Abstract
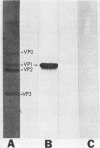
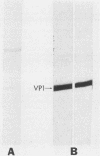
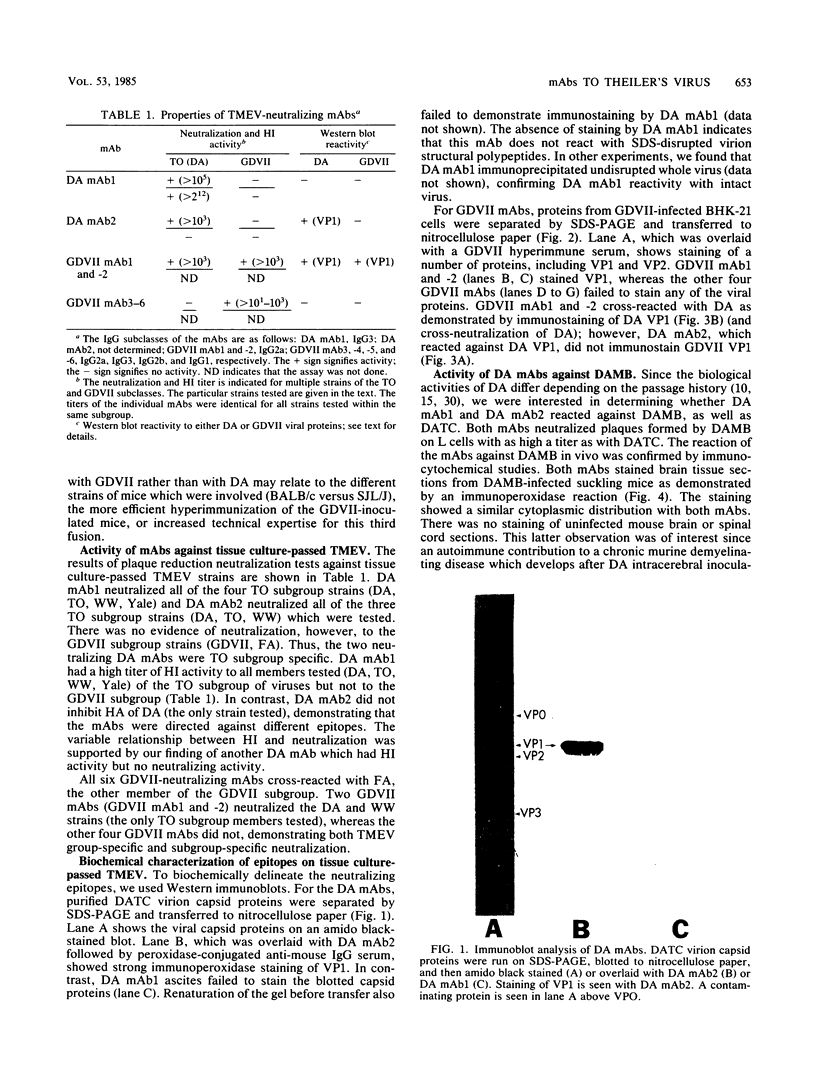
Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis viruses (TMEV) are serologically related picornaviruses which cause both enteric and neurological disease in mice. The biological activities of TMEV vary between the two different TMEV subgroups (TO and GDVII) and with different passage histories of the same TMEV strain (e.g., mouse brain-passed versus tissue culture-passed DA strain of the TO subgroup). We raised neutralizing monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against tissue culture-passed DA and GDVII strains of TMEV. We produced two mAbs against the DA strain which neutralized all members of the TO subgroup, but not the GDVII subgroup strains (GDVII and FA); these two DA mAbs reacted similarly with both mouse brain-passed DA and tissue culture-passed DA. Of six neutralizing GDVII mAbs, four reacted only to GDVII and FA, whereas two neutralized TO strains as well. These mAbs demonstrate the presence of TMEV group-specific as well as subgroup-specific neutralization and substantiate the division of TMEV into two distinct subgroups. On Western immunoblots one of the two DA mAbs reacted against isolated DA VP1, two GDVII mAbs (which were TMEV group specific) reacted against isolated GDVII VP1 and DA VP1, and the other DA mAb and four other GDVII mAbs required an intact virion conformation for reactivity. An analysis of the epitopes recognized by these mAbs may elucidate sites important in TMEV biological activities.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baxt B., Morgan D. O., Robertson B. H., Timpone C. A. Epitopes on foot-and-mouth disease virus outer capsid protein VP1 involved in neutralization and cell attachment. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):298–305. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.298-305.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blondel B., Akacem O., Crainic R., Couillin P., Horodniceanu F. Detection by monoclonal antibodies of an antigenic determinant critical for poliovirus neutralization present on VP1 and on heat-inactivated virions. Virology. 1983 Apr 30;126(2):707–710. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(83)80027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen B., Steinberg J., Laemmli U. K., Weintraub H. The detection of DNA-binding proteins by protein blotting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):1–20. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Jameson B. A., Lewis A. J., Larsen G. R., Wimmer E. Poliovirus neutralization epitopes: analysis and localization with neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):997–1005. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.997-1005.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Jameson B. A., Wimmer E. Priming for and induction of anti-poliovirus neutralizing antibodies by synthetic peptides. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):699–703. doi: 10.1038/304699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. M., Minor P. D., Schild G. S., Almond J. W. Critical role of an eight-amino acid sequence of VP1 in neutralization of poliovirus type 3. Nature. 1983 Aug 4;304(5925):459–462. doi: 10.1038/304459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann A., Lipton H. L. Replication of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis viruses in BHK21 cells: an electron microscopic study. Virology. 1980 Mar;101(2):389–398. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90452-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrich J. R., Arnason B. G., Hochberg F. H. Demyelinative myelopathy in mice induced by the DA virus. J Neurol Sci. 1976 Oct;29(2-4):149–160. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(76)90167-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L. Characterization of the TO strains of Theiler's mouse encephalomyelitis viruses. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):869–872. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.869-872.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L., Dal Canto M. C. The TO strains of Theiler's viruses cause "slow virus-like" infections in mice. Ann Neurol. 1979 Jul;6(1):25–28. doi: 10.1002/ana.410060106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L., Dal Canto M. C. Theiler's virus-induced demyelination: prevention by immunosuppression. Science. 1976 Apr 2;192(4234):62–64. doi: 10.1126/science.176726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L., Gonzalez-Scarano F. Central nervous system immunity in mice infected with theiler's virus. I. Local neutralizing antibody response. J Infect Dis. 1978 Feb;137(2):145–151. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.2.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L. Persistent Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus infection in mice depends on plaque size. J Gen Virol. 1980 Jan;46(1):169–177. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-46-1-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L., Rozhon E. J., Black D. Theiler's virus-specified polypeptides made in BHK-21 cells. J Gen Virol. 