Abstract
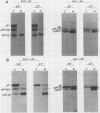
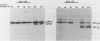
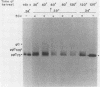
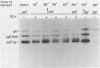
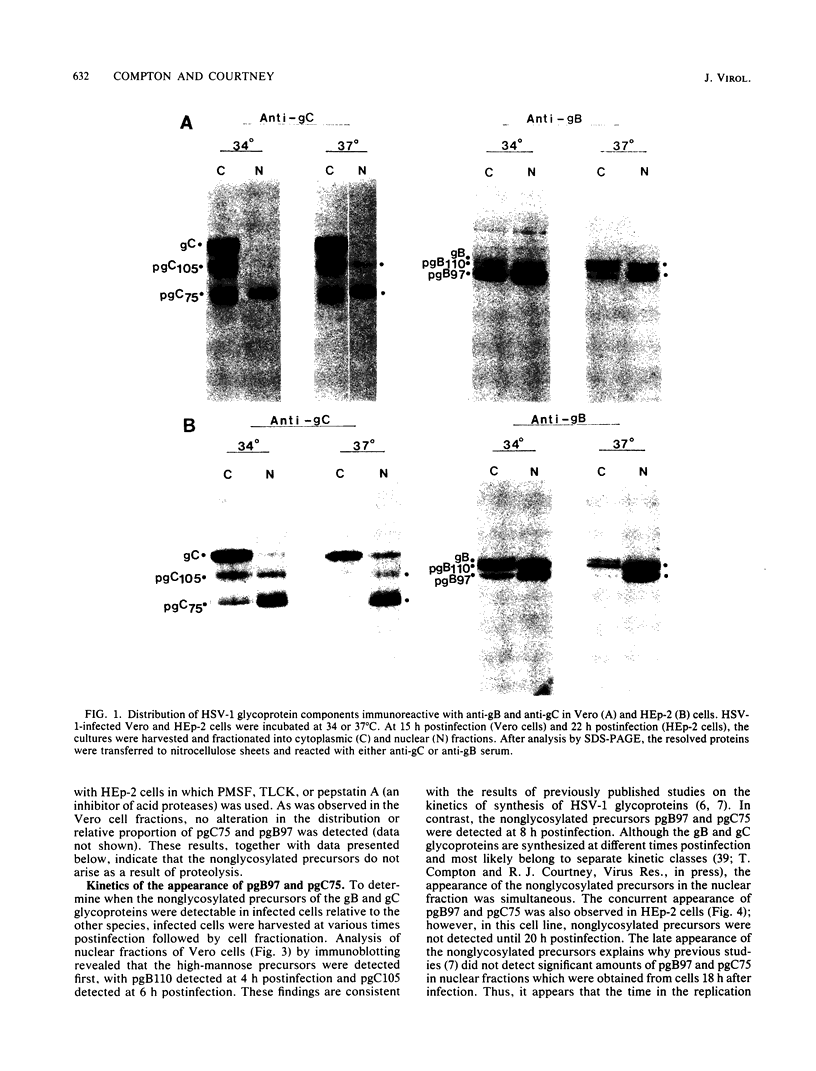
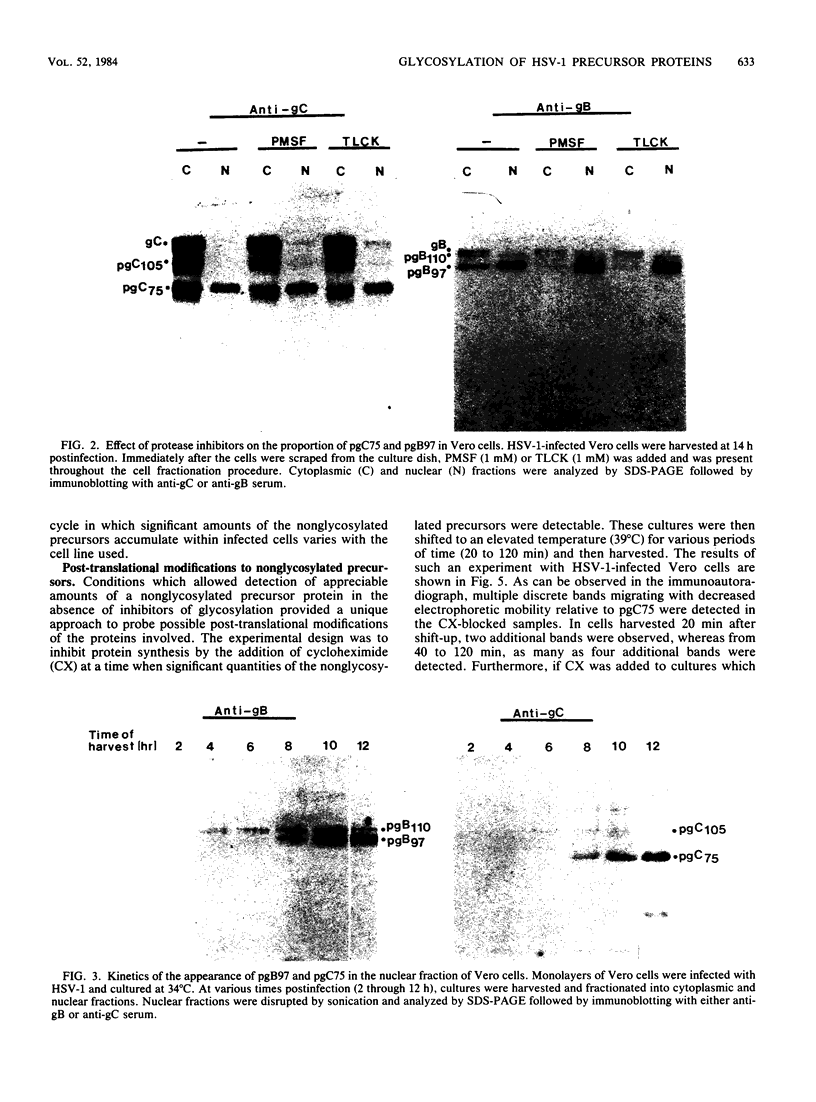
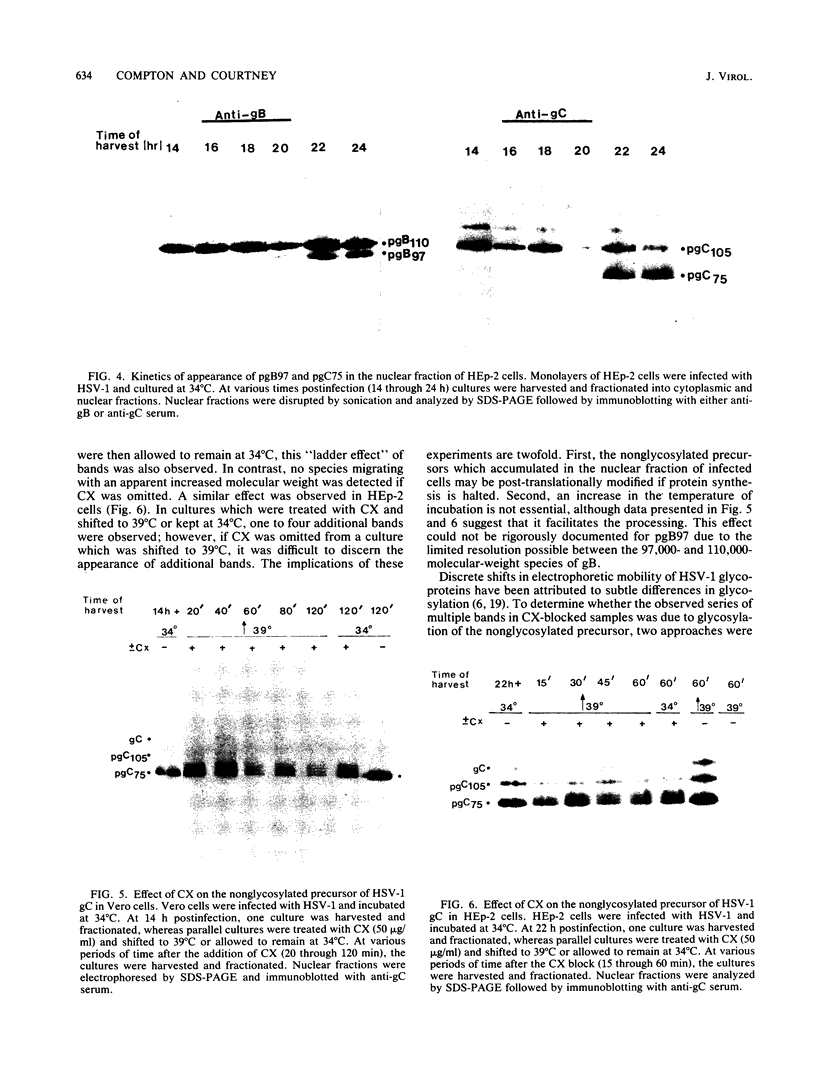
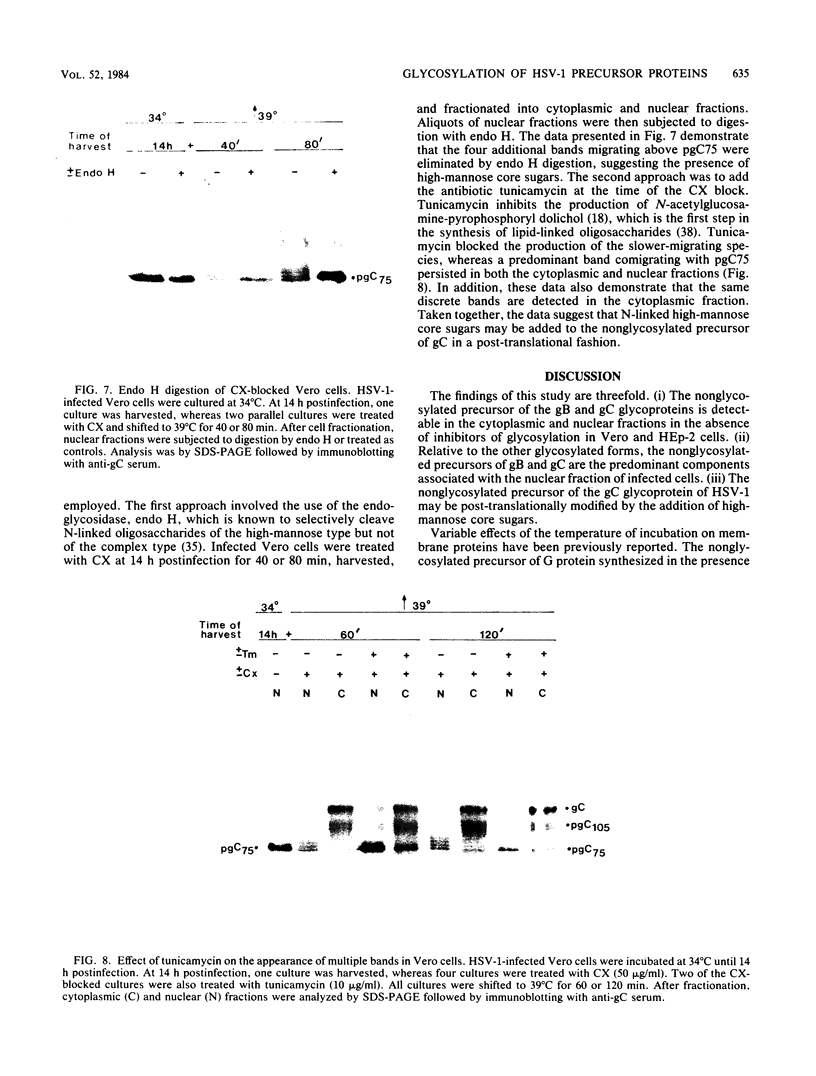
Incubation of herpes simplex virus type 1-infected Vero and HEp-2 cells at a reduced temperature (34 degrees C) enhanced the detection of the nonglycosylated precursors (pgB97 and pgC75) to the gB and gC glycoproteins in the cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions. Relative to the fully glycosylated and high-mannose forms detected, the nonglycosylated precursors were the predominant components associated with the nuclear fraction of infected cells. Furthermore, addition of protease inhibitors to the fractionation buffers did not affect the distribution or abundance of the nonglycosylated precursors, suggesting that the presence of pgB97 and pgC75 was not the result of proteolysis. When infected Vero or HEp-2 cells were harvested at various times postinfection, the nonglycosylated precursors were detected after the initial appearance of the high mannose components (pgB110 and pgC105). In Vero cells, pgB97 and pgC75 were detected simultaneously at 8 h postinfection, whereas detection was not apparent in HEp-2 cells until 20 h postinfection. Conditions which favored detection of appreciable amounts of nonglycosylated precursors provided an unique approach to probe possible post-translational modifications in the absence of inhibitors of glycosylation. In nuclear fractions isolated from cycloheximide-treated HEp-2 or Vero cells, numerous discrete gC-immunoreactive bands migrating with decreased electrophoretic mobility relative to the nonglycosylated precursor pgC75 were observed. This series of one to four additional bands was eliminated by digestion with endoglycosidase H, and the appearance of these bands was blocked by the addition of tunicamycin. Collectively, the data suggest that high-mannose core oligosaccharides may be added to the nonglycosylated precursor of the gC glycoprotein of herpes simplex virus type 1 in a post-translational fashion.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baucke R. B., Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. V. Identification of an Fc-binding glycoprotein. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):779–789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.779-789.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann J. E., Singer S. J. Immunoelectron microscopic studies of the intracellular transport of the membrane glycoprotein (G) of vesicular stomatitis virus in infected Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1777–1787. