Abstract
The vibrational Stark effect (VSE) has proven to be an effective method for the study of electric fields in proteins via the use of infrared probes. In order to explore the use of VSE in nucleic acids, the Stark spectroscopy of nine structurally diverse nucleosides was investigated. These nucleosides contained nitrile or azide probes in positions that correspond to both the major and minor grooves of DNA. The nitrile probes showed better characteristics and exhibited absorption frequencies over a broad range; i.e., from 2253 cm−1 for 2′-O-cyanoethyl ribonucleosides 8 and 9 to 2102 cm−1 for a 13C-labeled 5-thiocyanatomethyl-2’-deoxyuridine 3c. The largest Stark tuning rate observed was |Δµ| = 1.1 cm−1/(MV/cm) for both 5-cyano-2′-deoxyuridine 1 and N2-nitrile-2′-deoxyguanosine 7. The latter is a particularly attractive probe because of its high extinction coefficient (ε = 412 M−1cm−1) and ease of incorporation into oligomers.
Keywords: Stark spectroscopy, tuning rate, electrostatics, electric field, nucleosides, nitriles, azides, DNA, RNA
Introduction
DNA and RNA are polyanions, with one formal negative charge per monomer unit, where the phosphate charge ensures that water solubility and electrostatic interactions play important roles in their structure and function. Electrostatic interactions in nucleic acids have been extensively studied by a variety of theoretical methods,1–7 often with conflicting results. In contrast, relatively little experimental data on electric fields in nucleic acids are available, including only one spin-labeling electron-electron double-resonance EPR study9–11 and one fluorescein pKa shift experiment.12,13 The probes used in both of these studies are large relative to a single nucleoside, and this presents two potential limitations: they cannot properly address changes in electrostatic potential over short distances, and they may also disrupt the native structure of the DNA.
Recently, the vibrational Stark effect (VSE), which describes the sensitivity of a vibrational probe to an external electric field, has been used to measure electric fields in proteins.14–18 In this method, a probe vibration is calibrated by measuring the Stark tuning rate of the transition in a known external electric field, after which it is used as a reporter of electrostatic environment in an organized system whose electric field changes in response to a mutation, folding or binding event. This change in electric field, interacts with the change in dipole moment or Stark tuning rate, for the vibrational transition to produce a frequency shift, (in cm−1):
where h is Planck’s constant and c is the speed of light. With calibrated in a defined external electric field, frequency shifts can be measured in a variety of environments by conventional IR spectroscopy and interpreted in terms of the projection of on the resulting can be directly compared with electrostatics calculations.
The ideal properties of a VSE probe for a biomolecule14,19,20 include: (1) an absorption frequency that is in a clear region of the IR spectrum; (2) an absorption band that is narrow with a relatively high extinction coefficient; (3) an absorption band that is as sensitive as possible to changes in the local electrostatic environment, i.e. has the largest possible Stark tuning rate (given in units of cm−1/(MV/cm), which describes the shift in cm−1 of an IR absorption band per unit of electric field projected on the vibrator bond axis); (4) small size so that the perturbation of the native structure is minimized; and (5) chemical stability. Nitriles (R-CN) meet all of these requirements.14,19–26 Azides (R-N3) may also be useful, though they are less stable than nitriles, their IR spectra are more complex, and contributions from different resonance structures may complicate the analysis. On the other hand, azides have been incorporated into carbohydrates,27 proteins,28 and nucleic acids29 due to their ability to undergo selective reactions, such as "click" cycloadditions with alkynes.30
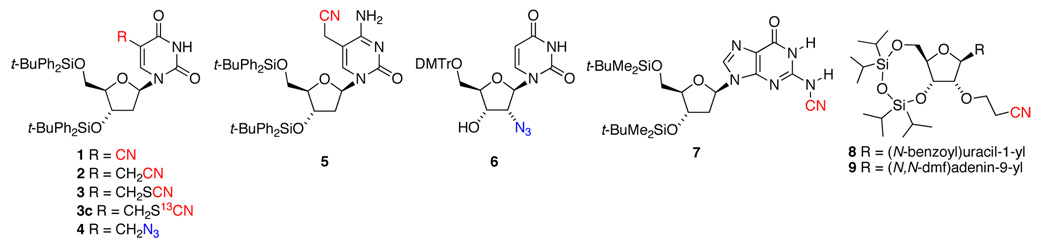
Nitriles, thiocyanates, and azides can be readily incorporated into DNA31–39 and RNA.38–40 Previously, these functional groups were incorporated into oligomers by accident,31,32 or they were synthesized in order to test medicinal, biochemical, or electronic properties. It is desirable to have probes in both the major and minor grooves, Figure 1, requiring structural diversity in the nucleosides containing the vibrational probe. To this end, we have prepared nine nucleosides with nitrile, thiocyanate, or azide groups, shown in Chart I, and explored their potential to act as vibrational probes.
