Abstract
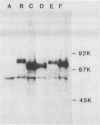
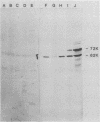
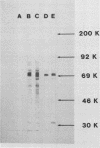
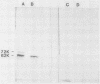
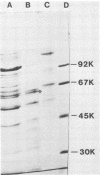
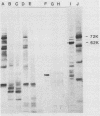
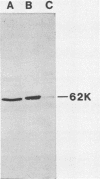
A 62,000-dalton (62K) cell protein reacts with antisera to the 72K polypeptide of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (EBNA) in immunoblots. This protein was initially detected in EBNA-negative as well as EBNA-positive cell lines with anti-EBNA-positive human sera. A monoclonal antibody raised against the 72K EBNA and an antiserum from a rabbit immunized with the glycine-alanine domain of EBNA also reacted with the cellular protein. The cellular protein was partially purified from Epstein-Barr virus genome-positive and -negative cell lines. Absorption experiments identified a shared antigenic determinant between the 72K EBNA and 62K cellular protein. A comparison of the 62K protein and EBNA by protease digestion did not reveal similar peptides.
Full text
PDF

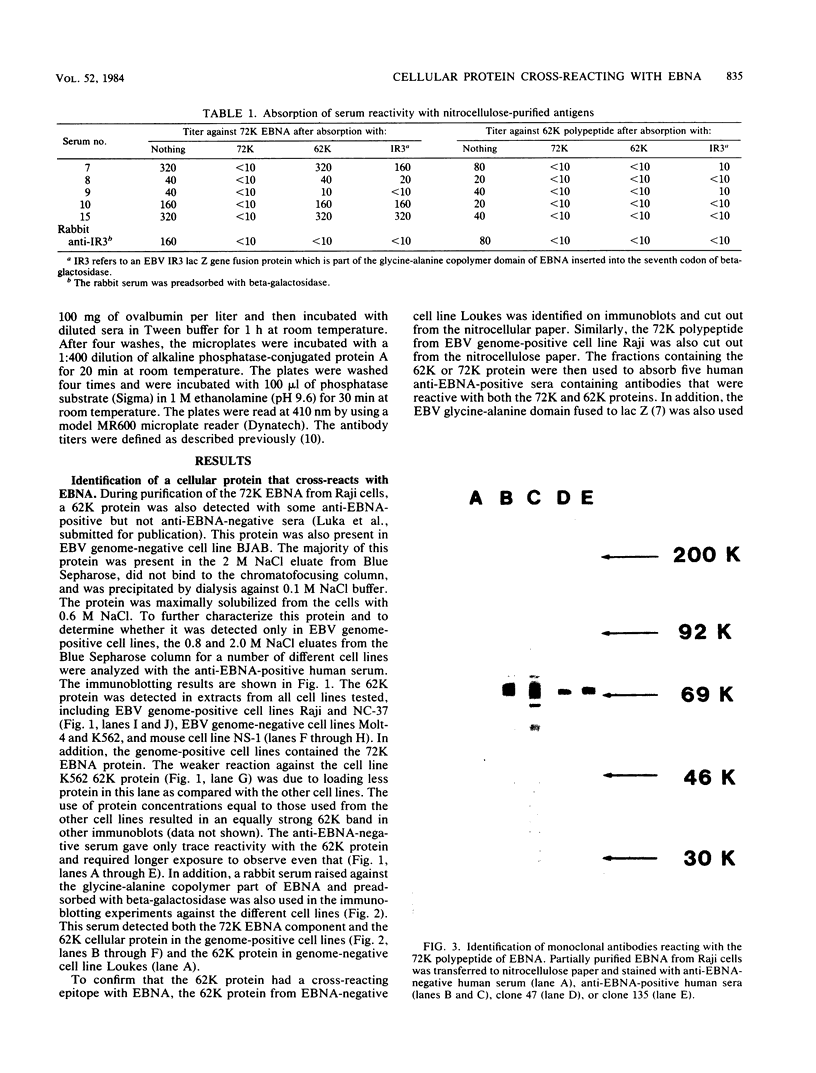



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer D. K., Robert M. F., Shedd D., Summers W. P., Robinson J. E., Wolak J., Stefano J. E., Miller G. Identification of Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen polypeptide in mouse and monkey cells after gene transfer with a cloned 2.9-kilobase-pair subfragment of the genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):43–47. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser R., Boyd A., Stoerker J., Holliday J. Functional mapping of the Epstein-Barr virus genome: identification of sites coding for the restricted early antigen, the diffuse early antigen, and the nuclear antigen. Virology. 1983 Aug;129(1):188–198. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90405-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock K., Tsang V. C. India ink staining of proteins on nitrocellulose paper. Anal Biochem. 1983 Aug;133(1):157–162. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller M., Henderson A., Kieff E. Repeat array in Epstein-Barr virus DNA is related to cell DNA sequences interspersed on human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5916–5920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller M., van Santen V., Kieff E. Simple repeat sequence in Epstein-Barr virus DNA is transcribed in latent and productive infections. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):311–320. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.311-320.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Heller M., van Santen V., Kieff E. Simple repeat array in Epstein-Barr virus DNA encodes part of the Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen. Science. 1983 Jun 24;220(4604):1396–1398. doi: 10.1126/science.6304878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Kieff E. One of two Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigens contains a glycine-alanine copolymer domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5665–5669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luka J., Chase R. C., Pearson G. R. A sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) against the major EBV-associated antigens. I. Correlation between ELISA and immunofluorescence titers using purified antigens. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Feb 24;67(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90093-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luka J., Jörnvall H., Klein G. The Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen: a previously identified 48K component and higher-molecular-weight forms of the antigen are structurally related. Intervirology. 1983;20(4):213–222. doi: 10.1159/000149394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo T., Hibi N., Nishi S., Hirai H., Osato T. Studies on Epstein-Barr virus-related antigens. III. Purification of the virus-determined nuclear antigen (EBNA) from non-producer Raji cells. Int J Cancer. 1978 Dec;22(6):747–752. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910220618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qualtiere L. F., Chase R., Vroman B., Pearson G. R. Identification of Epstein-Barr virus strain differences with monoclonal antibody to a membrane glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):616–620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reading C. L. Theory and methods for immunization in culture and monoclonal antibody production. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Sep 30;53(3):261–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90175-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G. Cellular localization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):499–520. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sculley T. B., Kreofsky T., Pearson G. R., Spelsberg T. C. Partial purification of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen(s). J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3974–3982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spelsberg T. C., Sculley T. B., Pikler G. M., Gilbert J. A., Pearson G. R. Evidence for two classes of chromatin-associated Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):555–565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.555-565.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strnad B. C., Schuster T. C., Hopkins R. F., 3rd, Neubauer R. H., Rabin H. Identification of an Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen by fluoroimmunoelectrophoresis and radioimmunoelectrophoresis. J Virol. 1981 Jun;38(3):996–1004. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.3.996-1004.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]