Abstract
To establish the distribution of blood lipid concentrations and the prevalences of other risk factors for cardiovascular disease in Britain 12 092 men and women aged 25-59 in Glasgow, Leicester, London, and Oxford were studied. Subjects were selected by opportunistic case finding, in which patients consulting their general practitioner for any reason were offered a health check by appointment, or random selection from age-sex registers, in which an invitation for a health check was posted. The overall rate of response was 73%, being 91-94% by opportunistic case finding and 36-63% by random selection. At the health check subjects answered a brief questionnaire about risk factors for cardiovascular disease, and their height, weight, and blood pressure were recorded; a blood sample was taken for measuring plasma concentrations of cholesterol, triglyceride, high density lipoprotein cholesterol, and glucose.
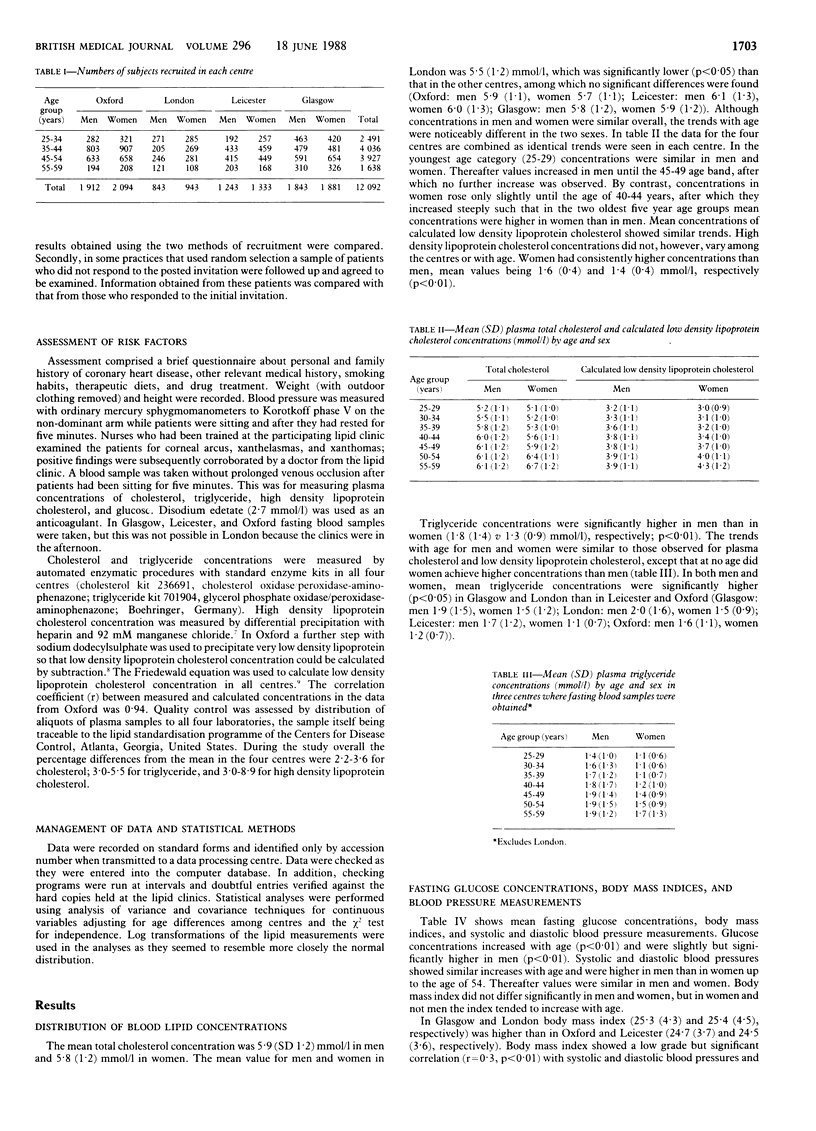
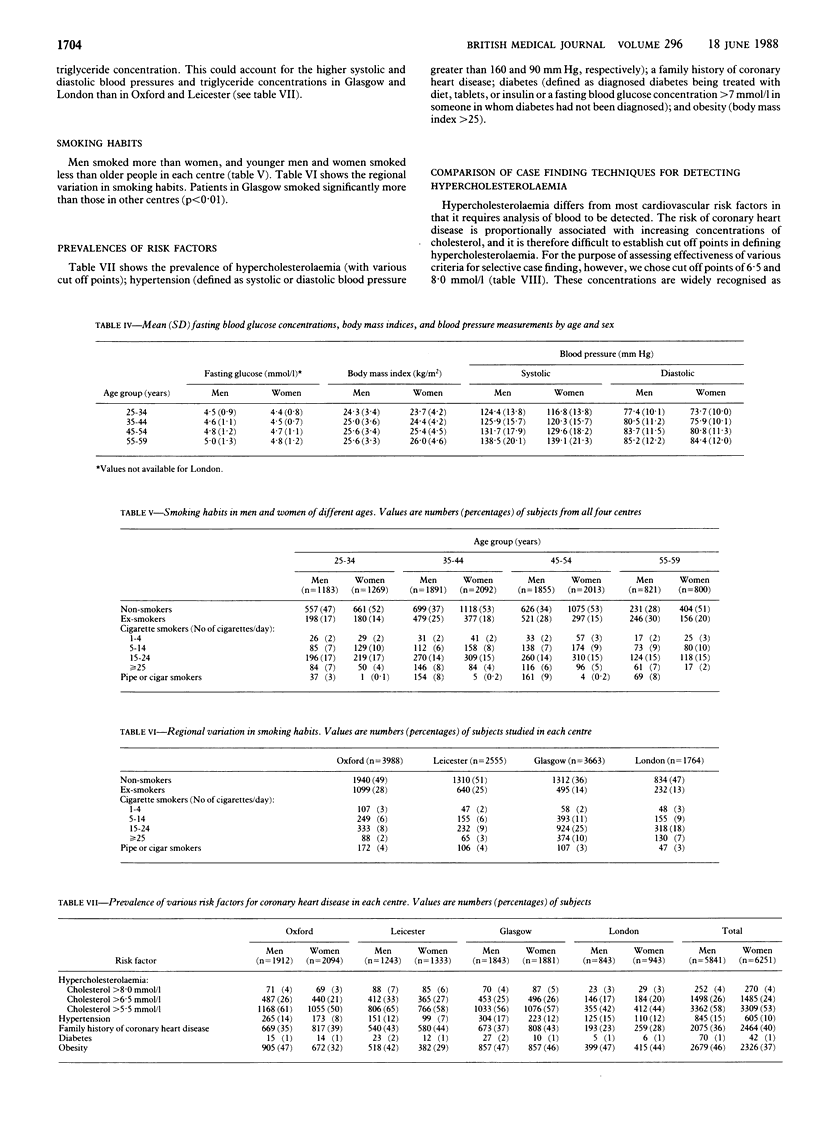
The mean cholesterol concentrations were 5·9 (SD 1·2) and 5·8 (1·2) mmol/l in men and women, respectively. In London the mean value was 5·5 (1·2) mmol/l for both men and women and was significantly lower than mean values in the three other centres, among which there were no significant differences. In men and women aged 25-29 concentrations were similar but they increased in men until the age of 45-49, after which they showed no further increase; in women concentrations did not increase until the age of 40-44 and by the age of 50-59 values were higher than in men. Mean triglyceride concentrations were significantly higher in men than in women (1·8 (1·4) v 1·3 (0·9) mmol/l, respectively), and trends with age were similar to those for cholesterol concentrations, except that at no age were values higher in women than in men. Mean triglyceride values overall were higher in Glasgow and London than in Oxford and Leicester. Body mass index was higher in Glasgow and London than in the other two centres and correlated with systolic and diastolic blood pressures and triglyceride concentration. In addition, subjects in Glasgow smoked significantly more than those in the other centres. These observations could contribute to the higher rate of coronary heart disease in Glasgow. Plasma lipid concentrations and the prevalences of other risk factors for cardiovascular disease were similar in subjects selected by opportunistic case finding and by random selection.