Figure 1.
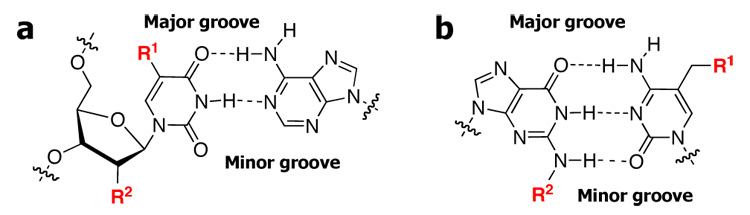
a. Thymine-adenine base pair. b. Guanine-cytosine base pair. (R1 = major groove vibrational probe; R2 = minor groove vibrational probe)
Chart I.
Materials and Methods
The nucleosides studied were known compounds (6, 8, 9) or prepared from known compounds.41 All new compounds (1–5, 7) had 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, and mass spectral properties that are fully consistent with the assigned structures.41 The experimental setup for measurement of Stark tuning rates and the equations used to determine the Stark tuning rate from the spectral data have been described in detail elsewhere.14 All Stark spectra were carried out on 25 µm - thick samples in frozen glass solvents to prevent poling of the sample in response to the applied electric field. Typically, external electric fields of up to 1.4 MV/cm were achieved.
Results and Discussion
Nitriles satisfy all of the criteria for probe selection described above, and therefore we synthesized an array of nucleosides containing this functional group. It is known that aromatic nitriles generally have larger Stark tuning rates than aliphatic ones;19 however, in the interest of creating a structurally diverse set of probes, we chose to synthesize nucleosides containing either type of nitrile. As expected, a large Stark tuning rate was seen in 1 (|Δµ| = 1.1 cm−1/(MV/cm)), in which the nitrile is directly bound to the uracil ring (Table I). This is a larger Stark tuning rate than that observed for 4-cyanophenylalanine, a VSE probe for protein electrostatics,14 making this compound an excellent choice for probing the DNA major groove. As an illustration of the superiority of aromatic over aliphatic nitriles, the major groove probe 2, which differs from 1 by a single methylene group between the nitrile and the uracil ring, is less suitable, having low intensity (ε = 23 M−1cm−1) and no observable Stark effect even at 500 mM concentration in an applied electric field of up to 1.4 MV/cm. Likewise, the cytidine-based probe 5, also containing a cyanomethyl group on the aromatic ring, has low intensity (ε = 22 M−1cm−1) and no observable Stark effect. Despite the poor characteristics of these cyanomethyl groups, significant Stark effects were observed for aliphatic nitriles at remote positions to the bases. For example, the RNA minor groove probes 8 and 9, which have a cyanoethyl group on the ribose moiety, have Stark tuning rates nearly half that of the aromatic nitrile 1 (|Δµ| = 0.46 and 0.50 cm−1/(MV/cm), respectively). We expect a similar Stark tuning rate for other 2’-cyanoethyl-ribose-labeled nucleosides, making this a versatile motif for probing electric fields in a wide range of oligonucleotides.
Table I.