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann J. E., Tokuyasu K. T., Singer S. J. Passage of an integral membrane protein, the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein, through the Golgi apparatus en route to the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1746–1750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Walter P., Chang C. N., Goldman B. M., Erickson A. H., Lingappa V. R. Translocation of proteins across membranes: the signal hypothesis and beyond. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1979;33:9–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone D. R., Courtney R. J. A temperature-sensitive mutant of herpes simplex virus type 1 defective in the synthesis of the major capsid polypeptide. J Gen Virol. 1974 Jul;24(1):17–27. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-1-17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Long D., Eisenberg R. J. Synthesis and processing of glycoproteins gD and gC of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):429–439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.429-439.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton T., Courtney R. J. Virus-specific glycoproteins associated with the nuclear fraction of herpes simplex virus type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):594–597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.594-597.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney R. J. Herpes simplex virus protein synthesis in the presence of 2-deoxy-D-glucose. Virology. 1976 Aug;73(1):286–294. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn W. A., Hubbard A. L., Aronson N. N., Jr Low temperature selectively inhibits fusion between pinocytic vesicles and lysosomes during heterophagy of 125I-asialofetuin by the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5971–5978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberle R., Courtney R. J. Preparation and characterization of specific antisera to individual glycoprotein antigens comprising the major glycoprotein region of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):902–917. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.902-917.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberle R., Courtney R. J. gA and gB glycoproteins of herpes simplex virus type 1: two forms of a single polypeptide. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):665–675. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.665-675.