Abstract
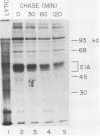
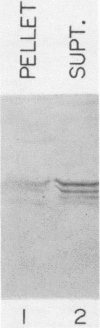
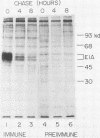
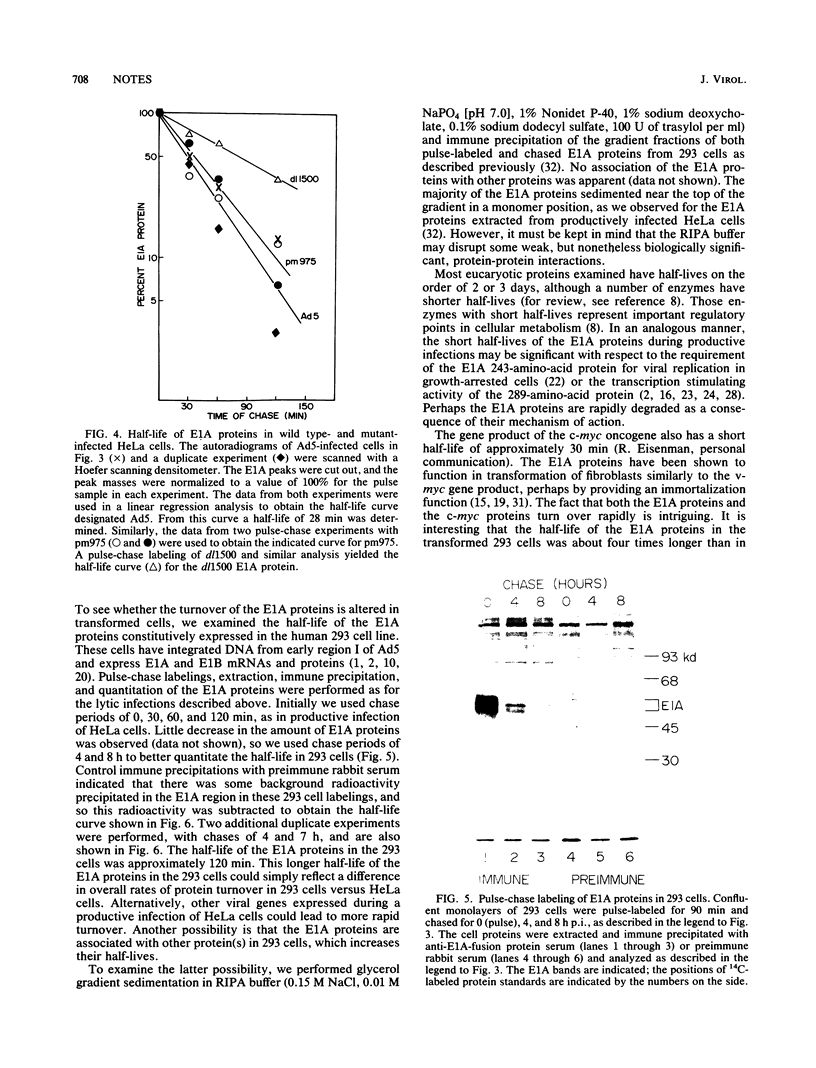
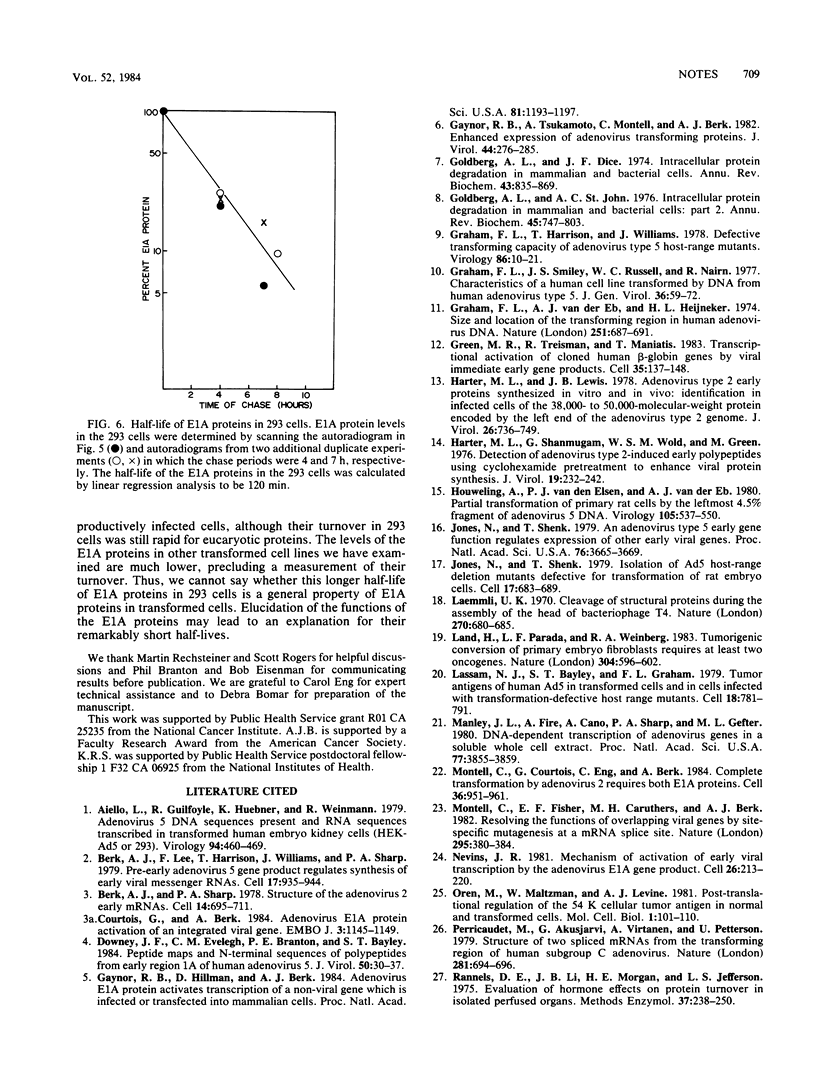
The half-life of the adenovirus 5 early region 1A (E1A) proteins was examined in productively infected and transformed cells. In HeLa cells infected with adenovirus 5, the half-life of the E1A proteins was approximately 30 min; in the transformed 293 cells, the constitutively expressed E1A proteins had a half-life of approximately 120 min. In HeLa cells, the E1A proteins produced by an adenovirus mutant that expresses only the 13S mRNA had a half-life of about 35 min; E1A proteins produced by a mutant that express only the 12S mRNA had a half-life of about 80 min. This difference in the stability of these two classes of E1A proteins helps explain why the steady-state level of the 12S class is usually equal to or greater than that of the 13S class, despite the fact that the concentration of the 13S mRNA is about four times greater than the concentration of the 12S mRNA.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiello L., Guilfoyle R., Huebner K., Weinmann R. Adenovirus 5 DNA sequences present and RNA sequences transcribed in transformed human embryo kidney cells (HEK-Ad-5 or 293). Virology. 1979 Apr 30;94(2):460–469. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90476-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Lee F., Harrison T., Williams J., Sharp P. A. Pre-early adenovirus 5 gene product regulates synthesis of early viral messenger RNAs. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):935–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Structure of the adenovirus 2 early mRNAs. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):695–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90252-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtois G., Berk A. Adenovirus E1A protein activation of an integrated viral gene. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1145–1149. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01943.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downey J. F., Evelegh C. M., Branton P. E., Bayley S. T. Peptide maps and N-terminal sequences of polypeptides from early region 1A of human adenovirus 5. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):30–37. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.30-37.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor R. B., Hillman D., Berk A. J. Adenovirus early region 1A protein activates transcription of a nonviral gene introduced into mammalian cells by infection or transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1193–1197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor R. B., Tsukamoto A., Montell C., Berk A. J. Enhanced expression of adenovirus transforming proteins. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):276–285. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.276-285.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., Dice J. F. Intracellular protein degradation in mammalian and bacterial cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):835–869. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.004155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., St John A. C. Intracellular protein degradation in mammalian and bacterial cells: Part 2. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:747–803. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Harrison T., Williams J. Defective transforming capacity of adenovirus type 5 host-range mutants. Virology. 1978 May 1;86(1):10–21. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J., Heijneker H. L. Size and location of the transforming region in human adenovirus type 5 DNA. Nature. 1974 Oct 25;251(5477):687–691. doi: 10.1038/251687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Treisman R., Maniatis T. Transcriptional activation of cloned human beta-globin genes by viral immediate-early gene products. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90216-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harter M. L., Lewis J. B. Adenovirus type 2 early proteins synthesized in vitro and in vivo: identification in infected cells of the 38,000- to 50,000- molecular-weight protein encoded by the left end of the adenovirus type 2 genome. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):736–749. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.736-749.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harter M. L., Shanmugam G., Wold W. S., Green M. Detection of adenovirus type 2-induced early polypeptides using cycloheximide pretreatment to enhance viral protein synthesis. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):232–242. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.232-242.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houweling A., van den Elsen P. J., van der Eb A. J. Partial transformation of primary rat cells by the leftmost 4.5% fragment of adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1980 Sep;105(2):537–550. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. An adenovirus type 5 early gene function regulates expression of other early viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3665–3669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. Isolation of adenovirus type 5 host range deletion mutants defective for transformation of rat embryo cells. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):683–689. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassam N. J., Bayley S. T., Graham F. L. Tumor antigens of human Ad5 in transformed cells and in cells infected with transformation-defective host-range mutants. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):781–791. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Courtois G., Eng C., Berk A. Complete transformation by adenovirus 2 requires both E1A proteins. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):951–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Fisher E. F., Caruthers M. H., Berk A. J. Resolving the functions of overlapping viral genes by site-specific mutagenesis at a mRNA splice site. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):380–384. doi: 10.1038/295380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Mechanism of activation of early viral transcription by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90304-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M., Maltzman W., Levine A. J. Post-translational regulation of the 54K cellular tumor antigen in normal and transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):101–110. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perricaudet M., Akusjärvi G., Virtanen A., Pettersson U. Structure of two spliced mRNAs from the transforming region of human subgroup C adenoviruses. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):694–696. doi: 10.1038/281694a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rannels D. E., Li J. B., Morgan H. E., Jefferson L. S. Evaluation of hormone effects on protein turnover in isolated perfused organs. Methods Enzymol. 1975;37:238–250. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)37020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Jones R. L., Cepko C. L., Sharp P. A., Roberts B. E. Expression of early adenovirus genes requires a viral encoded acidic polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6121–6125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. T., Graham F. L., Branton P. E. Intracellular localization of adenovirus type 5 tumor antigens in productively infected cells. Virology. 1983 Sep;129(2):456–468. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. T., Yee S. P., Otis J., Graham F. L., Branton P. E. Characterization of human adenovirus type 5 early region 1A polypeptides using antitumor sera and an antiserum specific for the carboxy terminus. Virology. 1983 Jun;127(2):253–271. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90142-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E. Adenovirus early region 1A enables viral and cellular transforming genes to transform primary cells in culture. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):602–606. doi: 10.1038/304602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindler K. R., Rosser D. S., Berk A. J. Analysis of adenovirus transforming proteins from early regions 1A and 1B with antisera to inducible fusion antigens produced in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):132–141. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.132-141.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Eb A. J., Mulder C., Graham F. L., Houweling A. Transformation with specific fragments of adenovirus DNAs. I. Isolation of specific fragments with transforming activity of adenovirus 2 and 5 DNA. Gene. 1977;2(3-4):115–132. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee S. P., Rowe D. T., Tremblay M. L., McDermott M., Branton P. E. Identification of human adenovirus early region 1 products by using antisera against synthetic peptides corresponding to the predicted carboxy termini. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):1003–1013. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.1003-1013.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]