IR and Stark Spectroscopic Data for Nucleoside Vibrational Probes
| Compound | Peak Position (cm−1) |
FWH M (cm−1) |
ε (M1cm−1) |
Tuning Rate (cm−1/MV/cm) | Solvent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNA Major | |||||
| Groove | |||||
| 1 | 2231 | 8 | 332 | 1.1 | 2-MeTHF |
| 2 | 2252 | 14 | 23 | 2-MeTHF | |
| 3c | 2102 | 8 | 175 | 0.30 | 2-MeTHF |
| 4 | 2117, | 0.51 | 2-MeTHF | ||
| 2104, | |||||
| 2076 | |||||
| 5 | 2250 | 10 | 22 | 2-MeTHF | |
| DNA Minor | |||||
| Groove | |||||
| 6 | 2139, | 0.45 | 2-MeTHF | ||
| 2120, | |||||
| 2097 | |||||
| 7 | 2170 | 29 | 412 | 1.1 | 4:1 PhMe/DMSO |
| RNA Minor | |||||
| Groove | |||||
| 8 | 2253 | 10 | 41 | 0.48 | 2-MeTHF |
| 9 | 2253 | 9 | 25 | 0.50 | 1:1 PhMe/MeOH |
Abbreviations: DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide), MeOH (methanol), 2-MeTHF (2-methyltetrahydrofuran), PhMe (toluene)
One advantage to using VSE probes in oligonucleotides is that it is straightforward to incorporate any number of modified nucleosides by standard solid-phase synthesis techniques. This provides an opportunity to incorporate multiple spectrally-resolved probes in order to get information about the electrostatic environment at several locations simultaneously. To this end, we have examined several aminenitriles and thiocyanates, which are expected to have peaks at lower energies than standard carbon-bound nitriles. Indeed, the aminenitrile 7 has a CN stretch that is more than 60 cm−1 lower in energy than in any of the carbon-bound nitriles. Despite the relative broadness of this peak compared to carbon-bound nitriles, it has the highest intensity and Stark tuning rate of any compound that we examined (ε = 412 M−1cm−1; |Δµ| = 1.1 cm−1/(MV/cm)), making it a useful probe of the DNA minor groove. An additional benefit of probe 7 stems from the fact that it can be easily incorporated into oligomers using the known conversion of a dimethylforamidine (dmf) protecting group to a nitrile as part of the solid-phase synthesis.31 The method involves the use of the commercially available dmf protection only on the deoxyguanosine(s) undergoing conversion to the nitrile probe and the traditional isobutyryl protection on all others.42 We have found that the most effective method for conversion is to treat the oligomer with a small quantity of iodine and ammonia after the synthesis cycle is complete but prior to the final deprotection.42 To get to even lower energy, we have synthesized the 13C-labeled thiocyanate 3c, which has its peak at 2102 cm−1. This compound has a smaller Stark tuning rate (|Δµ| = 0.30 cm−1/(MV/cm)), making it less useful as an individual probe, but still allowing it to complement 1 and 7 in a three-probe oligonucleotide sequence.
In addition to the variety of nitrile-containing nucleosides that we have studied, we have also synthesized two azide-containing nucleosides: probe 4 is analogous to the nitrile-containing 2, and probe 6 has an azide directly bound to the 2’ position on the ribose moiety. Both 4 and 6 have three overlapping IR absorption bands in the azide region due to the presence of coupled symmetric and antisymmetric stretching modes. Stark effects were observable for each of the bands, and for both probes, the Stark tuning rate is similar although not identical across the three azide bands. We report an averaged value of the Stark tuning rate for each of these azide-containing compounds in Table 1; however, the inability to deconvolute the Stark tuning rates of the individual bands makes the interpretation of peak shifts as a function of electrostatic field potentially more difficult for the azides than for the simpler nitrile probes.
In conclusion, we have laid the foundation for the use of VSE as a new experimental method to measure electric fields in nucleic acids by measuring the Stark tuning rates for a variety of nitrile and azide probes. Nitrilede-oxyuridine 1 and nitrile-deoxyguanosine 7 appear to be particularly attractive probes for the major and minor grooves, respectively, of DNA. Work on Stark shifts of nitriles incorporated into DNA oligomers is ongoing.