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. J., Hydrean-Stern C., Cohen G. H. Structural analysis of precursor and product forms of type-common envelope glycoprotein D (CP-1 antigen) of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1979 Sep;31(3):608–620. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.3.608-620.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferro-Novick S., Hansen W., Schauer I., Schekman R. Genes required for completion of import of proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum in yeast. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):44–53. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferro-Novick S., Novick P., Field C., Schekman R. Yeast secretory mutants that block the formation of active cell surface enzymes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):35–43. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frink R. J., Eisenberg R., Cohen G., Wagner E. K. Detailed analysis of the portion of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome encoding glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):634–647. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.634-647.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson R., Schlesinger S., Kornfeld S. The nonglycosylated glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus is temperature-sensitive and undergoes intracellular aggregation at elevated temperatures. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3600–3607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. R. The biochemistry and ultrastructure of the nuclear envelope. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 10;515(1):55–104. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(78)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heifetz A., Keenan R. W., Elbein A. D. Mechanism of action of tunicamycin on the UDP-GlcNAc:dolichyl-phosphate Glc-NAc-1-phosphate transferase. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2186–2192. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Spear P. G. O-linked oligosaccharides are acquired by herpes simplex virus glycoproteins in the Golgi apparatus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):987–997. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90083-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Schekman R., Thorner J. Glycosylation and processing of prepro-alpha-factor through the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):309–318. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki T., Yamashina I. Isolation and characterization of glycopeptides from rat liver nuclear membrane. J Biochem. 1972 Dec;72(6):1517–1525. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li E., Tabas I., Kornfeld S. The synthesis of complex-type oligosaccharides. I. Structure of the lipid-linked oligosaccharide precursor of the complex-type oligosaccharides of the vesicular stomatitis virus G protein. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 10;253(21):7762–7770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Bolzau E., Helenius A. Penetration of Semliki Forest virus from acidic prelysosomal vacuoles. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):931–940. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Simons K. Reduced temperature prevents transfer of a membrane glycoprotein to the cell surface but does not prevent terminal glycosylation. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):233–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90154-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson S., Blomberg J., Lycke E. O-glycosidic carbohydrate-peptide linkages of Herpes simplex virus glycoproteins. Arch Virol. 1981;70(4):321–329. doi: 10.1007/BF01320247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson S., Sjöblom I., Lundström M., Jeansson S., Lycke E. Glycoprotein C of herpes simplex virus type 1: characterization of O-linked oligosaccharides. J Gen Virol. 1983 Dec;64(Pt 12):2735–2747. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-12-2735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S. RNA metabolism in the HeLa cell nucleus. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):117–130. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizer L. I., Cohen G. H., Eisenberg R. J. Effect of tunicamycin on herpes simplex virus glycoproteins and infectious virus production. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):142–153. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.142-153.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Courtney R. J. Polypeptide synthesized in herpes simplex virus type 2-infected HEp-2 cells. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini D. D., Kreibich G., Morimoto T., Adesnik M. Mechanisms for the incorporation of proteins in membranes and organelles. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):1–22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini-Cessi F., Campadelli-Fiume G. Studies on benzhydrazone, a specific inhibitor of herpesvirus glycoprotein synthesis. Size distribution of glycopeptides and endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase-H treatment. Arch Virol. 1981;70(4):331–343. doi: 10.1007/BF01320248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. I. Identification of four glycoprotein precursors and their products in type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):991–1008. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.991-1008.