In Britain cholesterol values have changed little during the past 12 years despite dietary recommendations and health education. Identifying subjects at particularly high risk of coronary heart disease is required to supplement advice to the general population to reduce the prevalence of this disease. Opportunistic case finding would be an appropriate method of identifying such subjects in general practice, although none of the potential markers for hyperlipidaemia was particularly useful in identifying all subjects at high risk.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burstein M., Scholnick H. R., Morfin R. Rapid method for the isolation of lipoproteins from human serum by precipitation with polyanions. J Lipid Res. 1970 Nov;11(6):583–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler G. The general practitioner's role in the prevention of coronary heart disease. Practitioner. 1986 Oct;230(1420):859-62, 864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedewald W. T., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem. 1972 Jun;18(6):499–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullard E., Fowler G., Gray M. Promoting prevention in primary care: controlled trial of low technology, low cost approach. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Apr 25;294(6579):1080–1082. doi: 10.1136/bmj.294.6579.1080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiss G., Tamir I., Davis C. E., Tyroler H. A., Rifkand B. M., Schonfeld G., Jacobs D., Frantz I. D., Jr Lipoprotein-cholesterol distributions in selected North American populations: the lipid research clinics program prevalence study. Circulation. 1980 Feb;61(2):302–315. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.61.2.302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B., Chait A., Wootton I. D., Oakley C. M., Krikler D. M., Sigurdsson G., February A., Maurer B., Birkhead J. Frequency of risk factors for ischaemic heart-disease in a healthy British population. With particular reference to serum-lipoprotein levels. Lancet. 1974 Feb 2;1(7849):141–146. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92438-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B., Mann J. I., Mancini M. Reducing the risks of coronary heart disease in individuals and in the population. Lancet. 1986 Apr 26;1(8487):956–959. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onongbu I. C., Lewis B. Lipoprotein fractionation by a precipitation method. A simple quantitative procedure. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Sep 20;71(3):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90090-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyörälä K., Salonen J. T., Valkonen T. Trends in coronary heart disease mortality and morbidity and related factors in Finland. Cardiology. 1985;72(1-2):35–51. doi: 10.1159/000173839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid D. D., Hamilton P. J., McCartney P., Rose G., Jarrett R. J., Keen H. Smoking and other risk factors for coronary heart-disease in British civil servants. Lancet. 1976 Nov 6;2(7993):979–984. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90830-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose G., Heller R. F., Pedoe H. T., Christie D. G. Heart disease prevention project: a randomised controlled trial in industry. Br Med J. 1980 Mar 15;280(6216):747–751. doi: 10.1136/bmj.280.6216.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J., Betteridge D. J., Durrington P., Laker M., Lewis B., Mann J., Miller J. P., Reckless J. P., Thompson G. R. Strategies for reducing coronary heart disease and desirable limits for blood lipid concentrations: guidelines of the British Hyperlipidaemia Association. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Nov 14;295(6608):1245–1246. doi: 10.1136/bmj.295.6608.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamler J. The marked decline in coronary heart disease mortality rates in the United States, 1968-1981; summary of findings and possible explanations. Cardiology. 1985;72(1-2):11–22. doi: 10.1159/000173836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelle D. S., Shaper A. G., Whitehead T. P., Bullock D. G., Ashby D., Patel I. Blood lipids in middle-aged British men. Br Heart J. 1983 Mar;49(3):205–213. doi: 10.1136/hrt.49.3.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorogood M., Carter R., Benfield L., McPherson K., Mann J. I. Plasma lipids and lipoprotein cholesterol concentrations in people with different diets in Britain. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Aug 8;295(6594):351–353. doi: 10.1136/bmj.295.6594.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



