Abstract
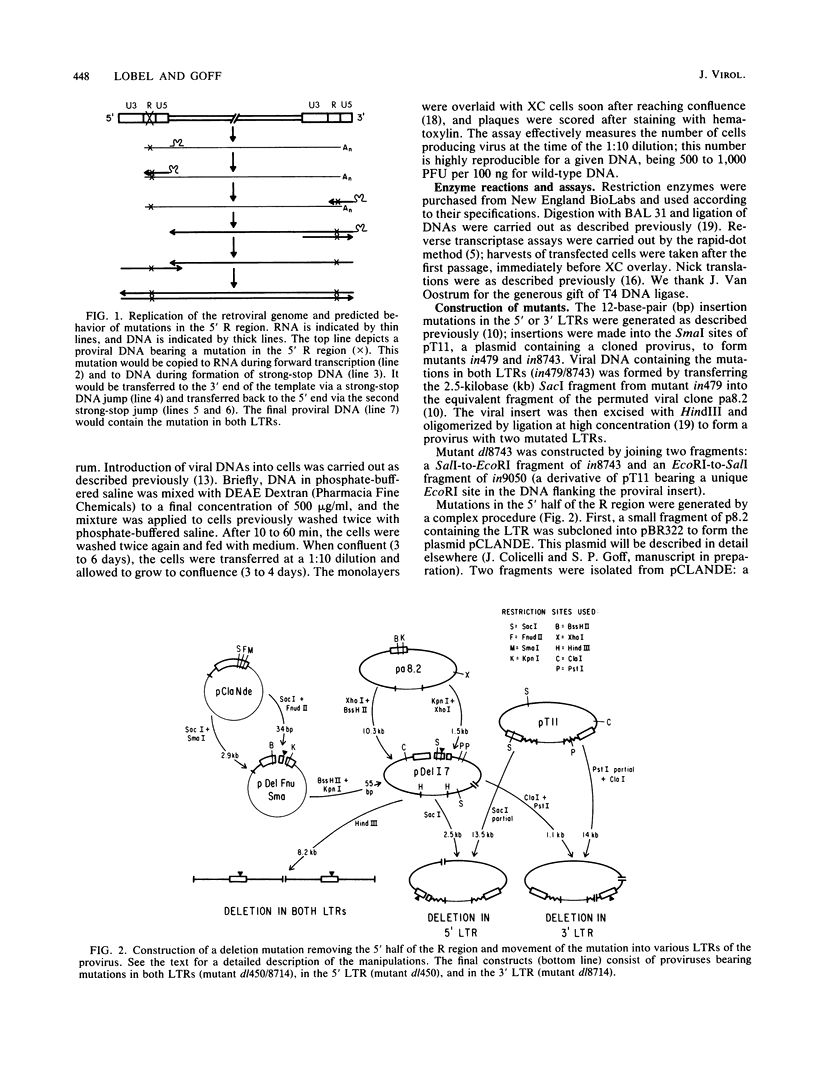
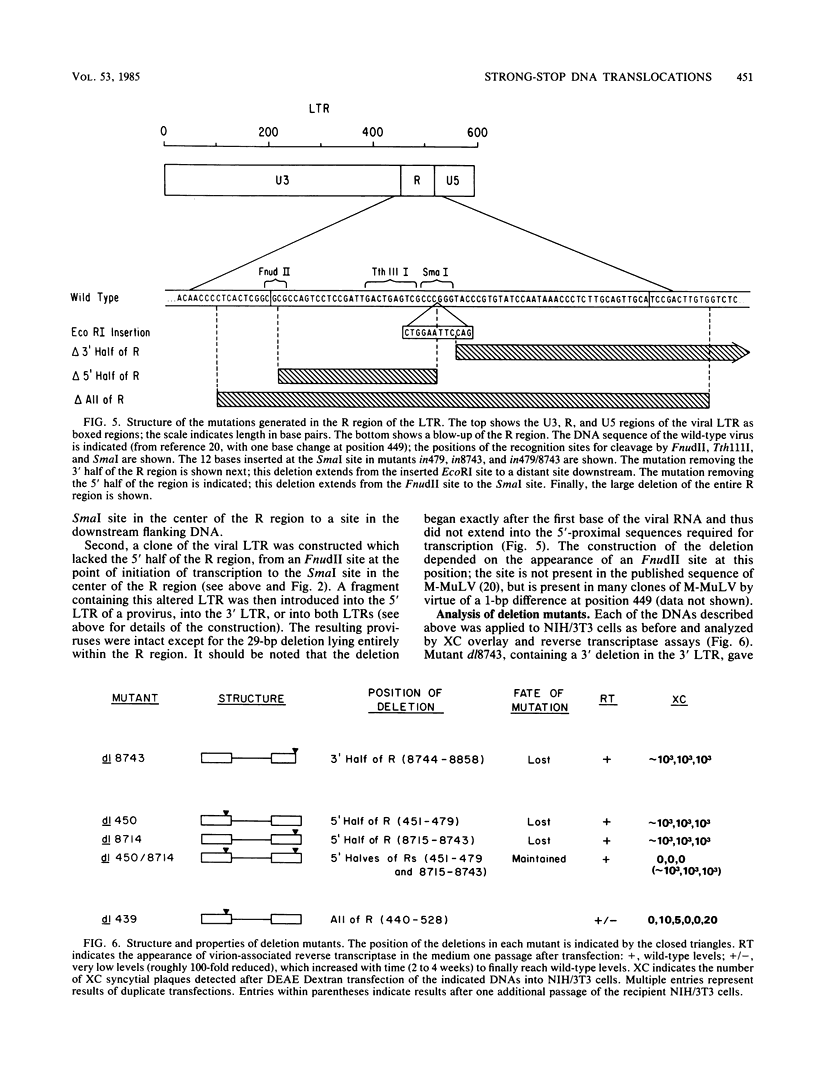
The process of reverse transcription of retroviral genomes begins with the synthesis of a short DNA molecule near the 5' end of the RNA template. This molecule, termed minus-strand strong-stop DNA, is then translocated to the 3' end of the viral RNA by means of a repeated sequence, the R region, present at both ends of the template. The translocation should result in the transfer of genetic information from the 5' R region to the 3' R region. We have generated a series of mutants of Moloney murine leukemia virus with alterations in the R regions by in vitro mutagenesis of a cloned DNA copy of the viral genome. The altered DNAs were introduced into mouse cells by transfection, and the translocation of the mutations during viral replication was assessed. Some mutations were not transferred from the 5' R region to the 3' R region; these results were not in accord with current models for reverse transcription. The results can be explained if DNA molecules shorter than strong-stop DNA, formed by premature termination of synthesis, are sometimes translocated. A number of mutants with large deletions in the R region were tested and were able to replicate with normal strong-stop DNA translocation. Thus, short stretches of homology can be used by the virus to carry out strong-stop translocations.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Battula N., Loeb L. A. The infidelity of avian myeloblastosis virus deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase in polynucleotide replication. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4086–4093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz E. W., Jr, Wydro R. M., Nadal-Ginard B., Dina D. Moloney murine sarcoma proviral DNA is a transcriptional unit. Nature. 1980 Dec 25;288(5792):665–669. doi: 10.1038/288665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin J. M., Hageman T. C., Maxam A. M., Haseltine W. A. Structure of the genome of Moloney murine leukemia virus: a terminally redundant sequence. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):761–773. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90226-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilboa E., Mitra S. W., Goff S., Baltimore D. A detailed model of reverse transcription and tests of crucial aspects. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):93–100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90357-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S., Traktman P., Baltimore D. Isolation and properties of Moloney murine leukemia virus mutants: use of a rapid assay for release of virion reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):239–248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.239-248.