Abstract
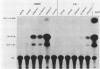
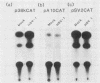
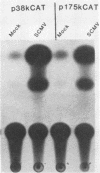
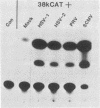
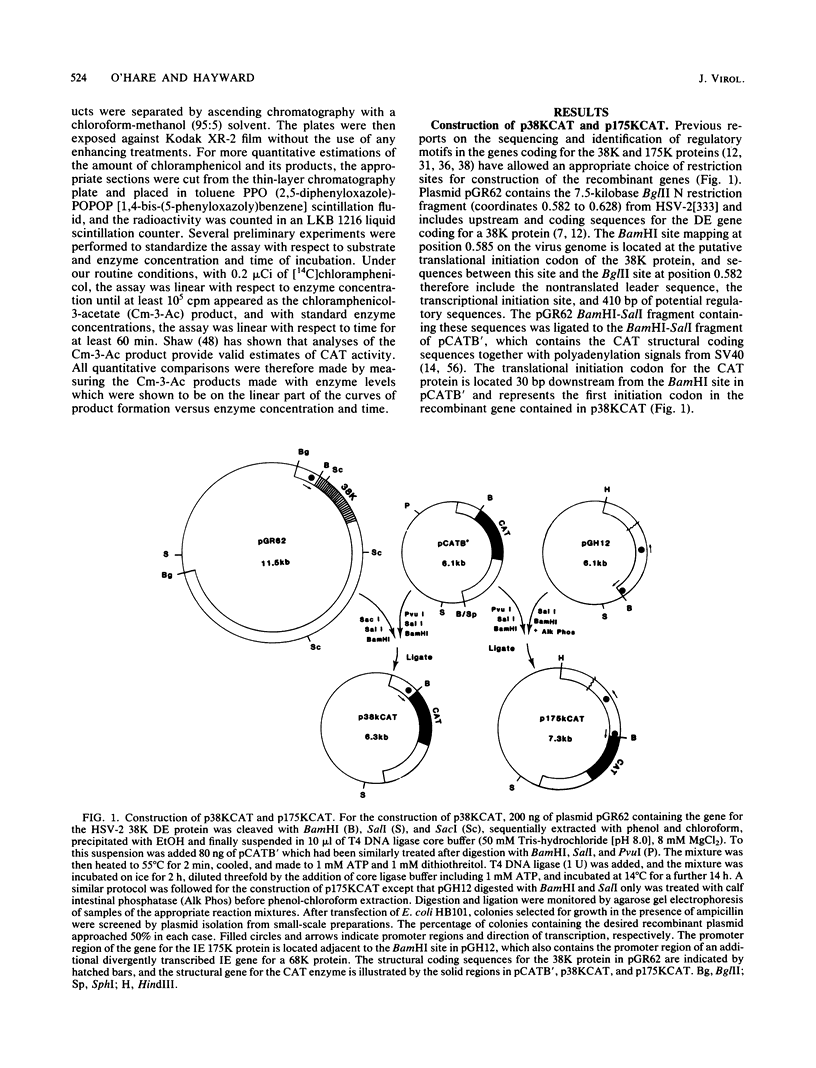
The promoter-regulatory regions from the herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) gene for the immediate-early, 175,000-molecular-weight (175K) protein and the HSV-2 delayed-early gene for a 38K protein were linked to the readily assayable bacterial gene for the enzyme chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT). Unexpectedly, in measurements of the constitutive expression of the recombinant genes 40 to 50 h after transfection of Vero cells, enzyme levels expressed from the delayed-early 38K-promoter-CAT construct (p38KCAT) were at least as high as those from the immediate-early 175K-promoter-CAT construct (p175KCAT). In contrast, enzyme levels expressed after transfection of a similar recombinant gene containing a second delayed-early promoter region, that of the HSV-1 thymidine kinase gene, were ca. 20-fold lower. The amounts of enzyme expressed from both p38KCAT and p175KCAT could be increased by up to 20- to 40-fold after infection of the transfected cells with HSV. In comparison, virus infection had no significant effect on enzyme levels expressed from recombinant CAT genes containing the simian virus 40 early promoter region, with or without the 72-base-pair enhancer element. Experiments with the temperature-sensitive mutants HSV-1 tsB7 and HSV-1 tsK indicate that induction of expression from p175KCAT was mediated by components of the infecting virus particle, whereas that from p38KCAT required de novo expression of virus immediate-early proteins. In addition, we show that functions required to induce expression from both p175KCAT and p38KCAT could also be provided by infection with pseudorabies virus and cytomegalovirus.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K. P., Costa R. H., Holland L. E., Wagner E. K. Characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 RNA present in the absence of de novo protein synthesis. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):9–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.9-27.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batterson W., Roizman B. Characterization of the herpes simplex virion-associated factor responsible for the induction of alpha genes. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):371–377. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.371-377.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun D. K., Batterson W., Roizman B. Identification and genetic mapping of a herpes simplex virus capsid protein that binds DNA. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):645–648. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.645-648.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. B., Watson R. J., Wilkie N. M. Temporal regulation of herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription: location of transcripts on the viral genome. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley M. G., Campbell M. E., Preston C. M. Functional analysis of a herpes simplex virus type 1 promoter: identification of far-upstream regulatory sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2347–2365. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Draper K. G., Banks L., Powell K. L., Cohen G., Eisenberg R., Wagner E. K. High-resolution characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 transcripts encoding alkaline exonuclease and a 50,000-dalton protein tentatively identified as a capsid protein. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):591–603. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.591-603.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. J., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Preston C. M. Identification of a virus-specific polypeptide associated with a transforming fragment (BglII-N) of herpes simplex virus type 2 DNA. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):126–132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.126-132.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. A detailed analysis of an HSV-1 early promoter: sequences involved in trans-activation by viral immediate-early gene products are not early-gene specific. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3037–3056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. DNA sequence elements required for regulated expression of the HSV-1 glycoprotein D gene lie within 83 bp of the RNA capsites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 11;11(19):6647–6666. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.19.6647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick M. L., Walker M. J. Suppression of the synthesis of cellular macromolecules by herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1978 Oct;41(1):37–51. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-1-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway D. A., Goldstein L. C., Lewis J. B. Identification of proteins encoded by a fragment of herpes simplex virus type 2 DNA that has transforming activity. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):530–537. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.530-537.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway D. A., Swain M. A. Organization of the left-hand end of the herpes simplex virus type 2 BglII N fragment. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):724–730. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.724-730.