Supplementary Material
Experimental details for the synthesis and characterization of compounds 1–5 and 7; literature references for the synthesis of 6, 8, 9; and Stark spectra and data fits for compounds 1, 3, 4, 6–9. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
Acknowledgment
We thank Dr. Todd Trout of Lancaster Country Day School for the syntheses of compounds 3 and 3c and Scott Morrow of Johns Hopkins University for his work on the synthesis of nitrile-oligonucleotides. We gratefully acknowledge the help of Beth Buckwalter, Lisa Mertzman, and Carol Strausser, of Franklin & Marshall. Finally, we gratefully acknowledge financial support for this work from the NSF (0412901) for purchase of a 500 MHz NMR at Franklin & Marshall, and the William M. and Lucille M. Hackman Scholars Program at F&M; this work was also supported in part by a grant from the NIH (GM27738 to S.G.B.).
Contributor Information
Steven G. Boxer, Email: sboxer@stanford.edu.
Edward E. Fenlon, Email: efenlon@fandm.edu.
References
- 1.Reddy SY, Leclerc F, Karplus M. Biophys. J. 2003;84:1421–1449. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74957-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Khandogin J, York DM. J. Phys. Chem. 2002;106:7693–7703. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kornyshev AA, Leikin S. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1998;95:13579–13584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.23.13579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chin K, Sharp KA, Honig B, Pyle AM. Nat. Struct. Bio. 1999;11:1055–1061. doi: 10.1038/14940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Draper DE, Grilley D, Soto AM. Ions and RNA folding. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2005;34:221–243. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.34.040204.144511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cherstvy AG. Effect of DNA charge helicity on B–Z DNA transition. J. Chem. Phys. 2005;123:116101-1–16101-3. doi: 10.1063/1.2036990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Misra VK, Honig B. The electrostatic contribution to the B to Z transition of DNA. Biochemistry. 1996;35:1115–1124. doi: 10.1021/bi951463y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Honig B, Nicholls A. Classical electrostatics in biology and chemistry. Science. 1995;268:1144–1149. doi: 10.1126/science.7761829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Shin Y-K, Hubbell WL. Biophys. J. 1992;61:1443–1453. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81950-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hecht JL, Honig B, Shin Y-K, Hubbell WL. 1995;99:7782–7786. [Google Scholar]
- 11.For more on the spin-label approach, see:Likhtenshtein GI, Adin I, Novoselsky A, Shames A, Vaisbuch I, Glaser R. Biophys. J. 1999;77:443–453. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(99)76902-X.
- 12.Sjöback R, Nygren J, Kubista M. Biopolymers. 1998;46:445–453. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0282(199812)46:7<445::AID-BIP2>3.0.CO;2-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.The electrostatic difference between DNA and its solution has also been investigated recently, see:Carrasco M, Coca R, Cruz I, Daza S, Espina M, Garcia-Fernandez E, Guerra FJ, León R, Marchena MJ, Pérez I, Puente M, Suárez E, Valencia I, Villalba I, Jiménez R. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2007;441:148–151.
- 14.Suydam IT, Boxer SG. Biochemistry. 2003;42:12050–12055. doi: 10.1021/bi0352926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Suydam IT, Snow CD, Pande VS, Boxer SG. Science. 2006;313:200–204. doi: 10.1126/science.1127159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.(a) Park ES, Andrews SS, Hu RB, Boxer SG. J. Phys. Chem. B. 1999;103:9813–9817. [Google Scholar]; (b) Park ES, Thomas MR, Boxer SG. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000;122:12297–12303. [Google Scholar]; (c) Fafarman AT, Webb LJ, Chuang JI, Boxer SG. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006;128:13356–13357. doi: 10.1021/ja0650403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.(a) Kriegl JM, Nienhaus K, Deng P, Fuchs J, Nienhaus GH. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2003;100:7069–7074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1231856100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Lehle H, Kriegl JM, Nienhaus K, Deng P, Fengler S, Nienhaus GU. Biophys. J. 2004;88:1978–1990. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.048140. and references therein. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.For calculations on the VSE, see:Dalsosto SD, Vanderkooi JM, Sharp KA. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2004;108:6450–6457. doi: 10.1021/jp0310697.Brewer SH, Franzen S. J. Chem. Phys. 2003;119:851–858.
