Arlinghaus R. B. Partial characterization of a moloney murine sarcoma virus 85,000-dalton polypeptide whose expression correlates with the transformed phenotype in cells infected with a temperature-sensitive mutant virus. Virology. 1980 Sep;105(2):516–525. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn J. P., Wood T. G., Murphy E. C., Jr, Blair D. G., Arlinghaus R. B. A selective temperature-sensitive defect in viral RNA expression in cells infected with a ts transformation mutant of murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90229-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. L., Ostrowski M. C., Berard D., Hager G. L. Glucocorticoid regulation of the Ha-MuSV p21 gene conferred by sequences from mouse mammary tumor virus. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90408-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan P. L., Anderson M., Ozanne B. Transforming growth factor(s) production enables cells to grow in the absence of serum: an autocrine system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):485–489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan P. L., Ozanne B. Cellular responsiveness to growth factors correlates with a cell's ability to express the transformed phenotype. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):931–938. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. H., Verma I. M. Genome organization of retroviruses. VIII. Nonproducer cell lines of mouse fibroblasts transformed by Moloney murine sarcoma virus DNA synthesized in vitro. Virology. 1980 Jul 30;104(2):407–417. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90343-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F., Mulligan R., Berg P., Ringold G. Glucocorticoids regulate expression of dihydrofolate reductase cDNA in mouse mammary tumour virus chimaeric plasmids. Nature. 1981 Nov 19;294(5838):228–232. doi: 10.1038/294228a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons D. D., Murphy E. C., Jr, Mong S. M., Arlinghaus R. B. The translation products of Moloney murine sarcoma virus-124 RNA. Virology. 1980 Aug;105(1):60–70. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90156-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Slamon D. J., Tremblay J. M., Cline M. J., Verma I. M. Differential expression of cellular oncogenes during pre- and postnatal development of the mouse. Nature. 1982 Oct 14;299(5884):640–644. doi: 10.1038/299640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozanne B., Fulton R. J., Kaplan P. L. Kirsten murine sarcoma virus transformed cell lines and a spontaneously transformed rat cell-line produce transforming factors. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Oct;105(1):163–180. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041050118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papkoff J., Hunter T., Beemon K. In vitro translation of virion RNA from Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):91–103. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90486-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papkoff J., Hunter T. Detection of an 85,000-dalton phosphoprotein in ts110 murine sarcoma virus-infected cells with antiserum against a v-mos peptide. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1177–1182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1177-1182.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papkoff J., Lai M. H., Hunter T. Analysis of v-mos encoded proteins in cells transformed by several related murine sarcoma viruses. J Cell Biochem. 1982;19(4):349–362. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240190405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papkoff J., Lai M. H., Hunter T., Verma I. M. Analysis of transforming gene products from Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90365-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papkoff J., Nigg E. A., Hunter T. The transforming protein of Moloney murine sarcoma virus is a soluble cytoplasmic protein. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):161–172. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90345-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papkoff J., Verma I. M., Hunter T. Detection of a transforming gene product in cells transformed by Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):417–426. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90158-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., Galleshaw J. A., Jonas V., Berns A. J., Doolittle R. F., Donoghue D. J., Verma I. M. Nucleotide sequence and formation of the transforming gene of a mouse sarcoma virus. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):258–262. doi: 10.1038/289258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M. From c-fos to v-fos. Nature. 1984 Mar 22;308(5957):317–317. doi: 10.1038/308317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei C. M., Gibson M., Spear P. G., Scolnick E. M. Construction and isolation of a transmissible retrovirus containing the src gene of Harvey murine sarcoma virus and the thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):935–944. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.935-944.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Growth factors from murine sarcoma virus-transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):4001–4005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.4001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]