Abstract
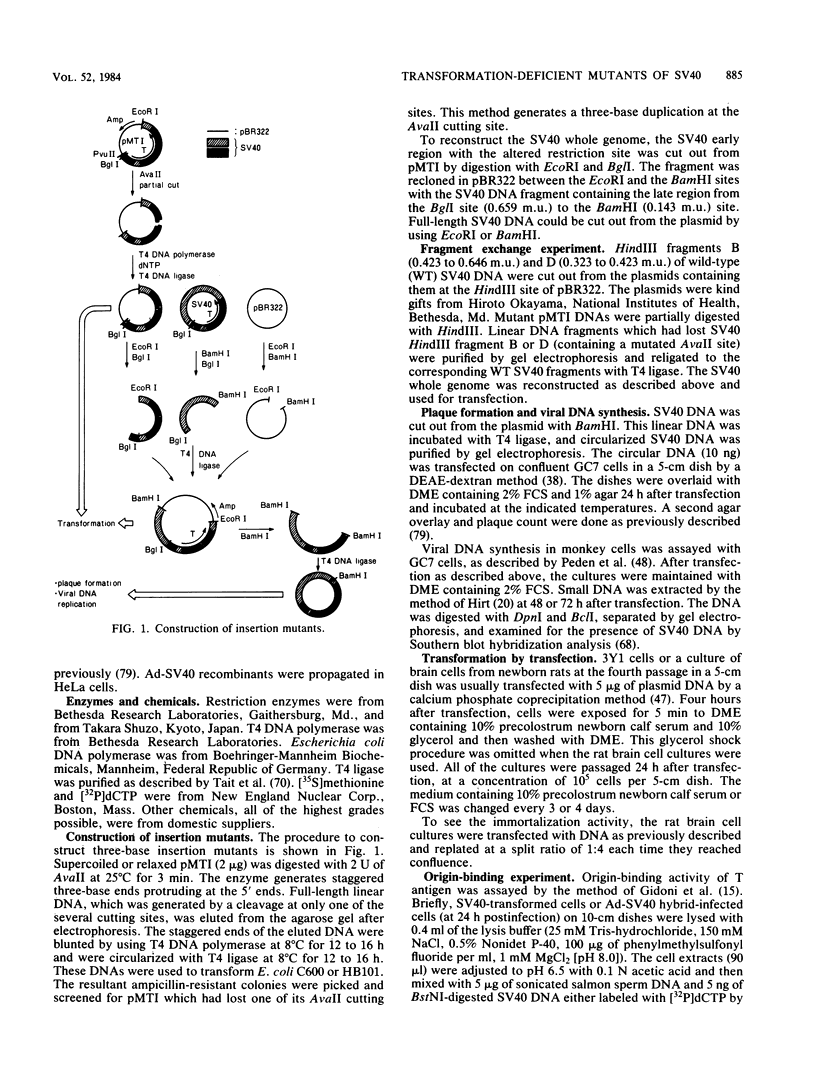
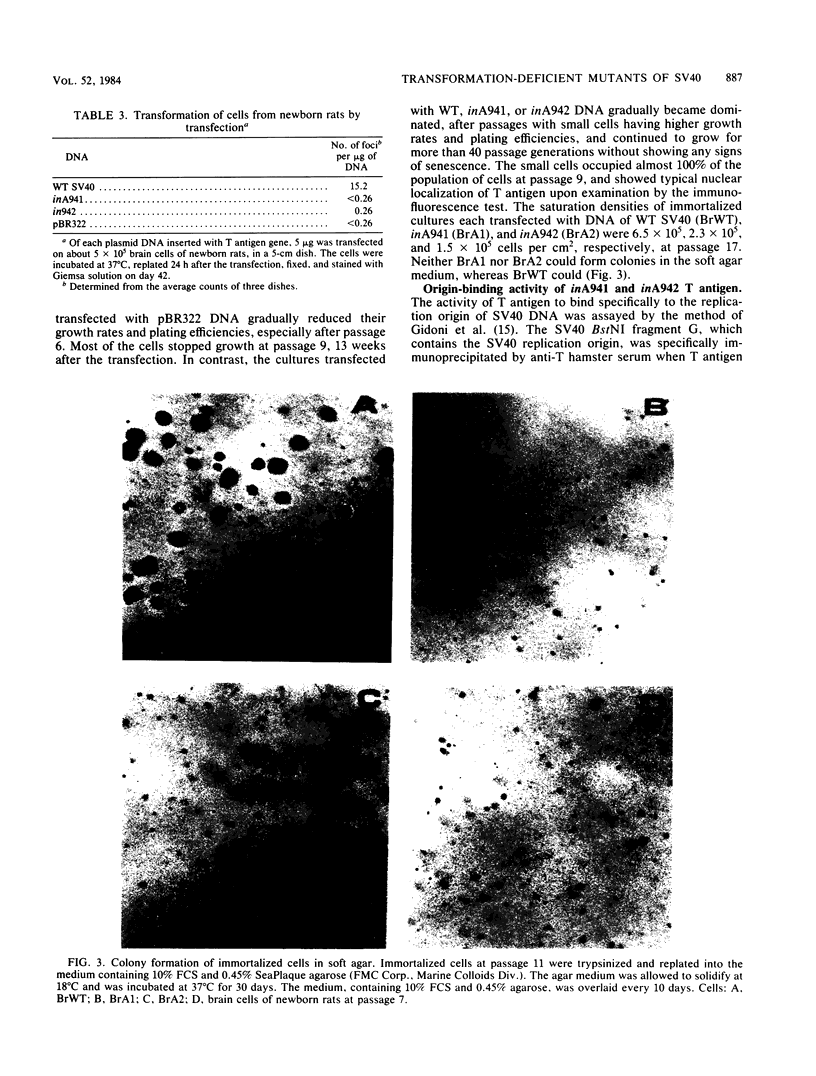
We constructed two mutants of simian virus 40 (SV40) by introducing a three-base duplication at AvaII cutting sites within the large T antigen coding region, and we examined these mutants for their abilities to replicate in monkey GC7 cells, to transform rat cell line 3Y1 cells, and to transform and immortalize primary cells from newborn rats. Neither of the mutants could replicate in GC7 cells. One mutant with the duplication at 0.335 SV40 map units (m.u.) (inA942) could transform 3Y1 cells, but the other mutant with the duplication at 0.636 m.u. (inA941) could not. The two mutants could not transform primary rat cells but retained immortalization activity. The results suggest that transformation of primary cells by SV40 requires at least two distinct activities of the large T antigen, one of which can be replaced by a cellular function(s) expressed in immortalized 3Y1 cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Reed S. I., Stark G. R. Characterization of the autoregulation of simian virus 40 gene A. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):22–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.22-27.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ariga H., Sugano S. Initiation of simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):481–491. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.481-491.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockman W. W. Transformation of BALB/c-3T3 cells by tsA mutants of simian virus 40: temperature sensitivity of the transformed phenotype and retransofrmation by wild-type virus. J Virol. 1978 Mar;25(3):860–870. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.3.860-870.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Butel J. S. Role of simian virus 40 gene A function in maintenance of transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):619–635. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.619-635.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll R. B., Hager L., Dulbecco R. Simian virus 40 T antigen binds to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3754–3757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J. Y., Martin R. G. DNA infectivity and the induction of host DNA synthesis with temperature-sensitive mutants of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1975 Jan;15(1):145–150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.1.145-150.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R., Lane D. P., Tjian R. Use of monoclonal antibodies as probes of simian virus 40 T antigen ATPase activity. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11854–11858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton C. E., Murphy D., Lovett M., Rigby P. W. A fragment of the SV40 large T-antigen gene transforms. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):59–61. doi: 10.1038/299059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby W. W., Shenk T. Fragments of the simian virus 40 transforming gene facilitate transformation of rat embryo cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5189–5193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Crawford L. V., Berg P. Simian virus 40 mutants with deletions at the 3' end of the early region are defective in adenovirus helper function. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):683–691. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.683-691.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosman D. J., Tevethia M. J. Characterization of a temperature-sensitive, DNA-positive, nontransforming mutant of simian virus 40. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):605–624. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90306-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey G., Lewis J. B., Grodzicker T., Bothwell A. Characterization of a fused protein specified by the adenovirus type 2-simian virus 40 hybrid Ad2+ND1 dp2. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):201–217. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.201-217.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman M. P., Lyons M. J., Ginsberg H. S. Biochemical consequences of type 2 adenovirus and Simian virus 40 double infections of African green monkey kidney cells. J Virol. 1970 May;5(5):586–597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.5.586-597.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanti N., Jonak G. J., Soprano K. J., Floros J., Kaczmarek L., Weissman S., Reddy V. B., Tilghman S. M., Baserga R. Characterization and biological activity of cloned simian virus 40 DNA fragments. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 25;256(12):6469–6474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacherio D., Hager L. P. A poly(dT)-stimulated ATPase activity associated with simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8113–8116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Scheller A., Barnet B., Hantzopoulos P., Oren M., Prives C. Different forms of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen varying in their affinities for DNA. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):456–466. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.456-466.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y., Ahrens B. SV40 early mutants that are defective for viral DNA synthesis but competent for transformation of cultured rat and simian cells. Virology. 1982 Nov;123(1):78–92. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90296-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodzicker T., Lewis J. B., Anderson C. W. Conditional lethal mutants of adenovirus type 2-simian virus 40 hybrids. II. Ad2+ND1 host-range mutants that synthesize fragments of the Ad2+ND1 30K protein. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):559–571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.559-571.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiscott J. B., Defendi V. Simian virus 40 gene A regulation of cellular DNA synthesis. I. In permissive cells. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):590–599. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.590-599.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiscott J. B., Defendi V. Simian virus 40 gene A regulation of cellular DNA synthesis. II. In nonpermissive cells. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):802–812. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.802-812.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houweling A., van den Elsen P. J., van der Eb A. J. Partial transformation of primary rat cells by the leftmost 4.5% fragment of adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1980 Sep;105(2):537–550. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessel D., Landau T., Hudson J., Lalor T., Tenen D., Livingston D. M. Identification of regions of the SV40 genome which contain preferred SV40 T antigen-binding sites. Cell. 1976 Aug;8(4):535–545. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90222-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., May E. Regulation of early and late simian virus 40 transcription: overproduction of early viral RNA in the absence of a functional T-antigen. J Virol. 1977 Jul;23(1):167–176. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.1.167-176.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura G. Genetic evidence for SV40 gene function in enhancement of replication of human adenovirus in simian cells. Nature. 1974 Apr 12;248(449):590–592. doi: 10.1038/248590a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura G., Itagaki A. Initiation and maintenance of cell transformation by simian virus 40: a viral genetic property. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):673–677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura G., Itagaki A., Summers J. Rat cell line 3y1 and its virogenic polyoma- and sv40- transformed derivatives. Int J Cancer. 1975 Apr 15;15(4):694–706. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910150419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchino T., Yamaguchi N. Characterization of T antigen in cells infected with a temperature-sensitive mutant of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1302–1307. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1302-1307.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Nathans D. A map of temperature-sensitive mutants of simian virus 40. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):70–81. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90179-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Crawford L. V. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):261–263. doi: 10.1038/278261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Levine A. J. Characterization of a 54K dalton cellular SV40 tumor antigen present in SV40-transformed cells and uninfected embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston D. M., Henderson I. C., Hudson J. SV40 T antigen: partial purification and properties. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):283–289. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G., Chou J. Y. Simian virus 40 functions required for the establishment and maintenance of malignant transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):599–612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.599-612.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May P., May E., Bordé J. Stimulation of cellular RNA synthesis in mouse-kidney cell cultures infected with SV40 virus. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Jul;100(2):433–436. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay R. D. Binding of a simian virus 40 T antigen-related protein to DNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 25;145(3):471–488. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90540-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay R., DiMaio D. Binding of an SV40 T antigen-related protein to the DNA of SV40 regulatory mutants. Nature. 1981 Feb 26;289(5800):810–813. doi: 10.1038/289810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller C., Graessmann A., Graessmann M. Mapping of early SV40-specific functions by microinjection of different early viral DNA fragments. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):579–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Expression of a bacterial gene in mammalian cells. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1422–1427. doi: 10.1126/science.6251549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda K., Dulbecco R. Induction of cellular mRNA synthesis in BSC-1 cells infected by SV40. Virology. 1968 Jul;35(3):439–444. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90222-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M., Winocour E., Prives C. Differential affinities of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen for DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):220–224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. SV40: T antigen, the A function and transformation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):267–276. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. Simian virus 40 gene A function and maintenance of transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):636–644. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.636-644.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPE J. H., ROWE W. P. DETECTION OF SPECIFIC ANTIGEN IN SV40-TRANSFORMED CELLS BY IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE. J Exp Med. 1964 Aug 1;120:121–128. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.2.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker B. A., Stark G. R. Regulation of simian virus 40 transcription: sensitive analysis of the RNA species present early in infections by virus or viral DNA. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):360–369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.360-369.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W., Pipas J. M., Pearson-White S., Nathans D. Isolation of mutants of an animal virus in bacteria. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1392–1396. doi: 10.1126/science.6251547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit C. A., Gardes M., Feunteun J. Immortalization of rodent embryo fibroblasts by SV40 is maintained by the A gene. Virology. 1983 May;127(1):74–82. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90372-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipas J. M., Peden K. W., Nathans D. Mutational analysis of simian virus 40 T antigen: isolation and characterization of mutants with deletions in the T-antigen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):203–213. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter C. W., McLaughlin B. C., Oxford J. S. Simian virus 40-induced T and tumor antigens. J Virol. 1969 Nov;4(5):574–579. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.5.574-579.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C., Barnet B., Scheller A., Khoury G., Jay G. Discrete regions of simian virus 40 large T antigen are required for nonspecific and viral origin-specific DNA binding. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):73–82. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.73-82.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pöckl E., Wintersberger E. Increased rate of RNA synthesis: early reaction of primary mouse kidney cells to infection with polyoma virus of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1980 Jul;35(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.1.8-19.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABSON A. S., O'CONOR G. T., BEREZESKY I. K., PAUL F. J. ENHANCEMENT OF ADENOVIRUS GROWTH IN AFRICAN GREEN MONKEY KIDNEY CELL CULTURES BY SV40. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 May;116:187–190. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassoulzadegan M., Cowie A., Carr A., Glaichenhaus N., Kamen R., Cuzin F. The roles of individual polyoma virus early proteins in oncogenic transformation. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):713–718. doi: 10.1038/300713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Ferguson J., Davis R. W., Stark G. R. T antigen binds to simian virus 40 DNA at the origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1605–1609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Stark G. R., Alwine J. C. Autoregulation of simian virus 40 gene A by T antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3083–3087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E. Adenovirus early region 1A enables viral and cellular transforming genes to transform primary cells in culture. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):602–606. doi: 10.1038/304602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Ullrich R., Thompson W. S., Lin P. S., Wallach D. F. Simian virus 40-specific proteins in the membranes of simian virus 40-transformed hamster and mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5069–5072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalloway D., Kleinberger T., Livingston D. M. Mapping of SV40 DNA replication origin region binding sites for the SV40 T antigen by protection against exonuclease III digestion. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):411–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90627-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D. R., Margolskee R. F., Nathans D. Mutational analysis of the simian virus 40 replicon: pseudorevertants of mutants with a defective replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6128–6131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D. Construction of an adenovirus-SV40 recombinant producing SV40 T antigen from an adenovirus late promoter. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90509-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L. M., Gurney E. G., Danna K. J. Stabilization of the 53,000-dalton nonviral tumor antigen is not required for transformation by simian virus 40. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):290–296. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soprano K. J., Jonak G. J., Galanti N., Floros J., Baserga R. Identification of an SV40 DNA sequence related to the reactivation of silent rRNA genes in human greater than mouse hybrid cells. Virology. 1981 Feb;109(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90477-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soule H. R., Lanford R. E., Butel J. S. Antigenic and immunogenic characteristics of nuclear and membrane-associated simian virus 40 tumor antigen. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):887–901. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.887-901.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer J. R. Mutant of simian virus 40 large T-antigen that is defective for viral DNA synthesis, but competent for transformation of cultured rat cells. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):854–864. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.854-864.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait R. C., Rodriguez R. L., West R. W., Jr The rapid purification of T4 DNA ligase from a lambda T4 lig lysogen. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):813–815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Function of simian virus 40 gene A in transforming infection. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):613–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.613-618.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Schwartz M., Collins J. K., Rundell K. Regulation of tumor antigen synthesis by simain virus 40 gene A. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):168–178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.168-178.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis: the viral replicon. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):591–598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.591-598.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Fey G., Graessmann A. Biological activity of purified simian virus 40 T antigen proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1279–1283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Robbins A. Enzymatic activities associated with a purified simian virus 40 T antigen-related protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):610–614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. The binding site on SV40 DNA for a T antigen-related protein. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):165–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Novak U., Favaloro J., Kamen R. Transformation of rat cells by an altered polyoma virus genome expressing only the middle-T protein. Nature. 1981 Aug 13;292(5824):595–600. doi: 10.1038/292595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Elsen P., Houweling A., Van der Eb A. Expression of region E1b of human adenoviruses in the absence of region E1a is not sufficient for complete transformation. Virology. 1983 Jul 30;128(2):377–390. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90264-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi N., Kuchino T. Temperature-sensitive mutants of simian virus 40 selected by transforming ability. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1297–1301. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1297-1301.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]