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz C., Roizman B. The alpha promoter regulator-ovalbumin chimeric gene resident in human cells is regulated like the authentic alpha 4 gene after infection with herpes simplex virus 1 mutants in alpha 4 gene. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):145–151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90343-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland L. E., Anderson K. P., Shipman C., Jr, Wagner E. K. Viral DNA synthesis is required for the efficient expression of specific herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA species. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):10–24. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90479-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XI. Identification and relative molar rates of synthesis of structural and nonstructural herpes virus polypeptides in the infected cell. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1347–1365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1347-1365.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: sequential transition of polypeptide synthesis requires functional viral polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Watson D. H. Unity and diversity in the herpesviruses. J Gen Virol. 1977 Oct;37(1):15–37. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-37-1-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman R. W. Identification of proteins tightly bound to herpes simplex virus DNA. Virology. 1980 Aug;105(1):254–255. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R. Activation of gene expression by adenovirus and herpesvirus regulatory genes acting in trans and by a cis-acting adenovirus enhancer element. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90215-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. C., Hayward G. S., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA VII. alpha-RNA is homologous to noncontiguous sites in both the L and S components of viral DNA. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):268–276. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.268-276.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Batterson W., Nosal C., Roizman B., Buchan A. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. VI. Characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutant defective in the expression of all early viral gene products. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):539–547. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.539-547.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Gruss P., Pozzatti R., Khoury G. Characterization of enhancer elements in the long terminal repeat of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):183–189. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.183-189.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Khoury G., Gorman C., Howard B., Gruss P. Host-specific activation of transcription by tandem repeats from simian virus 40 and Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6453–6457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang J. C., Spandidos D. A., Wilkie N. M. Transcriptional regulation of a herpes simplex virus immediate early gene is mediated through an enhancer-type sequence. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):389–395. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01817.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung W. C., Dimock K., Smiley J. R., Bacchetti S. Herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase transcripts are absent from both nucleus and cytoplasm during infection in the presence of cycloheximide. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):361–365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.361-365.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M., Jeffrey A., Wang J., Ladner R., Ptashne M., Pabo C. O. Structure of the operator-binding domain of bacteriophage lambda repressor: implications for DNA recognition and gene regulation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):435–440. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Differentiation between alpha promoter and regulator regions of herpes simplex virus 1: the functional domains and sequence of a movable alpha regulator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4917–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: the alpha 27 gene promoter-thymidine kinase chimera is positively regulated in converted L cells. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1015–1023. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1015-1023.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: transcription-initiation sites and domains of alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7122–7126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Gavis E. R., Kingsbury R., Axel R. Analysis of transcriptional regulatory signals of the HSV thymidine kinase gene: identification of an upstream control region. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):385–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L. The nucleotide sequence and transcript map of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):5949–5964. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.5949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Clements J. B. DNA sequence homology between two co-linear loci on the HSV genome which have different transforming abilities. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):1953–1961. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01684.