Abstract
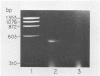
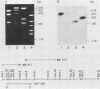
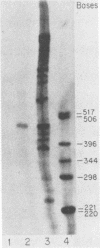
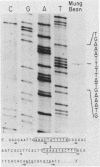
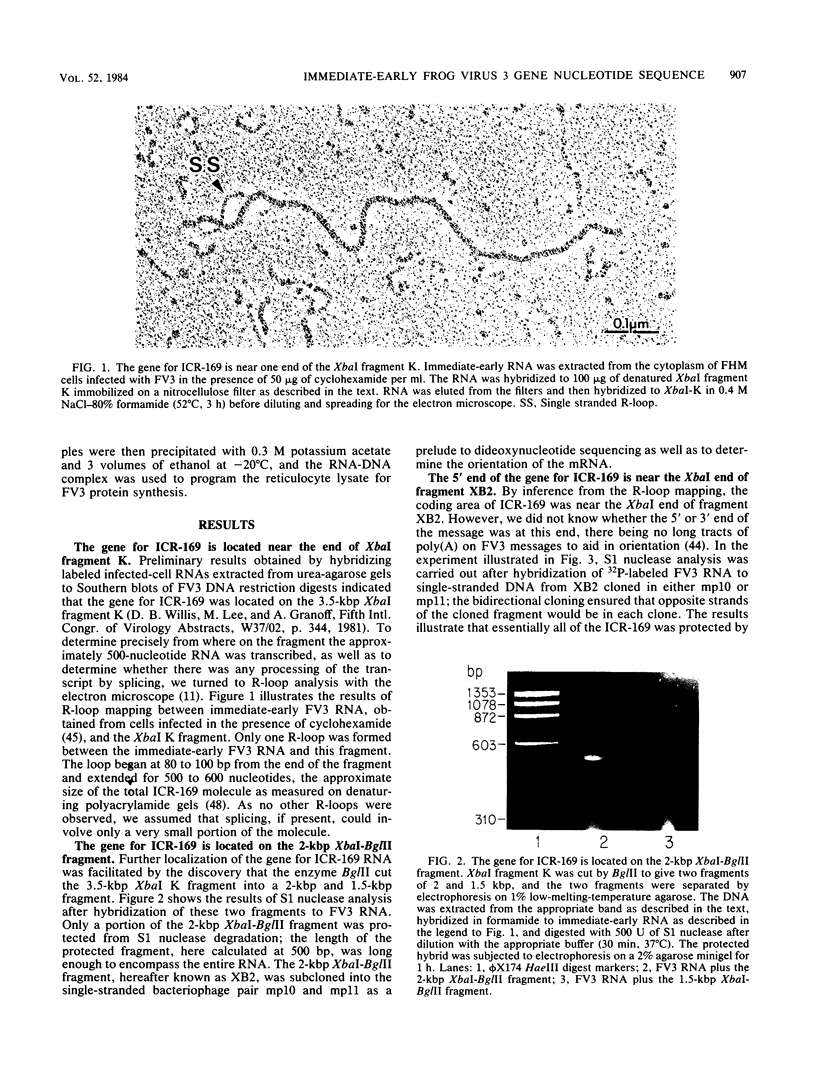
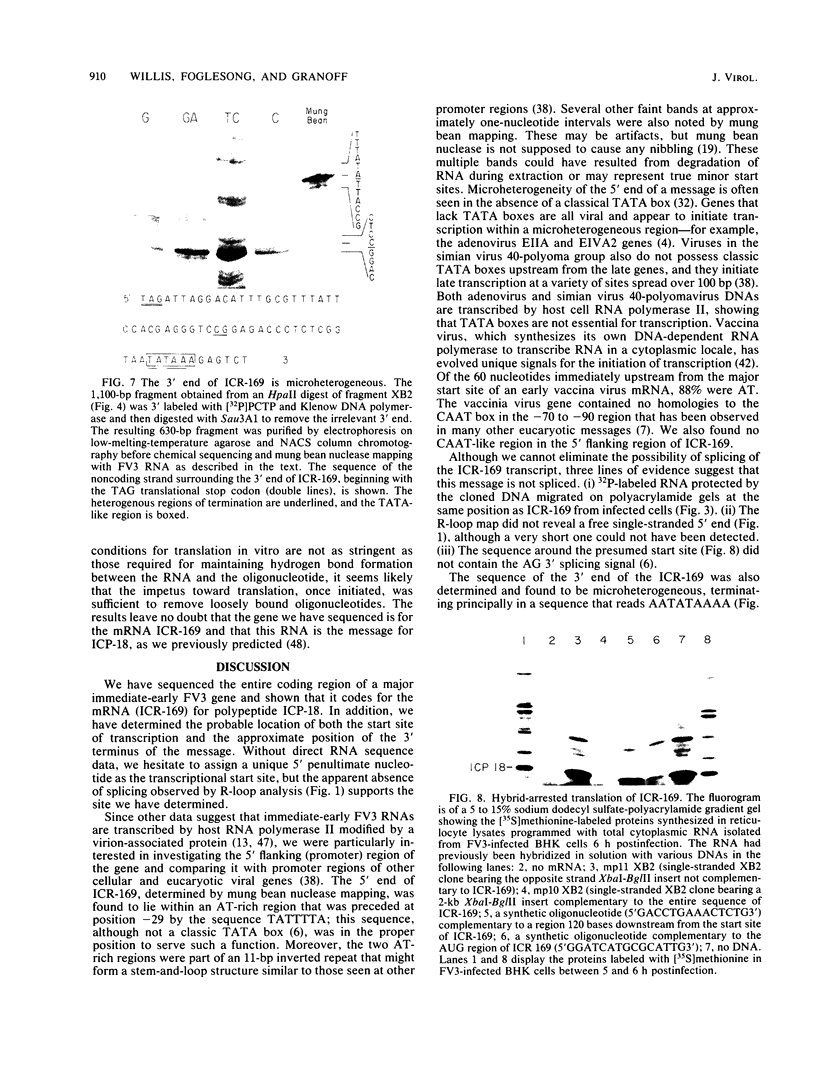
We have used "gene walking" with synthetic oligonucleotides and M13 dideoxynucleotide sequencing techniques to obtain the complete coding and flanking sequences of the gene encoding a major immediate-early RNA (molecular weight, 169,000) of frog virus 3. R-loop mapping of the cloned XbaI K fragment of frog virus 3 DNA with immediate-early RNA from infected cells showed that an RNA of approximately 500 to 600 nucleotides (the right size to code for the immediate-early viral 18-kilodalton protein of unknown function) hybridized to a region within 100 base pairs of one end of the XbaI K fragment; no evidence for splicing was observed in the electron microscope or by single-strand nuclease analysis. Further restriction mapping narrowed the location of the gene to the XbaI end of a 2-kilobase-pair XbaI-Bg/II fragment, which was bidirectionally subcloned into the bacteriophage pair mp10 and mp11 for sequencing. Mung bean nuclease mapping was used to identify both the 5' and the 3' ends of the mRNA. The 5' end mapped within an AT-rich region 19 base pairs upstream from two in-phase AUG start codons that were immediately followed by an open reading frame of 157 amino acids. Another AT-rich sequence was found at -29 base pairs from the 5' end of the mRNA start site; this sequence may function as a TATA box. The 3' end of the message displayed considerable microheterogeneity, but clearly terminated within a third AT-rich region 50 to 60 base pairs from the translation stop codon. The eucaryotic polyadenylic acid addition signal (AATAAA) was not present, a finding to be expected since frog virus 3 mRNA is not polyadenylated. Both the single-stranded mp10 clone of the XbaI-Bg/II fragment and a 15-base oligonucleotide complementary to the region flanking the two AUG translation start codons inhibited translation of the immediate-early 18-kilodalton protein in vitro, confirming the identity of the sequenced gene. As the regulatory sequences of this gene did not resemble those of known eucaryotic genes or of the cytoplasmic vaccinia virus, we conclude that frog virus 3 has evolved unique signals for the initiation and termination of transcription.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubertin A. M., Tondre L., Lopez C., Obert G., Kirn A. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-mediated transfer of electrophoretically separated DNA-binding proteins. Anal Biochem. 1983 May;131(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90143-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubertin A. M., Travo C., Kirn A. Proteins solubilized from frog virus 3 particles: effect on transcription. J Virol. 1976 Apr;18(1):34–41. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.1.34-41.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. C., Ziff E. B. Promoters and heterogeneous 5' termini of the messenger RNAs of adenovirus serotype 2. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 25;149(2):189–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckingham K. A plasmid cloning vector for Kpnl-cleaved DNA. Plasmid. 1980 Nov;4(3):354–356. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90074-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., O'Hare K., Breathnach R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene-sequence of putative control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):127–142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campadelli-Fiume G., Costanzo F., Foa'-Tomasi L., La Placa M. Modifications of cellular RNA-polymerase II after infection with frog virus 3. J Gen Virol. 1975 Jun;27(3):391–394. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-27-3-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler P. M. The use of single-stranded phage DNAs in hybrid arrest and release translation. Anal Biochem. 1982 Nov 15;127(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90137-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Roberts J. M., Lewis J. B., Broker T. R. A map of cytoplasmic RNA transcripts from lytic adenovirus type 2, determined by electron microscopy of RNA:DNA hybrids. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):819–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90294-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W. DNA methylation and gene activity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:93–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goorha R. Frog virus 3 DNA replication occurs in two stages. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):519–528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.519-528.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goorha R. Frog virus 3 requires RNA polymerase II for its replication. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):496–499. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.496-499.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goorha R., Granoff A. Macromolecular synthesis in cells infected by frog virus 3. I. Virus-specific protein synthesis and its regulation. Virology. 1974 Jul;60(1):237–250. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90381-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goorha R., Murti G., Granoff A., Tirey R. Macromolecular synthesis in cells infected by frog virus 3. VIII. The nucleus is a site of frog virus 3 DNA and RNA synthesis. Virology. 1978 Jan;84(1):32–50. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90216-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goorha R., Willis D. B., Granoff A. Macromolecular synthesis in cells infected by frog virus 3. XII. Viral regulatory proteins in transcriptional and post-transcriptional controls. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):442–448. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.442-448.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Roeder R. G. Definition of a novel promoter for the major adenovirus-associated virus mRNA. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):231–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90171-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R. M., Weintraub H., McKnight S. L. Transcription of DNA injected into Xenopus oocytes is influenced by template topology. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):38–43. doi: 10.1038/302038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itakura K., Riggs A. D. Chemical DNA synthesis and recombinant DNA studies. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1401–1405. doi: 10.1126/science.6106285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langridge J., Langridge P., Bergquist P. L. Extraction of nucleic acids from agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Apr;103(2):264–271. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90266-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. H., Willis D. B. Restriction endonuclease mapping of the frog virus 3 genome. Virology. 