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. V. Purification and structural proteins of the herpesvirion. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):143–159. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.143-159.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabas I., Schlesinger S., Kornfeld S. Processing of high mannose oligosaccharides to form complex type oligosaccharides on the newly synthesized polypeptides of the vesicular stomatitis virus G protein and the IgG heavy chain. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):716–722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Maley F. Purification and properties of an endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Streptomyces griseus. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):811–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrisi M. R., Pinto da Silva P. Compartmentalization of intracellular membrane glycocomponents is revealed by fracture-label. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):29–34. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARNER J. R., KNOPF P. M., RICH A. A multiple ribosomal structure in protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jan 15;49:122–129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waechter C. J., Lennarz W. J. The role of polyprenol-linked sugars in glycoprotein synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:95–112. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.000523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenske E. A., Bratton M. W., Courtney R. J. Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H sensitivity of precursors to herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins gB and gC. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):241–248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.241-248.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenske E. A., Courtney R. J. Glycosylation of herpes simplex virus type 1 gC in the presence of tunicamycin. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):297–301. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.297-301.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zezulak K. M., Spear P. G. Limited proteolysis of herpes simplex virus glycoproteins that occurs during their extraction from vero cells. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):258–262. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.258-262.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein A., Snider M. D., Lodish H. F. Synthesis and assembly of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 2):785–795. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]