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau P., Hen R., Wasylyk B., Everett R., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 base repair repeat has a striking effect on gene expression both in SV40 and other chimeric recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6047–6068. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murchie M. J., McGeoch D. J. DNA sequence analysis of an immediate-early gene region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome (map coordinates 0.950 to 0.978). J Gen Virol. 1982 Sep;62(Pt 1):1–15. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-62-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Mechanism of activation of early viral transcription by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90304-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker B. A., Stark G. R. Regulation of simian virus 40 transcription: sensitive analysis of the RNA species present early in infections by virus or viral DNA. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):360–369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.360-369.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Wolff M. H., Fenwick M., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. V. Properties of alpha polypeptides made in HSV-1 and HSV-2 infected cells. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):733–749. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90495-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: expression of chimeric genes produced by fusion of thymidine kinase with alpha gene promoters. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Purifoy D. J., Courtney R. J. The synthesis of herpes simplex virus proteins in the absence of virus DNA synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 2;66(1):262–271. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80323-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M. Control of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA synthesis in cells infected with wild-type virus or the temperature-sensitive mutant tsK. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):275–284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.275-284.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Cordingley M. G. mRNA- and DNA-directed synthesis of herpes simplex virus-coded exonuclease in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):386–394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.386-394.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan M. P., Chen L. B., Knipe D. M. The intranuclear location of a herpes simplex virus DNA-binding protein is determined by the status of viral DNA replication. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):857–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes G. R., Gavis E. R., Buchan A., Raj N. B., Hayward G. S., Pitha P. M. Expression of human beta-interferon cDNA under the control of a thymidine kinase promoter from herpes simplex virus. Nature. 1982 Jun 17;297(5867):598–601. doi: 10.1038/297598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase from chloramphenicol-resistant bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:737–755. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Wilkie N. M. Physical mapping of herpes simplex virus type 1 mutations by marker rescue. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):182–192. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.182-192.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Wilkie N. M. An improved technique for obtaining enhanced infectivity with herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. J Gen Virol. 1976 Dec;33(3):447–458. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-3-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenen D. G., Livingston D. M., Wang S. S., Martin R. G. Effect of a stem-loop structure within the SV40 replication origin upon SV40 T antigen binding to origin region sequences. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):629–639. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90395-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Clements J. B. A herpes simplex virus type 1 function continuously required for early and late virus RNA synthesis. Nature. 1980 May 29;285(5763):329–330. doi: 10.1038/285329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Clements J. B. Characterization of transcription-deficient temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1978 Dec;91(2):364–379. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90384-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Colberg-Poley A. M., Marcus-Sekura C. J., Carter B. J., Enquist L. W. Characterization of the herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D mRNA and expression of this protein in Xenopus oocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1507–1522. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. L., Jones N. C. E1A control of gene expression is mediated by sequences 5' to the transcriptional starts of the early viral genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1222–1234. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. A dominant role for DNA secondary structure in forming hypersensitive structures in chromatin. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1191–1203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90302-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Silverstein S., Lee L. S., Pellicer A., Cheng Y. c., Axel R. Transfer of purified herpes virus thymidine kinase gene to cultured mouse cells. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]