1983 Apr 15;126(1):317–327. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90481-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naegele R. F., Granoff A. Viruses and renal carcinoma of Rana pipiens. XI. Isolation of frog virus 3 temperature-sensitive mutants; complementation and genetic recombination. Virology. 1971 May;44(2):286–295. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90260-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. The pathway of eukaryotic mRNA formation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:441–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghow R., Granoff A. Cell-free translation of frog virus 3 messenger RNAs. Initiation factors from infected cells discriminate between early and late viral mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):571–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F. Determination of nucleotide sequences in DNA. Science. 1981 Dec 11;214(4526):1205–1210. doi: 10.1126/science.7302589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Corden J., Kédinger C., Chambon P. Promotion of specific in vitro transcription by excised "TATA" box sequences inserted in a foreign nucleotide environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):3941–3958. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.3941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenk T. Transcriptional control regions: nucleotide sequence requirements for initiation by RNA polymerase II and III. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;93:25–46. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68123-3_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Automation of the computer handling of gel reading data produced by the shotgun method of DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4731–4751. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan S., Baroudy B. M., Moss B. Distinctive nucleotide sequences adjacent to multiple initiation and termination sites of an early vaccinia virus gene. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):805–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90188-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis D. B., Goorha R., Granoff A. Nongenetic reactivation of frog virus 3 DNA. Virology. 1979 Oct 30;98(2):476–479. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90572-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis D. B., Goorha R., Miles M., Granoff A. Macromolecular synthesis in cells infected by frog virus 3. VII. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of virus gene expression. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):326–342. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.326-342.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis D. B., Granoff A. Frog virus 3 DNA is heavily methylated at CpG sequences. Virology. 1980 Nov;107(1):250–257. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90290-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis D. B., Granoff A. Macromolecular synthesis in cells infected by frog virus 3. IX. Two temporal classes of early viral RNA. Virology. 1978 May 15;86(2):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis D. B., Granoff A. Macromolecular synthesis in cells infected with frog virus 3. V. The absence of polyadenylic acid in the majority of frog virus 3-specific mRNA species. Virology. 1976 Sep;73(2):543–547. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90417-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]