1984 Jun;65(Pt 6):1095–1100. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-6-1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L. Theiler's virus infection in mice: an unusual biphasic disease process leading to demyelination. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):1147–1155. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.1147-1155.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorch Y., Friedmann A., Lipton H. L., Kotler M. Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus group includes two distinct genetic subgroups that differ pathologically and biologically. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):560–567. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.560-567.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorch Y., Friedmann A. Proteins induced in tissue culture by four isolates of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):496–504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.496-504.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorch Y., Kotler M., Friedmann A. Persistent and acute central nervous system infections are caused by Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis viruses which differ in RNA composition but code for only slightly different proteins. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):960–965. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.960-965.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKearn T. J., Sarmiento M., Weiss A., Stuart F. P., Fitch F. W. Selective suppression of reactivity to rat histocompatibility antigens by hybridoma antibodies. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:61–65. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Bootman J., Evans D. M., Ferguson M., Reeve P., Spitz M., Stanway G., Cann A. J., Hauptmann R. Location and primary structure of a major antigenic site for poliovirus neutralization. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):674–679. doi: 10.1038/301674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepom J. T., Weiner H. L., Dichter M. A., Tardieu M., Spriggs D. R., Gramm C. F., Powers M. L., Fields B. N., Greene M. I. Identification of a hemagglutinin-specific idiotype associated with reovirus recognition shared by lymphoid and neural cells. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):155–167. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos R. P., Graves M. C., Wollmann R. L., Chilcote R. R., Nixon J. Immunologic and virologic studies of measles inclusion body encephalitis in an immunosuppressed host: the relationship to subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Neurology. 1981 Oct;31(10):1263–1270. doi: 10.1212/wnl.31.10.1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos R. P., Lichter M. Silver staining of cerebrospinal fluid IgG in isoelectric focusing gels. J Neurosci Methods. 1983 Aug;8(4):375–380. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(83)90094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos R. P., Richards O. C., Ehrenfeld E. Analysis of Theiler's virus isolates from persistently infected mouse nervous tissue. J Gen Virol. 1983 Mar;64(Pt 3):701–706. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-3-701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos R. P., Richards O. C., Green J., Ehrenfeld E. Characterization of a cell culture persistently infected with the DA strain of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1118–1122. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1118-1122.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos R. P., Whitelaw P. J. Biochemical analysis of DA strain of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus obtained directly from acutely infected mouse brain. Infect Immun. 1984 Jun;44(3):642–649. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.3.642-649.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos R. P., Wollmann R. DA strain of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus induces demyelination in nude mice. Ann Neurol. 1984 May;15(5):494–499. doi: 10.1002/ana.410150516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefansson K., Marton L., Antel J. P., Wollmann R. L., Roos R. P., Chejfec G., Arnason B. G. Neuropathy accompanying IgM lambda monoclonal gammopathy. Acta Neuropathol. 1983;59(4):255–261. doi: 10.1007/BF00691490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroop W. G., Brahic M., Baringer J. R. Detection of tissue culture-adapted Theiler's virus RNA in spinal cord white matter cells throughout infection. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):763–770. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.763-770.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wychowski C., van der Werf S., Siffert O., Crainic R., Bruneau P., Girard M. A poliovirus type 1 neutralization epitope is located within amino acid residues 93 to 104 of viral capsid polypeptide VP1. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):2019–2024. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01694.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]