Abstract
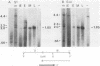
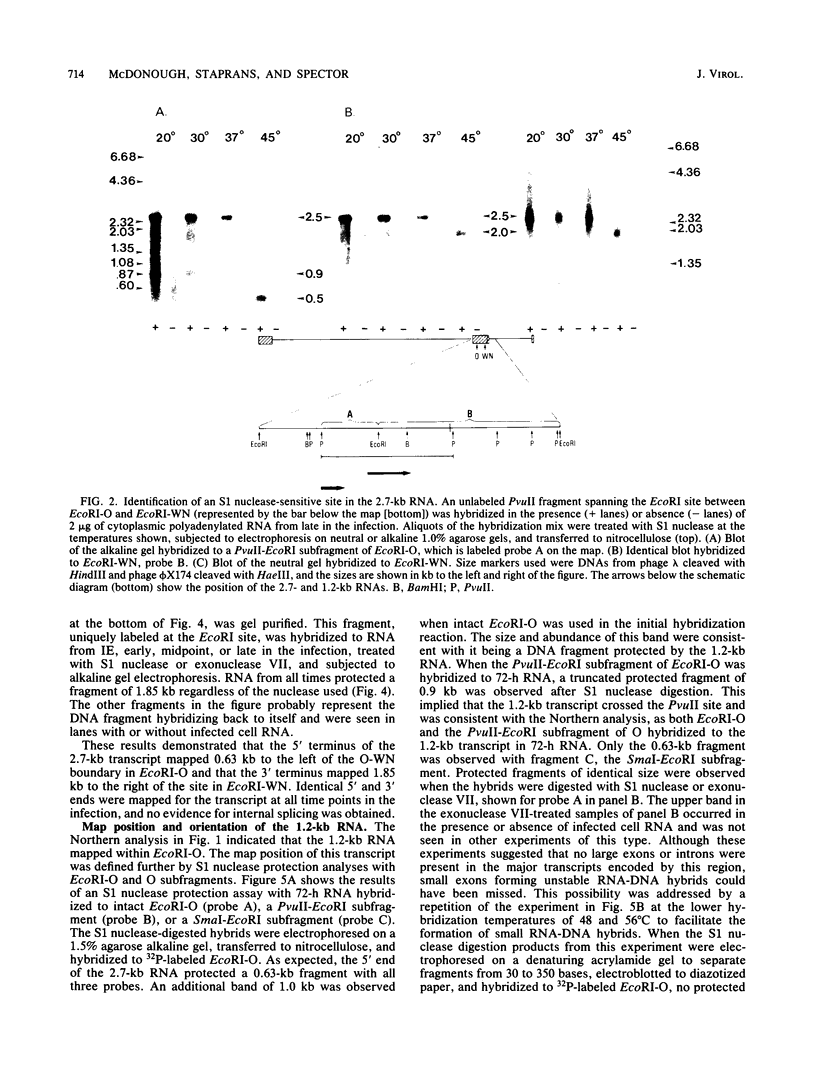
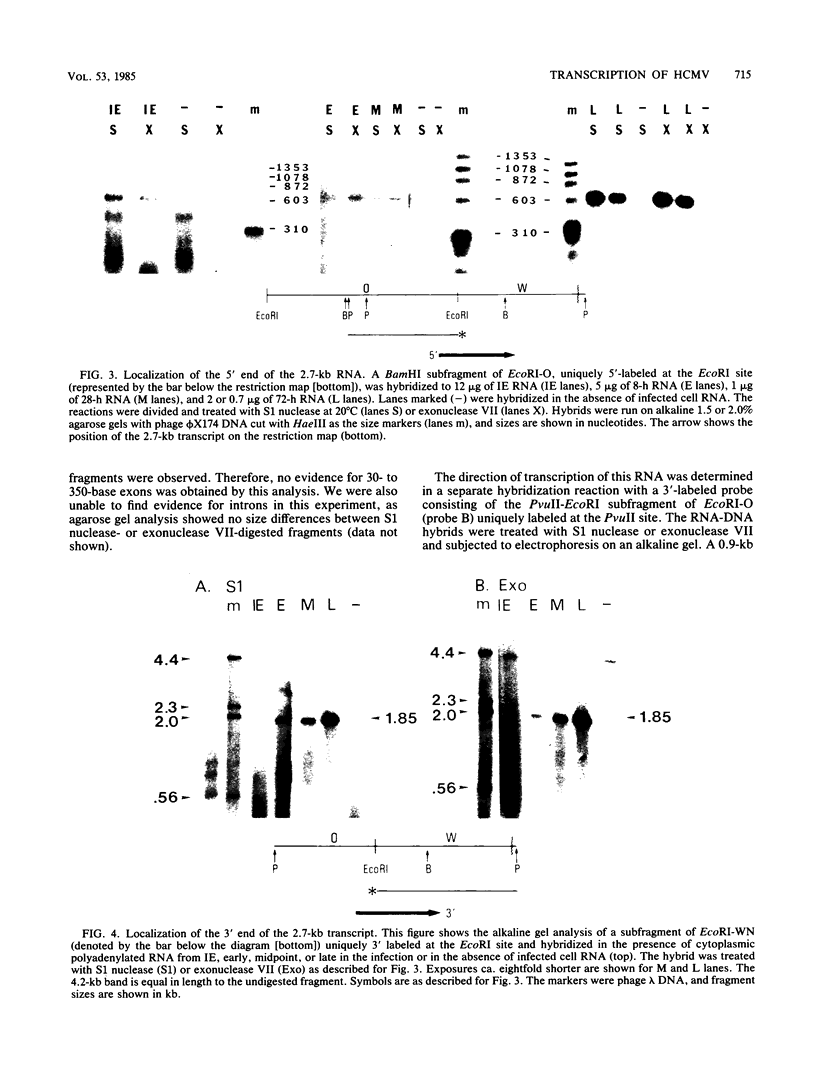
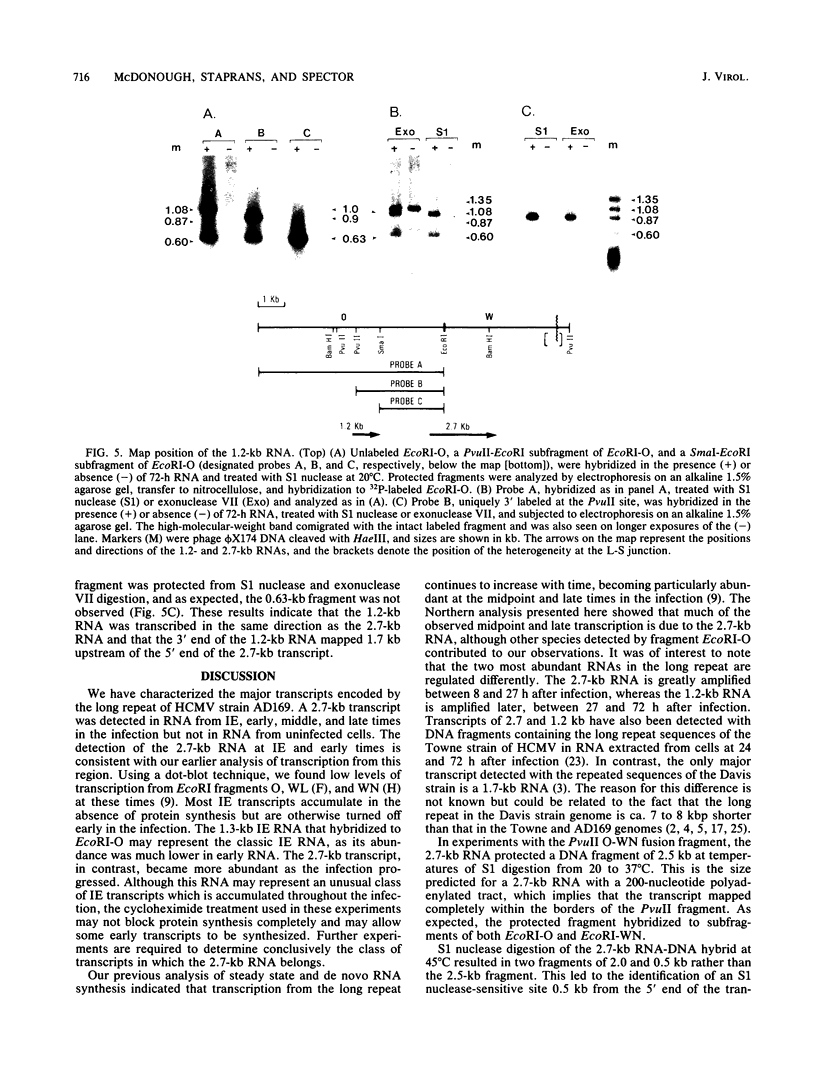
In this report, we describe the size and kinetics of appearance of RNAs from the long repeat of human cytomegalovirus. The most abundant RNA from this region was a 2.7-kilobase (kb) species that was detected throughout the infection and was most abundant at 27 and 72 h after infection. The 2.7-kb RNA was the only major species detected with a probe that included the terminus of the long repeat and the heterogeneous L-S junction region. Other transcripts were detected with probes from the internal portion of the long repeat, including an immediate-early RNA of 1.3 kb, early and late RNAs of 1.2 kb, and minor late transcripts of 4.4, 3.6, 3.3, and 1.8 kb. S1 nuclease and exonuclease VII protection analyses of RNA from immediate-early, early, midpoint, and late times in the infection indicated that the major 2.7-kb RNA was not spliced and that the RNA mapped within the long repeat, 1.6 kb from the heterogeneous region. No evidence for temporally regulated changes in transcription initiation, splicing, or choice of 3' end of this RNA was observed. Nuclease protection analysis also demonstrated that the second most abundant late RNA from this region, the 1.2-kb species, was not spliced and had the same polarity as the 2.7-kb RNA. The 1.2-kb also mapped entirely within the long repeat, with its 3' terminus 1.7 kb upstream from the 5' terminus of the 2.7-kb RNA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarchi J. M. Nature of the block in the expression of some early virus genes in cells abortively infected with human cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1983 Sep;129(2):287–297. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demarchi J. M. Human cytomegalovirus DNA: restriction enzyme cleavage maps and map locations for immediate-early, early, and late RNAs. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):23–38. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90249-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleckenstein B., Müller I., Collins J. Cloning of the complete human cytomegalovirus genome in cosmids. Gene. 1982 Apr;18(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90054-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Differentiation between alpha promoter and regulator regions of herpes simplex virus 1: the functional domains and sequence of a movable alpha regulator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4917–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Structural features of the herpes simplex virus alpha gene 4, 0, and 27 promoter-regulatory sequences which confer alpha regulation on chimeric thymidine kinase genes. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):939–949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.939-949.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough S. H., Spector D. H. Transcription in human fibroblasts permissively infected by human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Virology. 1983 Feb;125(1):31–46. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L. The nucleotide sequence and transcript map of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):5949–5964. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.5949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Clements J. B. Organization of the herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription unit encoding two early proteins with molecular weights of 140000 and 40000. J Gen Virol. 1983 May;64(Pt 5):997–1006. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-5-997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murchie M. J., McGeoch D. J. DNA sequence analysis of an immediate-early gene region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome (map coordinates 0.950 to 0.978). J Gen Virol. 1982 Sep;62(Pt 1):1–15. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-62-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oram J. D., Downing R. G., Akrigg A., Dollery A. A., Duggleby C. J., Wilkinson G. W., Greenaway P. J. Use of recombinant plasmids to investigate the structure of the human cytomegalovirus genome. J Gen Virol. 1982 Mar;59(Pt 1):111–129. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-59-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Hock L., Tamashiro J. C. Cleavage maps for human cytomegalovirus DNA strain AD169 for restriction endonucleases EcoRI, BglII, and HindIII. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):558–582. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.558-582.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamashiro J. C., Filpula D., Friedmann T., Spector D. H. Structure of the heterogeneous L-S junction region of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169 DNA. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):541–548. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.541-548.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamashiro J. C., Hock L. J., Spector D. H. Construction of a cloned library of the EcoRI fragments from the human cytomegalovirus genome (strain AD169). J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):547–557. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.547-557.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen D. R., Stenberg R. M., Goins W. F., Stinski M. F. Promoter-regulatory region of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):659–663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M. J., Sharp J. A., Summers W. C. Nucleotide sequence of the thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1441–1445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen M. W., Stinski M. F. Temporal patterns of human cytomegalovirus transcription: mapping the viral RNAs synthesized at immediate early, early, and late times after infection. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):462–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.462-477.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Sullivan M., Vande Woude G. F. Structures of two spliced herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early mRNA's which map at the junctions of the unique and reiterated regions of the virus DNA S component. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):431–444. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.431-444.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weststrate M. W., Geelen J. L., van der Noordaa J. Human cytomegalovirus DNA: physical maps for restriction endonucleases BglII, hindIII and XbaI. J Gen Virol. 1980 Jul;49(1):1–21. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-49-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]