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A., Kleid D. G., Panet A., Rothenberg E., Baltimore D. Ordered transcription of RNA tumor virus genomes. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 5;106(1):109–131. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90303-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz L., Kingsbury D. T., Helinski D. R. Stimulation by cyclic adenosine monophosphate of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid replication and catabolite repression of the plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):577–591. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.577-591.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobel L. I., Goff S. P. Construction of mutants of Moloney murine leukemia virus by suppressor-linker insertional mutagenesis: positions of viable insertion mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4149–4153. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. R., Dobkin C., Kramer F. R. Template-determined, variable rate of RNA chain elongation. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):541–550. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra S. W., Goff S., Gilboa E., Baltimore D. Synthesis of a 600-nucleotide-long plus-strand DNA by virions of Moloney murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4355–4359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzberg P., Colicelli J., Goff S. P. Deletion mutants of Moloney murine leukemia virus which lack glycosylated gag protein are replication competent. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):538–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.538-546.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramani S., Berg P. Homologous and nonhomologous recombination in monkey cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1040–1052. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake C. T., Wilson J. H. Simian virus 40 recombinants are produced at high frequency during infection with genetically mixed oligomeric DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2876–2880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Duesberg P. H., Robins T., Yokota H., Vogt P. K. The terminal oligonucleotides of avian tumor virus RNAs are genetically linked. Virology. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):472–492. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Saint Vincent B. R., Wahl G. M. Homologous recombination in mammalian cells mediates formation of a functional gene from two overlapping gene fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):2002–2006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]