- 19.Andrews SS, Boxer SG. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2000;104:11853–11863. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Getahum Z, Huang C-Y, Wang T, De Leon B, DeGrado WF, Gai F. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003;125:405–411. doi: 10.1021/ja0285262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.(a) Chattopadhyay A, Boxer SG. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995;117:1449–1450. [Google Scholar]; (b) Andrews SS, Boxer SG. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2002;106:469–477. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Reimers JR, Hall LE. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999;121:3730–3744. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Huang CY, Wang T, Gai F. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2003;371:731–738. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tucker MJ, Getahum Z, Nanda V, DeGrado WF, Gai F. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004;126:5078–5079. doi: 10.1021/ja032015d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Yoshikawa S, O'Keeffe DHD, Caughey WS. J. Biol. Chem. 1985;260:3518–3528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Schutz KC, Supekova L, Ryu Y, Xie J, Perera R, Schutlz PG. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006;128:13984–13985. doi: 10.1021/ja0636690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.(a) Perez-Balderas F, Ortega-Munoz M, Morales-Sanfrutos J, Hernandez-Mateo F, Calvo-Flores FG, Calvo-Asin JA, Isac-Garcia J, Santoyo-Gonzalez F. Org. Lett. 2003;5:1951–1954. doi: 10.1021/ol034534r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Bodine KD, Gin DY, Gin MS. Org. Lett. 2005;7:4479–4482. doi: 10.1021/ol051818y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.(a) Kiick KL, Saxon E, Tirrell DA, Bertozzi CR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2002;99:19–24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.012583299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Agard NJ, Prescher JA, Bertozzi CR. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004;126:15046–15047. doi: 10.1021/ja044996f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.(a) Seo TS, Li Z, Ruparel H, Ju J. J. Org. Chem. 2003;68:609–612. doi: 10.1021/jo026615r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Lu G, Burgess K. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006;16:3902–3905. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2006.05.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.(a) Kolb HC, Finn MG, Sharpless KB. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2001;40:2004–2021. doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20010601)40:11<2004::AID-ANIE2004>3.0.CO;2-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Rostovtsev VV, Green LG, Fokin VV, Sharpless KB. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2002;41:2596–2599. doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20020715)41:14<2596::AID-ANIE2596>3.0.CO;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Tornøe CW, Christensen C, Meldal M. J. Org. Chem. 2002;67:3057–3064. doi: 10.1021/jo011148j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Mullah B, Andrus A, Zhao H, Jones RA. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995;36:4373–4376. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Markley JC, Chirakul P, Sologub D, Sigurdsson S. Th. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2001;11:2453–2455. doi: 10.1016/s0960-894x(01)00461-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hayakawa T, Ono A, Udea T. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988;16:4761–4776. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.11.4761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Graham D, Parkinson JA, Brown T. J. Chem. Soc., Perkins Trans. 1. 1998:1131–1138. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ishikawa R, Kojima C, Ono A, Kainosho M. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2001;39:S159–S165. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hwang GT, Romesberg FE. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34:2037–2045. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Polushin NN, Smirnov IP, Verentchikov AN, Coull JM. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996;37:3227–3230. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bradley DH, Hanna MM. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992;33:6223–6226. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Evans RK, Haley BE. Biochemistry. 1987;26:269–276. doi: 10.1021/bi00375a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Saneyoshi H, Seio K, Sekine M. J. Org. Chem. 2005;70:10453–10460. doi: 10.1021/jo051741r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.See Supporting Information for more details.
- 42.Fenlon EE, Pitzer ME, Ankomah PO, Morrow S. 2007 unpublished results. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Experimental details for the synthesis and characterization of compounds 1–5 and 7; literature references for the synthesis of 6, 8, 9; and Stark spectra and data fits for compounds 1, 3, 4, 6–9. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.


