Abstract
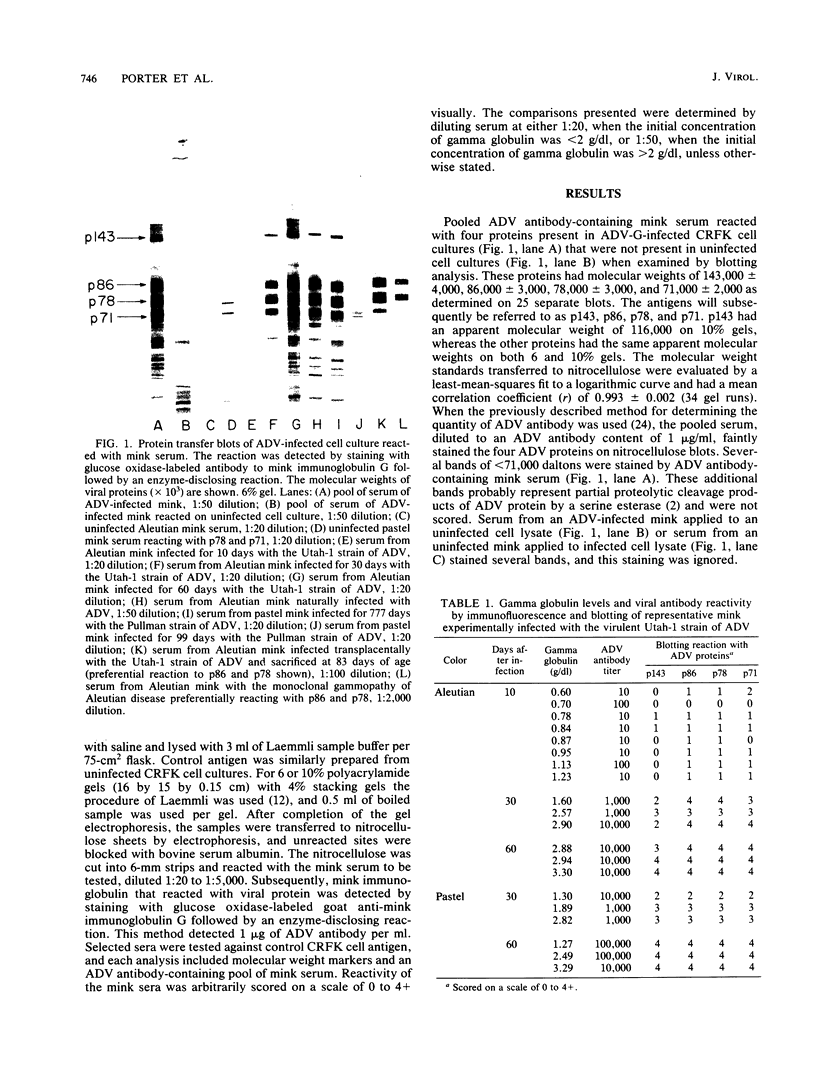
Aleutian disease virus (ADV), an autonomous parvovirus, persistently infects mink and induces very high levels of virus-specific antibody. All strains of ADV infect all mink, but only highly virulent strains cause progressive disease in non-Aleutian mink. The development of antibody to individual ADV proteins was evaluated by Western blotting by using the sera of 22 uninfected mink and 163 naturally or experimentally infected mink. ADV has virion proteins of 86,000 and 78,000 daltons that are closely related. A new, possibly nonvirion protein of 143,000 daltons was observed, as well as a known nonvirion protein of 71,000 daltons. Sera from mink experimentally or naturally infected with ADV of high or low virulence generally reacted about equally with all four proteins. The only exceptions noted were that 8 of 15 sera of mink infected transplacentally preferentially reacted with the two virion proteins and sera from mink with the monoclonal gammopathy of Aleutian disease reacted preferentially with either virion (10 of 12) or nonvirion (2 of 12) proteins.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aasted B. Purification and characterization of Aleutian disease virus. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1980 Dec;88(6):323–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb02650.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aasted B., Race R. E., Bloom M. E. Aleutian disease virus, a parvovirus, is proteolytically degraded during in vivo infection in mink. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):7–13. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.7-13.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Mayer L. W., Garon C. F. Characterization of the Aleutian disease virus genome and its intracellular forms. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):977–984. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.977-984.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Race R. E., Wolfinbarger J. B. Characterization of Aleutian disease virus as a parvovirus. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):836–843. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.836-843.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Race R. E., Wolfinbarger J. B. Identification of a nonvirion protein of Aleutian disease virus: mink with Aleutian disease have antibody to both virion and nonvirion proteins. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):608–616. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.608-616.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Sturzenbecker L. J., Tattersall P. The autonomous parvovirus MVM encodes two nonstructural proteins in addition to its capsid polypeptides. Virology. 1983 Sep;129(2):333–343. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90172-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford T. B., McGuire T. C., Porter D. D., Cho H. J. A comparative study of detection methods for Aleutian disease viral antibody. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1249–1251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund C. M., Hadlow W. J., Kennedy R. C., Boyle C. C., Jackson T. A. Aleutian disease of mink: properties of the etiologic agent and the host responses. J Infect Dis. 1968 Dec;118(5):510–526. doi: 10.1093/infdis/118.5.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadlow W. J., Race R. E., Kennedy R. C. Comparative pathogenicity of four strains of Aleutian disease virus for pastel and sapphire mink. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1016–1023. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1016-1023.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadlow W. J., Race R. E., Kennedy R. C. Royal pastel mink respond variously to inoculation with Aleutian disease virus of low virulence. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):38–41. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.38-41.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn E. C., Ramos L., Kenyon A. J. Characterization of deoxyribonucleic acid from cells infected with Aleutian disease virus. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Jul;44(7):1177–1181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederman M., Bates R. C., Stout E. R. In vitro and in vivo studies of bovine parvovirus proteins. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):10–17. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.10-17.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga Y., Matsuno S. Structural and nonstructural proteins of a rabbit parvovirus. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):627–633. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.627-633.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra R., Wali T., Valdez V., Fabisch P., Salzman L. A. Transcription and translation in the autonomous parvovirus KRV. Virology. 1983 Mar;125(2):349–360. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90207-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak B., Sullivan C., Sarnow P., Thomas R., Bricout F., Nicolas J. C., Fleckenstein B., Levine A. J. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies and polyclonal immune sera directed against human cytomegalovirus virion proteins. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):325–338. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER D. D., DIXON F. J., LARSEN A. E. THE DEVELOPMENT OF A MYELOMA-LIKE CONDITION IN MINK WITH ALEUTIAN DISEASE. Blood. 1965 May;25:736–742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Larsen A. E., Cox N. A., Porter H. G., Suffin S. C. Isolation of Aleutian disease virus of mink in cell culture. Intervirology. 1977;8(3):129–144. doi: 10.1159/000148888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Larsen A. E., Porter H. G. Aleutian disease of mink. Adv Immunol. 1980;29:261–286. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Larsen A. E., Porter H. G. Reduced severity of lesions in mink infected transplacentally with Aleutian disease virus. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):872–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Larsen A. E., Porter H. G. The pathogenesis of Aleutian disease of mink. I. In vivo viral replication and the host antibody response to viral antigen. J Exp Med. 1969 Sep 1;130(3):575–593. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.3.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Porter H. G. A glucose oxidase immunoenzyme stain for the detection of viral antigen or antibody on nitrocellulose transfer blots. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Aug 3;72(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90428-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Porter H. G., Larsen A. E. Much of the increased IgG in Aleutian disease of mink is viral antibody. J Exp Pathol. 1984;1(2):79–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Porter H. G., Suffin S. C., Larsen A. E. Immunoglobulin classes of Aleutian disease virus antibody. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):463–466. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.463-466.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter H. G., Porter D. D., Larsen A. E. Aleutian disease in ferrets. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):379–386. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.379-386.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd, Paradiso P. R. Parvovirus genome: nucleotide sequence of H-1 and mapping of its genes by hybrid-arrested translation. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):173–184. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.173-184.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selgrade M. K., Huang Y. S., Graham J. A., Huang C. H., Hu P. C. Humoral antibody response to individual viral proteins after murine cytomegalovirus infection. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):3032–3035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]